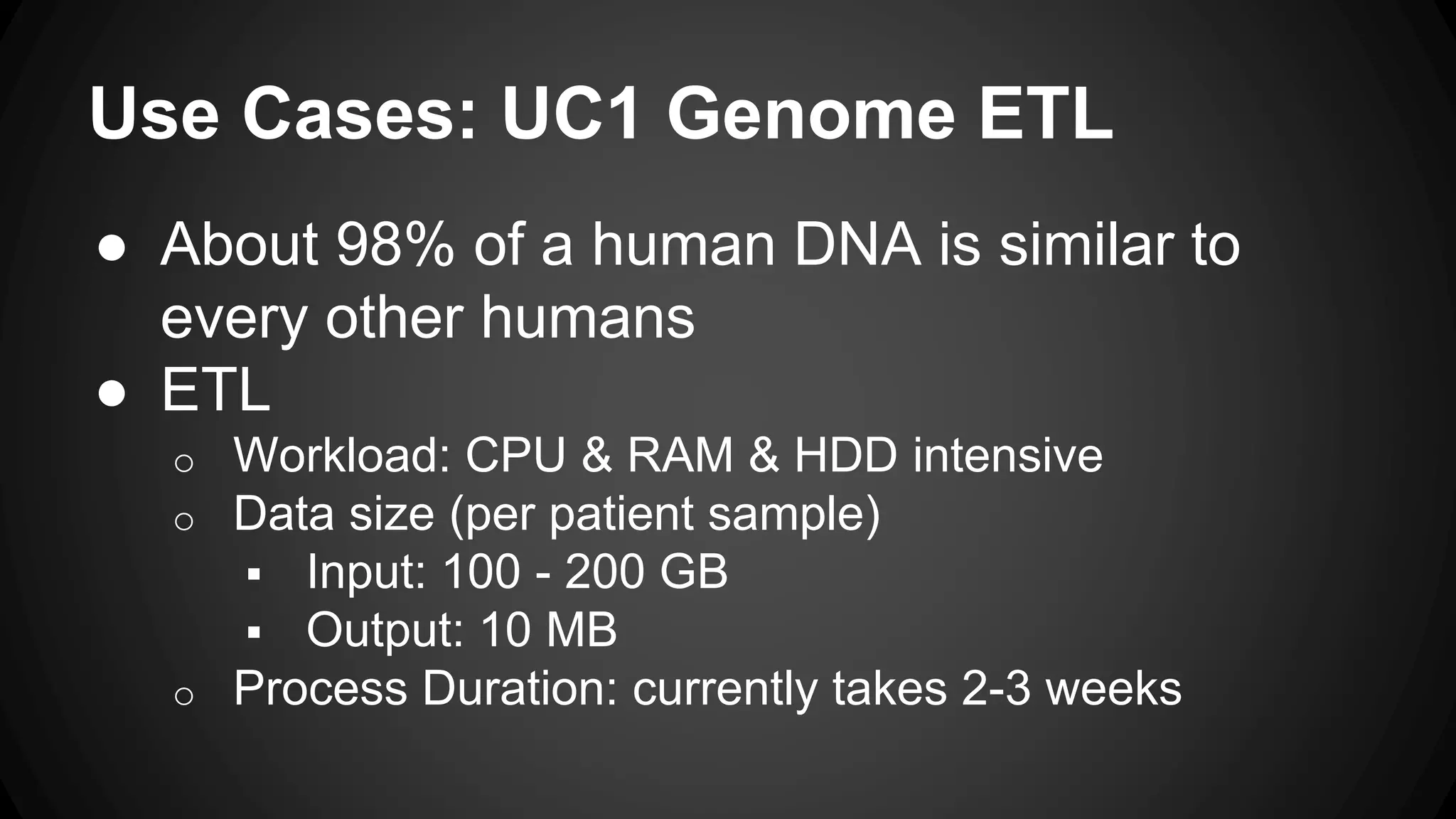
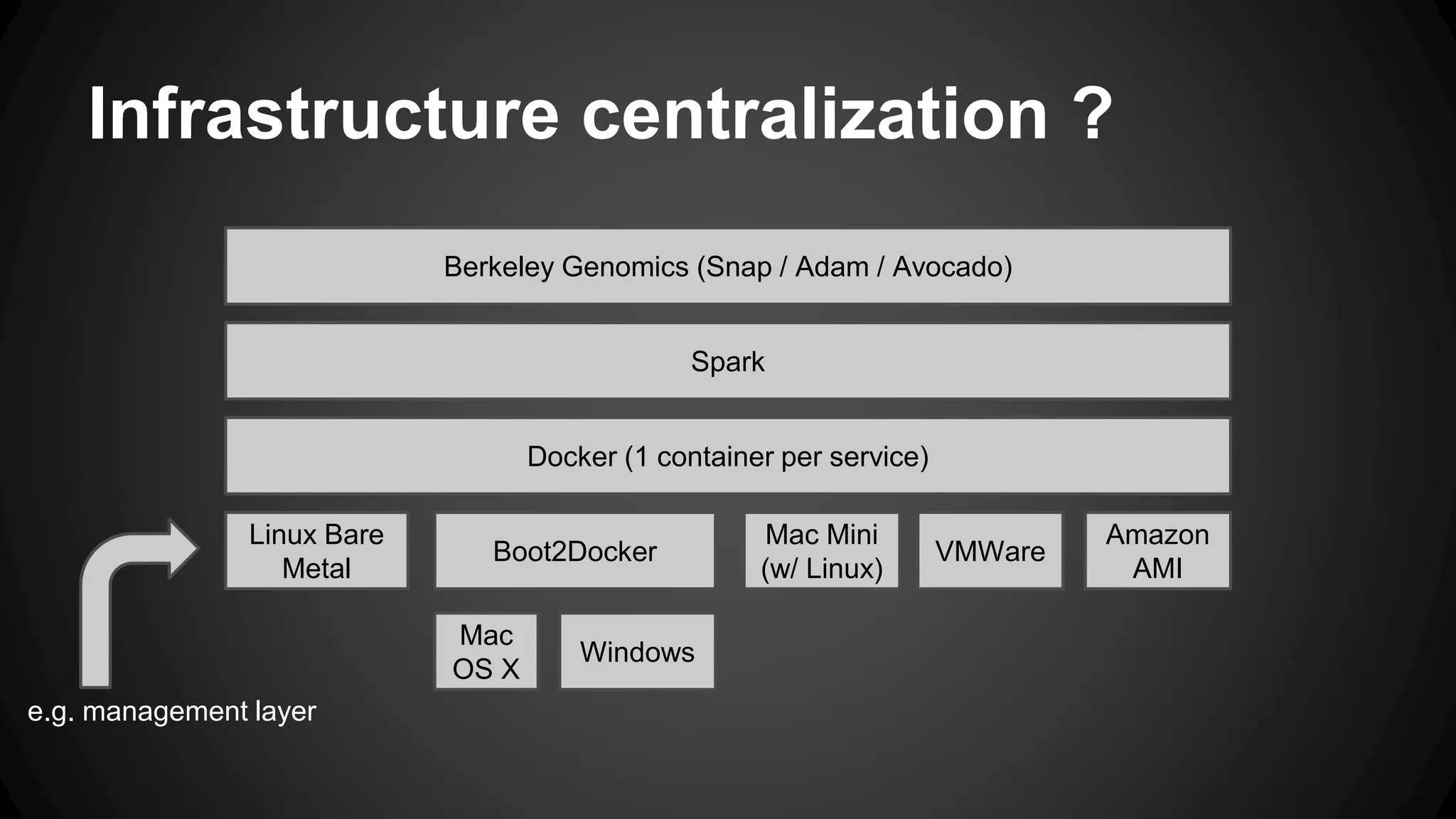
The document discusses a genomics project led by Sébastien Bonami and David Lauzon, which focuses on creating a cloud infrastructure to optimize genomics processing through a proof of concept. Key use cases include genome ETL and data mining, utilizing technologies such as Apache Spark and various Berkeley genomics tools. The project outlines planning steps, environment setups, and challenges such as understanding genomics and managing distributed systems.