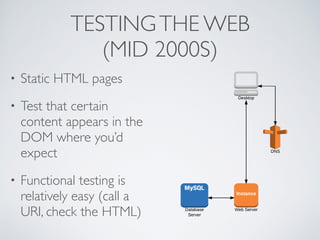
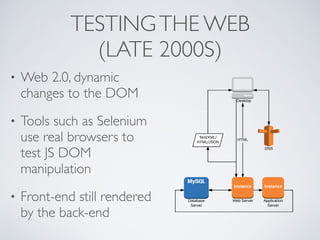
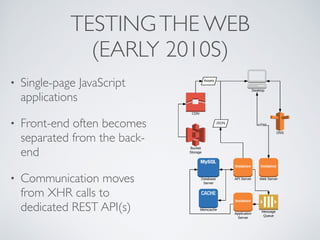
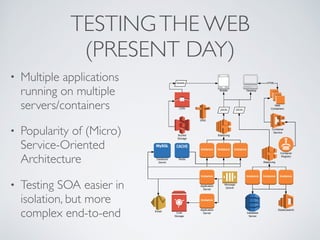
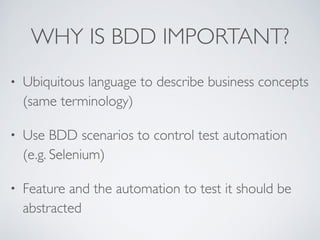
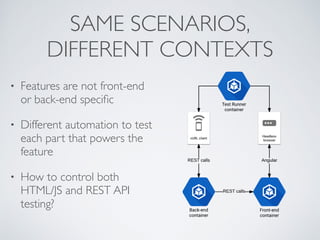
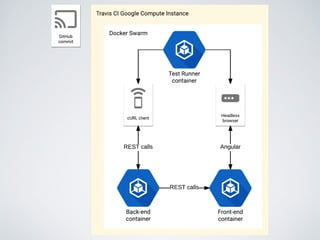
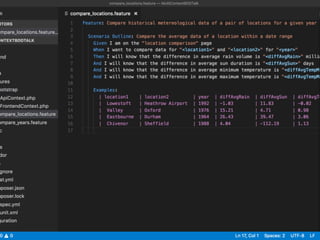
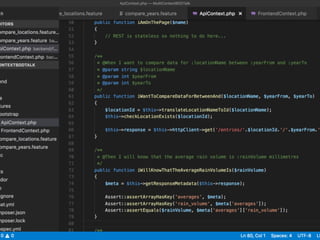
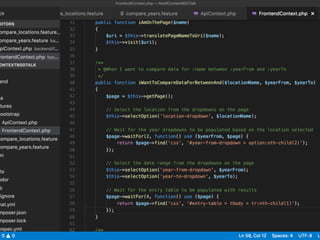
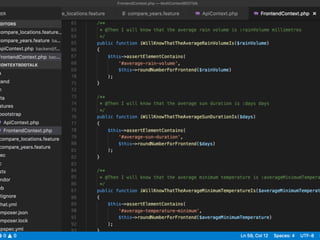
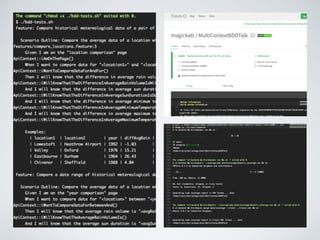
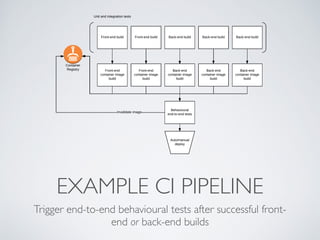
The document discusses behavior testing for single-page applications and APIs. It covers how testing the web has evolved as applications have become more dynamic and separated into front-end and back-end codebases. This has made end-to-end testing more complex. The document advocates for behavior driven development (BDD) using a tool like Behat, which allows writing tests in a business-readable language called Gherkin that can test both the front-end and back-end applications and their integration. Examples are given of how to set up BDD testing across multiple containers to test the full system behavior.