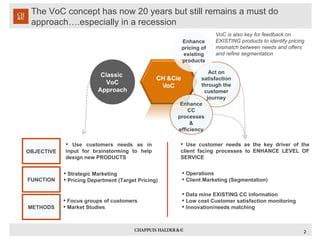
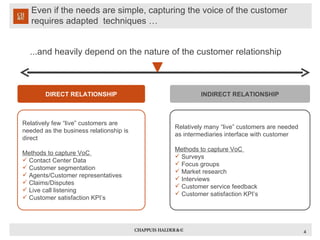
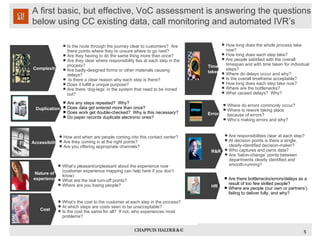
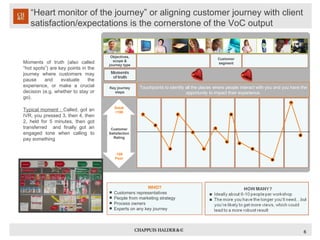
The document discusses using voice of the customer (VoC) techniques to understand customer needs and improve processes. It recommends capturing VoC through existing contact center data, call monitoring, surveys, and focus groups. Customer needs can typically be categorized into desires for simplicity, speed, accessibility, pleasant experiences, and lower costs. Understanding key moments in customers' journeys and identifying opportunities to improve satisfaction at touchpoints is important for aligning processes with customer expectations.