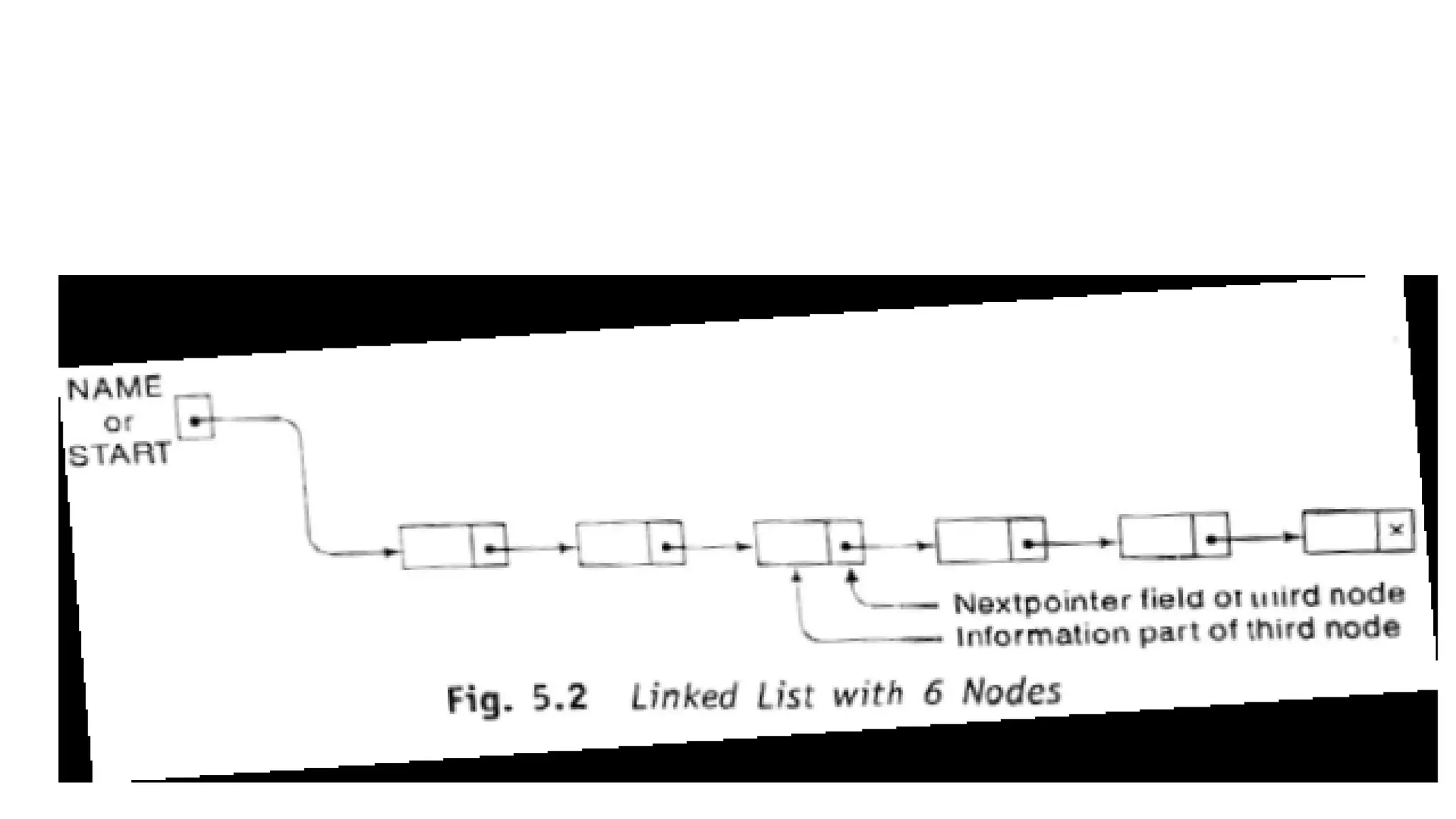
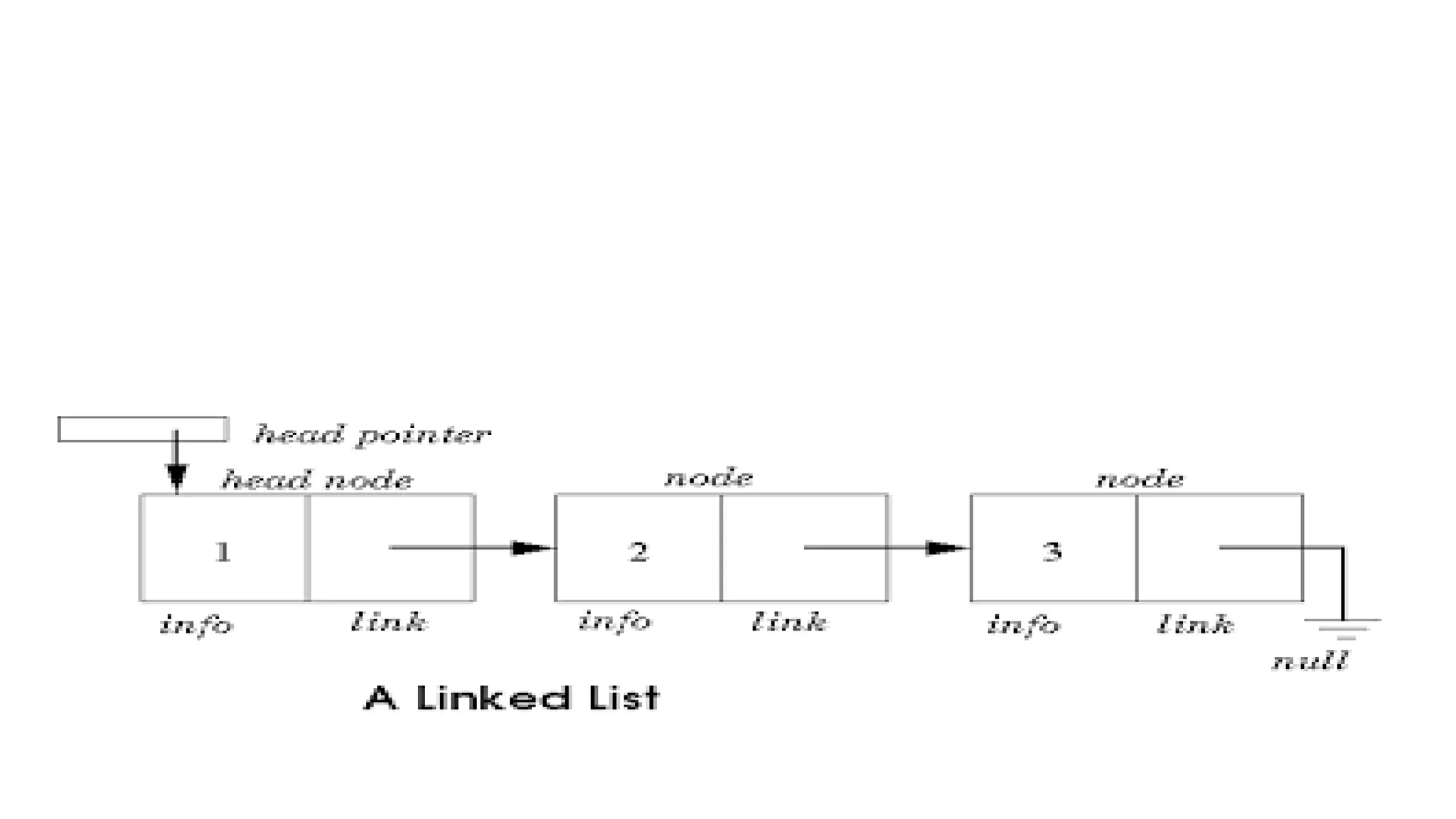
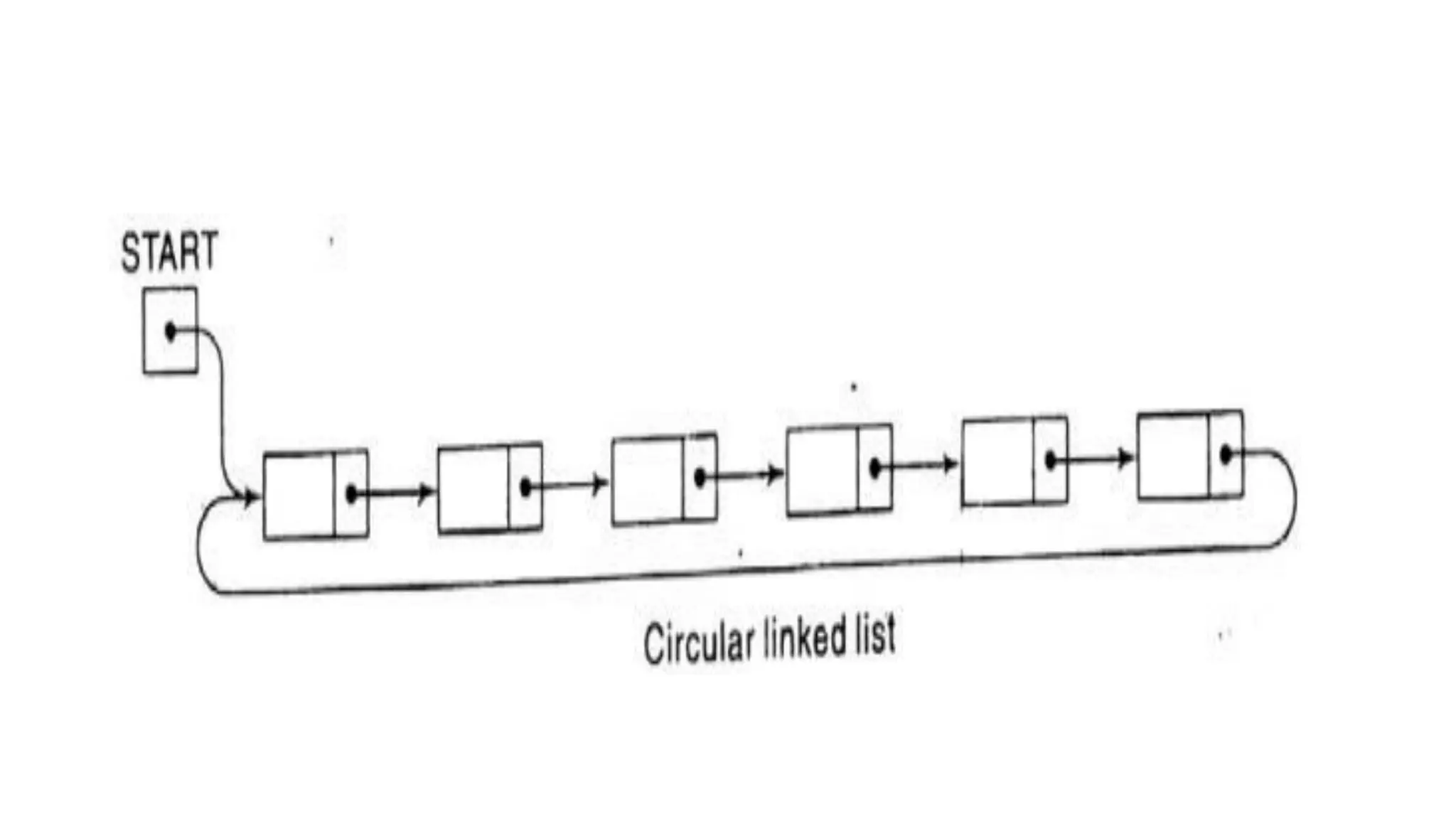
1. Linked lists are a linear data structure where each element contains a data field and a pointer to the next element. This allows flexible insertion and deletion compared to arrays.
2. Each node of a singly linked list contains a data field and a next pointer. Traversal follows the next pointers from head to tail. Doubly linked lists add a back pointer for bidirectional traversal.
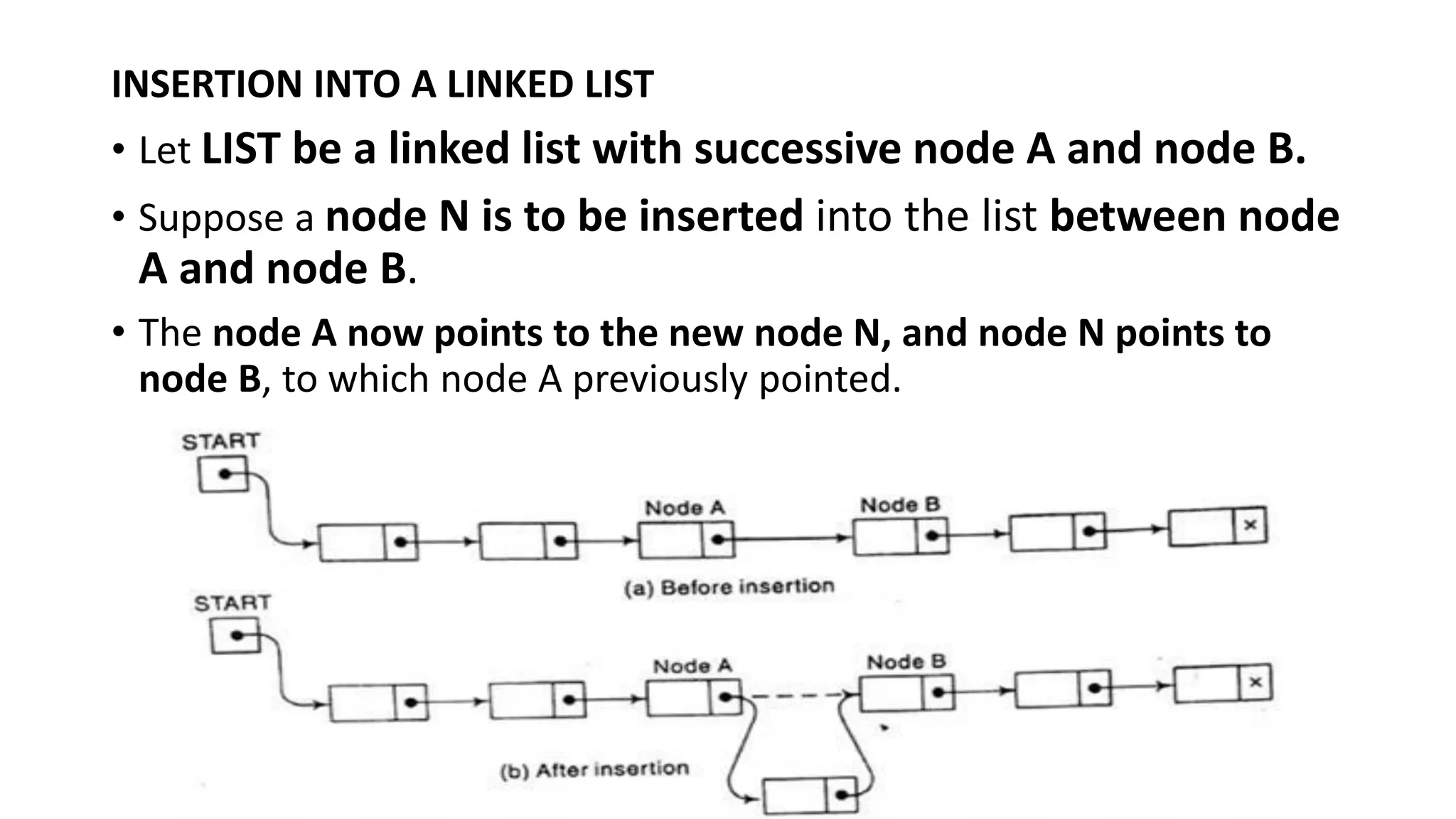
3. Common operations on linked lists include traversal, search, insertion at head/specific point, and deletion by adjusting pointers. Memory for new nodes comes from a free list, and deleted nodes return there.




![REPRESENTATION OF LINKED LIST IN MEMORY
• Let LIST be a linked list.
• Then LIST will be maintained in memory, unless otherwise specified or
implied.
• First of all, LIST requires two linear arrays – INFO and LINK- such that
• INFO[K] and LINK[K] contain, respectively, the information part and the
nextpointer field of a node of LIST.
• LIST also requires a variable name – such as START – which contain the
location of the beginning of the list, and a nextpointer sentinel – denoted
by a NULL – which indicates the end of the list.
• Since the subscripts of the arrays INFO and LINK will usually be positive, we
will choose NULL=0, unless and otherwise stated.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bcadatastructureslinkedlistmrs-220121094731/75/Bca-data-structures-linked-list-mrs-sowmya-jyothi-8-2048.jpg)
![The following diagram pictures a linked list
in memory where each node of the list
contains a single character. We can obtain
the actual list of characters, or as follows:
START=9, so INFO[9]=N is the first
character.
LINK[9]=3, so INFO[3]=O is the second
character.
LINK[3]=6, so INFO[6]= (blank) is the third
character.
LINK[6]=11, so INFO[11]=E is the fourth
character.
LINK[11]=7, so INFO[7]=X is the fifth
character.
LINK[7]=10, so INFO[10]=I is the sixth
character.
LINK[10]=4, so INFO[4]=T is the seventh
character.
LINK[4]=0, the NULL value, so the list has
ended.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bcadatastructureslinkedlistmrs-220121094731/75/Bca-data-structures-linked-list-mrs-sowmya-jyothi-9-2048.jpg)
![TRAVERSING A LINKED LIST i=1
• Let LIST be a linked list in memory. i=i+1=2
• Let INFO be the data in the current node,
• LINK points to the address of the next node,
• START is pointing to the address of the first node and NULL indicating the
end of the list.
• Suppose we want to traverse LIST in order to process
each node exactly once.
• The pointer variable PTR which points to the node that is currently being
processes.
• Accordingly, LINK[PTR] points to the next node to be processed.
• Thus the assignment PTR:=LINK[PTR] moves the pointer to the
next node in the list](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bcadatastructureslinkedlistmrs-220121094731/75/Bca-data-structures-linked-list-mrs-sowmya-jyothi-10-2048.jpg)
![pointer variable PTR which points to the node that is currently being
processes.
Accordingly, LINK[PTR] points to the next node to be processed.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bcadatastructureslinkedlistmrs-220121094731/75/Bca-data-structures-linked-list-mrs-sowmya-jyothi-11-2048.jpg)
![Algorithm 5.1: (Traversing a Linked List)
•Let LIST be a linked list in the memory. This algorithm
traverses LIST, by applying an operation PROCESS to each
element of the LIST.
•The variable PTR points to the node that is currently being
processed.
1. Set PTR:=START [Initializes pointer to PTR]
2. Repeat Steps 3 and 4 while PTR ≠ NULL
3. Apply PROCESS to INFO[PTR]
4. Set PTR:=LINK[PTR] [PTR now points to the next node]
[End of Step 2 Loop]
5. Exit.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bcadatastructureslinkedlistmrs-220121094731/75/Bca-data-structures-linked-list-mrs-sowmya-jyothi-12-2048.jpg)
![SEARCHING A LINKED LIST
•Let LIST be a linked list in memory.
•Suppose a specific ITEM of information is given, for
finding the location LOC of the node where ITEM
first appears in the LIST.
•Then, one searches for ITEM in LIST by traversing
through the list using a pointer variable PTR and
comparing ITEM with the contents of INFO[PTR] of
each node, one by one, of LIST.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bcadatastructureslinkedlistmrs-220121094731/75/Bca-data-structures-linked-list-mrs-sowmya-jyothi-13-2048.jpg)

![1. Set PTR:=START [Initializes pointer to PTR]
2. Repeat Steps 3 while PTR ≠ NULL
3. If ITEM=INFO[PTR] then
Set LOC:=PTR, and Exit.
Else:
Set PTR:=LINK[PTR] [PTR now points to the next node]
[End of If structure]
[End of Step 2 Loop]
4. Set LOC:=NULL. [Search is unsuccessful?]
5. Exit.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bcadatastructureslinkedlistmrs-220121094731/75/Bca-data-structures-linked-list-mrs-sowmya-jyothi-15-2048.jpg)






![NEW:=AVAIL, AVAIL:=LINK[AVAIL]
INFO[NEW]:=ITEM](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bcadatastructureslinkedlistmrs-220121094731/75/Bca-data-structures-linked-list-mrs-sowmya-jyothi-23-2048.jpg)
![INSERTION ALGORITHMS
• Since insertion algorithms will use a node in the AVAIL list, all of
the algorithms will include the following steps:
a) Checking to see if free space is available in the AVAIL list. If not,
that is, if AVAIL=NULL, then the algorithm will print the message
OVERFLOW.
b) Removing the first node from the AVAIL list.
Using the variable NEW to keep track of the location of the new
node, this step can be implemented by the pair of assignments
NEW:=AVAIL, AVAIL:=LINK[AVAIL]
c) Copying new information into the new node.
In other words, INFO[NEW]:=ITEM](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bcadatastructureslinkedlistmrs-220121094731/75/Bca-data-structures-linked-list-mrs-sowmya-jyothi-24-2048.jpg)
![INFO[NEW]:=ITEM
2. AVAIL:=LINK[AVAIL]
NEW:=AVAIL, AVAIL:=LINK[AVAIL]
1. NEW:=AVAIL](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bcadatastructureslinkedlistmrs-220121094731/75/Bca-data-structures-linked-list-mrs-sowmya-jyothi-25-2048.jpg)
![•Insert at the Beginning of a List
INFO[NEW]:=ITEM LINK [NEW]:=START START:=NEW
1
2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bcadatastructureslinkedlistmrs-220121094731/75/Bca-data-structures-linked-list-mrs-sowmya-jyothi-26-2048.jpg)
![Algorithm 5.4: INSFIRST(INFO, LINK, START, AVAIL, ITEM)
• This algorithm inserts ITEM as the first node in the list.
1. [OVERFLOW?] IF AVAIL=NULL, then Write: OVERFLOW, and Exit.
2. [Remove first node from AVAIL list]
Set NEW:=AVAIL and AVAIL:=LINK[AVAIL]
3. Set INFO[NEW]:=ITEM [Copies new data into the new node]
4. Set LINK [NEW]:=START [New node now points to the original first node]
5. Set START:=NEW [Change START so it points to the new node]
6. Exit](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bcadatastructureslinkedlistmrs-220121094731/75/Bca-data-structures-linked-list-mrs-sowmya-jyothi-27-2048.jpg)
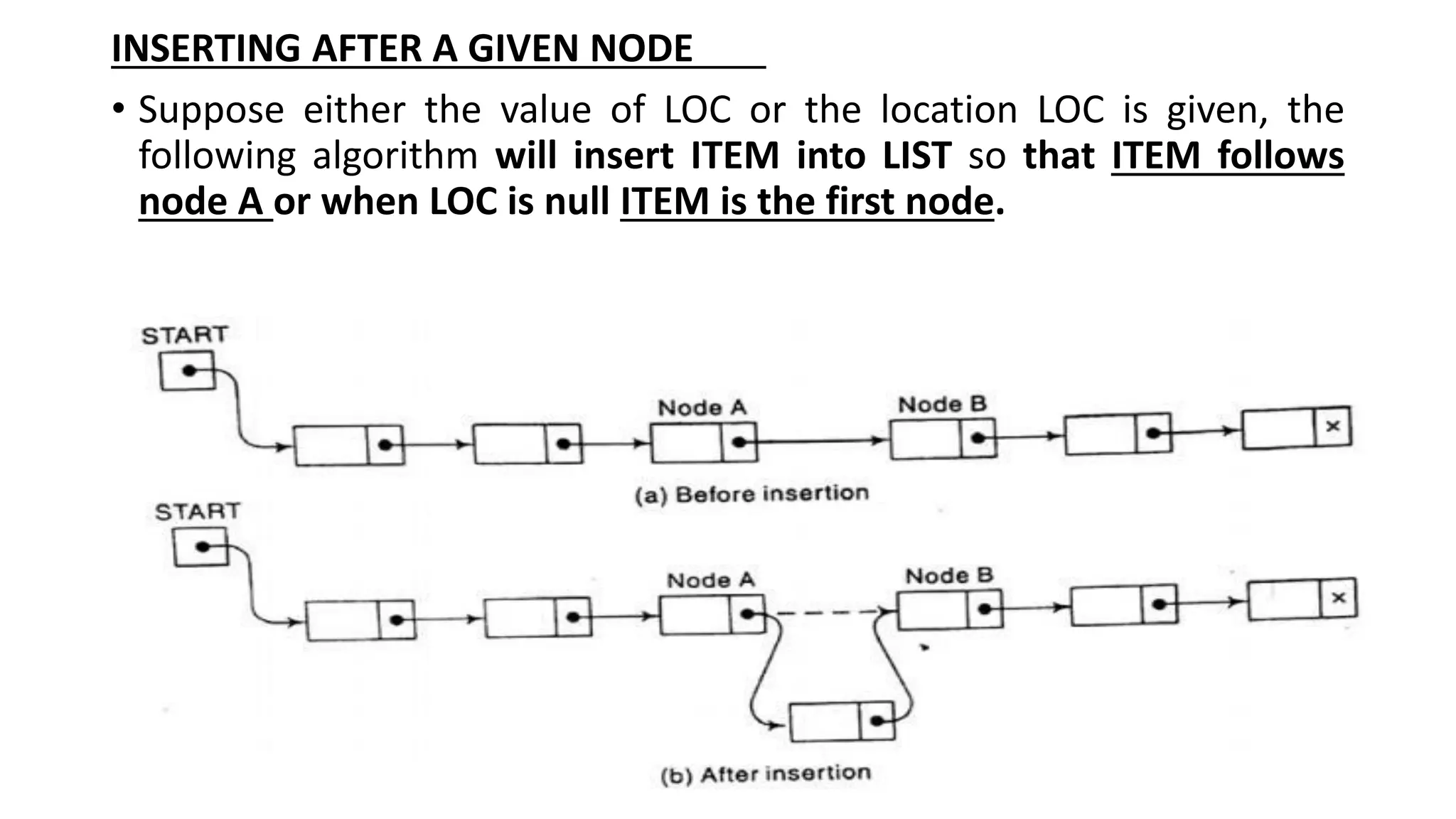
![Algorithm 5.5: INSLOC (INFO, LINK, START,AVAIL,LOC, ITEM)
• This algorithm inserts ITEM so that ITEM follows the node with location LOC or
inserts ITEM as the first node when LOC =NULL
1. IF AVAIL=NULL, then Write: OVERFLOW, and Exit. [OVERFLOW?]
2. [Remove first node from AVAIL list]
Set NEW:=AVAIL and AVAIL:=LINK[AVAIL]
3. Set INFO[NEW]:=ITEM [Copies new data into the new node]
4. If LOC=NULL, then:
[Insert as the first node.]
Set LINK[NEW]:=START and START:=NEW.
[Insert after the node with location LOC.]
Else:
Set LINK[NEW]:=LINK[LOC] and LINK[LOC]:=NEW.
5. Exit [End of If Structure]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bcadatastructureslinkedlistmrs-220121094731/75/Bca-data-structures-linked-list-mrs-sowmya-jyothi-29-2048.jpg)

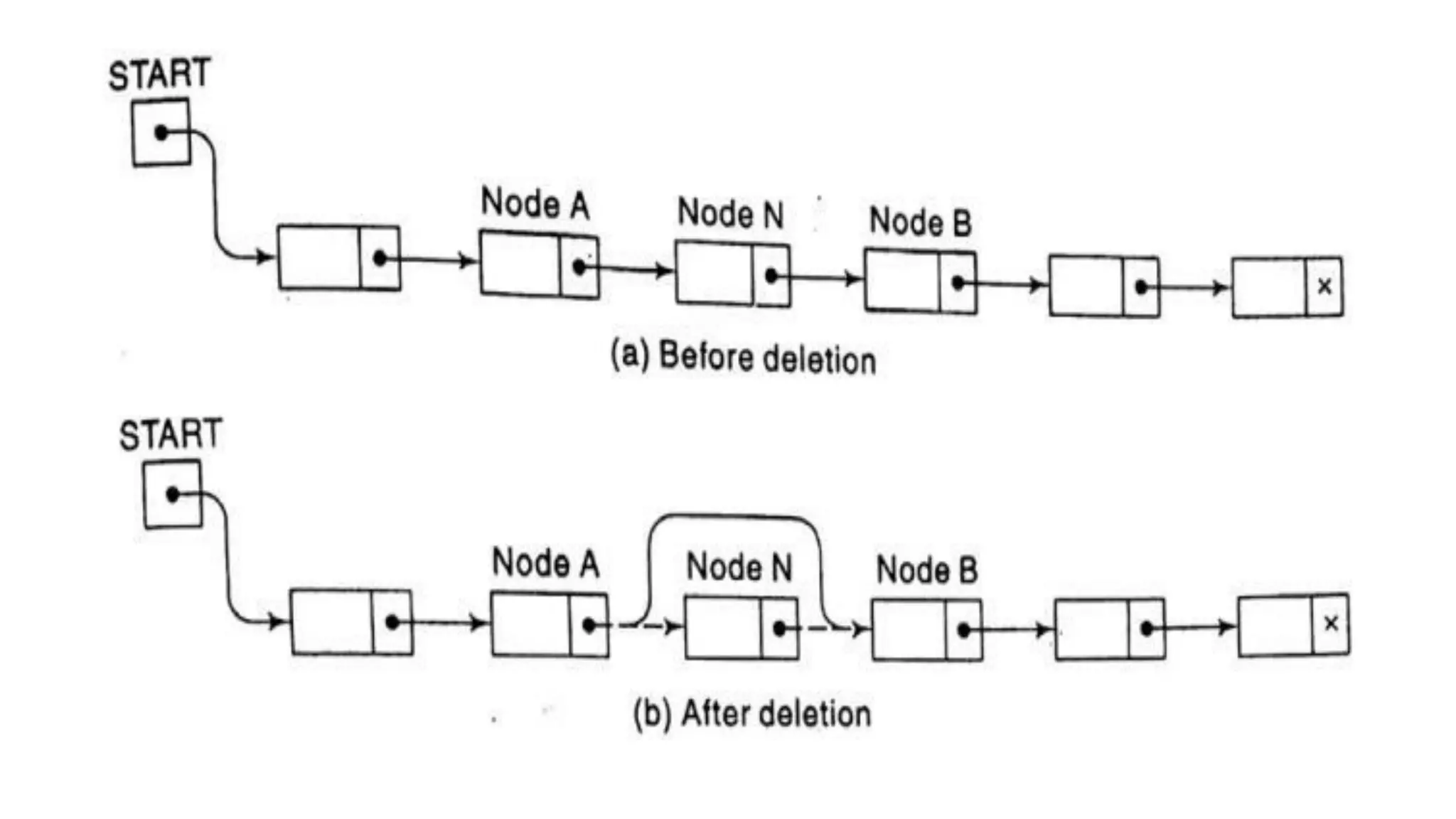

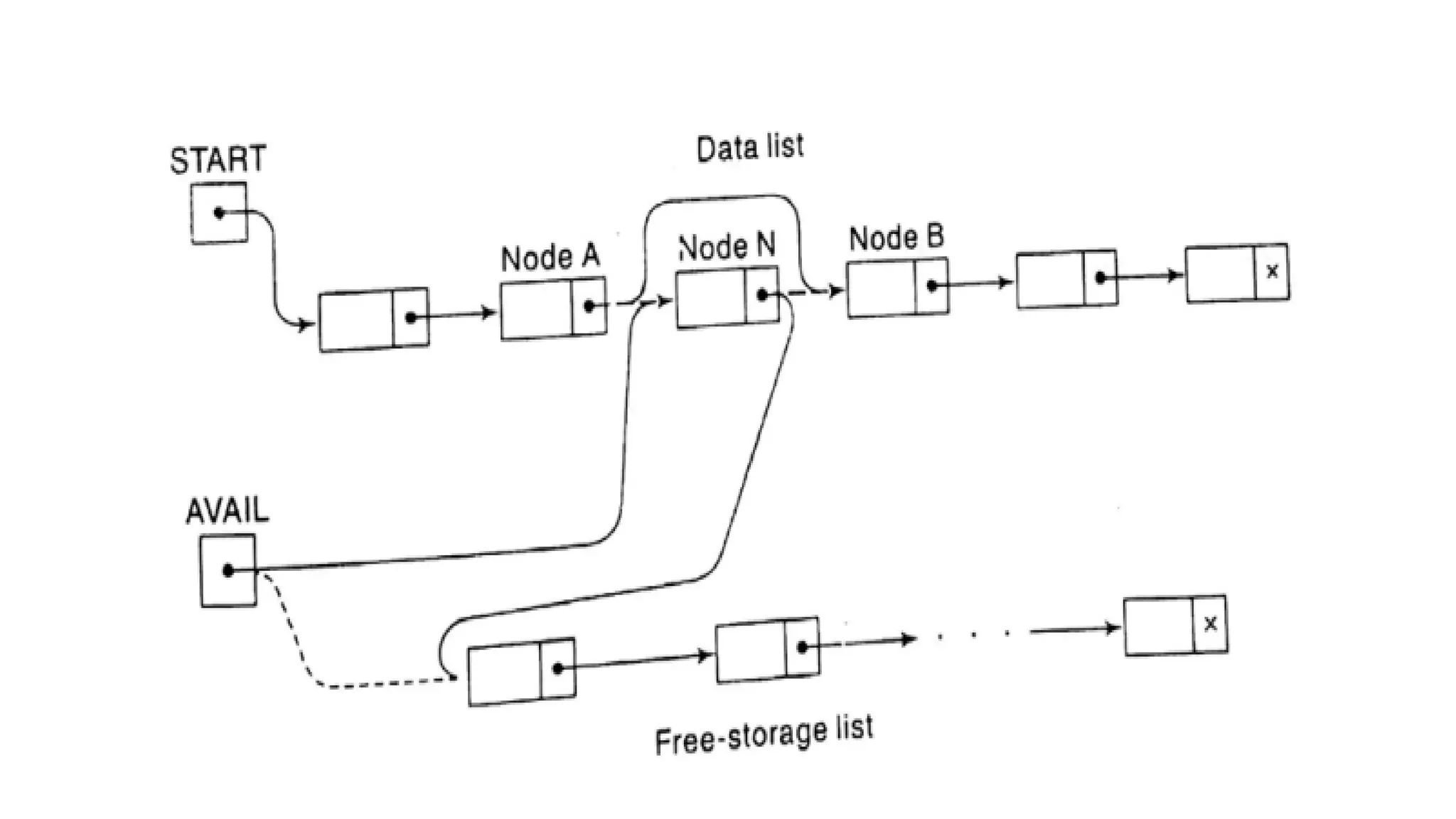

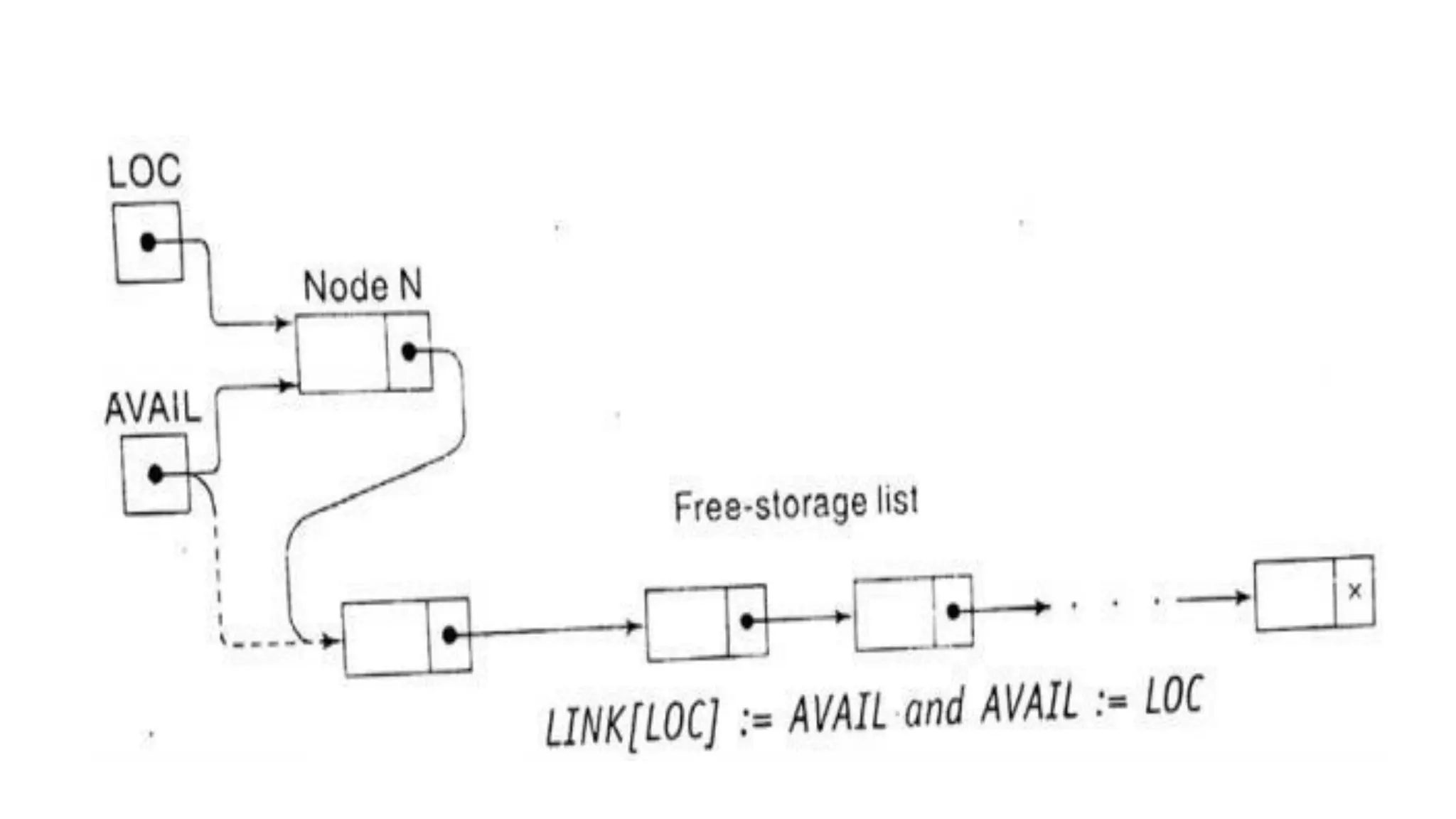

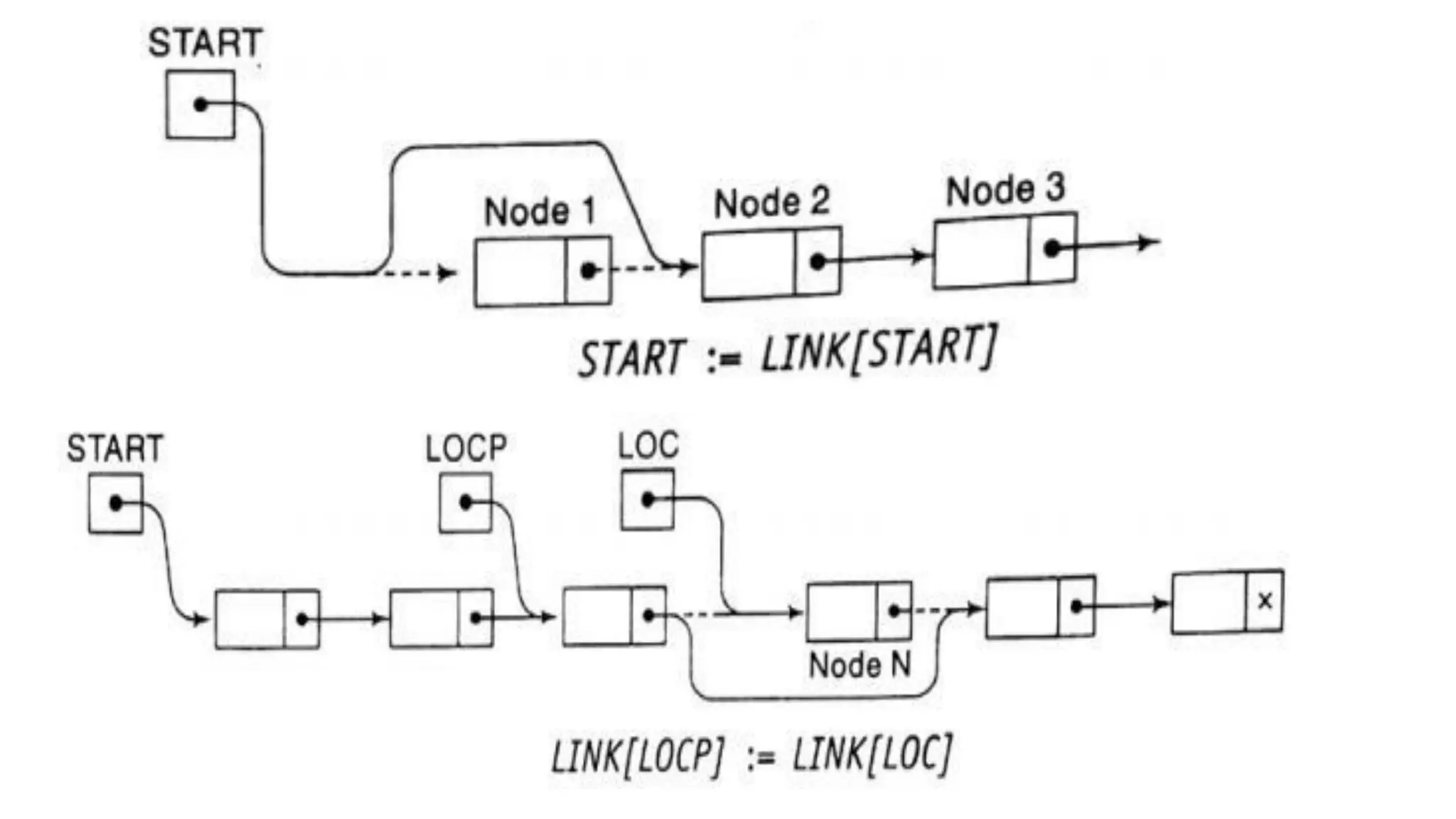
![1. If LOCP:=NULL, then:
Set START:=LINK[START] [Deletes the First node.]
Else:
Set LINK[LOCP]:=LINK[LOC] [Deletes node N.]
2. [Return deleted node to the AVAIL list.]
Set Link[LOC]:=AVAIL and AVAIL:=LOC.
3. Exit.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bcadatastructureslinkedlistmrs-220121094731/75/Bca-data-structures-linked-list-mrs-sowmya-jyothi-37-2048.jpg)



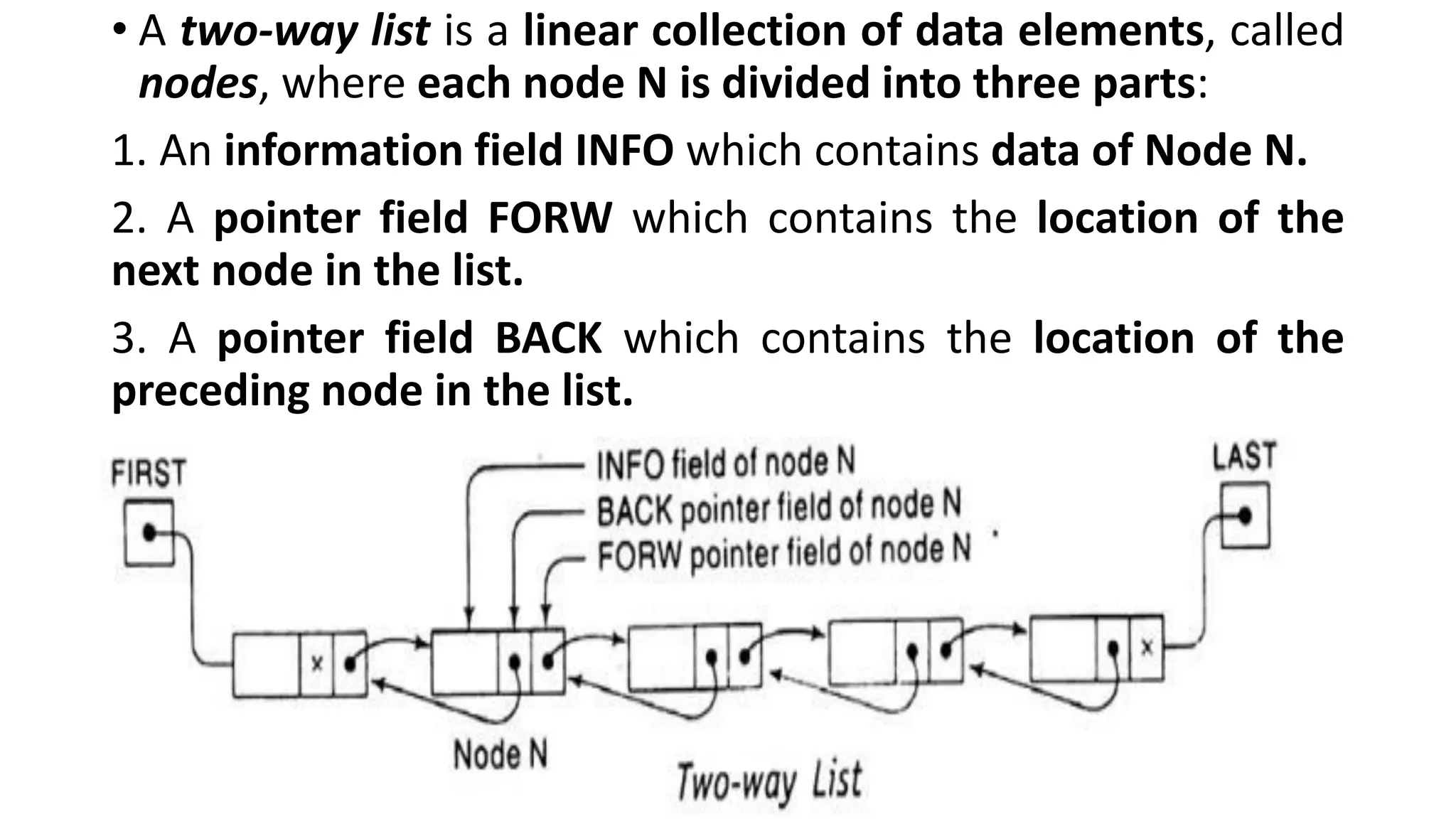
![• The list also requires two list pointer variables:
1. FIRST, which points to the first node in the list and LAST, which points to
the last node in the list as shown in the figure above.
2. NULL pointer appears in the FORW field of the last node and BACK field
of the first node in the list.
• FIRST and FORW can be used to traverse the list in forward direction and
LAST and BACK can be used to traverse the list in backward direction.
• Suppose LOCA and LOCB are the locations respectively, of Nodes A and
Node B in a two-way list.
• Then the way that the pointers FORW and BACK are defined gives the
following:
•Pointer property: FORW[LOCA]=LOCB if and only if BACK[LOCB]=LOCA.
• In other words, the statement that the Node B follows Node A is equivalent
to the statement that Node A precedes Node B.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bcadatastructureslinkedlistmrs-220121094731/75/Bca-data-structures-linked-list-mrs-sowmya-jyothi-44-2048.jpg)
![Operations on Two-Way Lists
• Traversing: A list can be traversed and each node can be processed
only once.
• Searching: A search for an ITEM in the linked list can be carried out
to find the location LOC of the ITEM in the list.
• Deleting: A node N can be deleted from the two-way list with the
help of FORW and BACK pointers as follows:
• FORW[BACK[LOC]]:=FORW[LOC] and
BACK[FORW[LOC]]:=BACK[LOCK],
• The deleted node N can then be returned to the list of available
nodes AVAIL by the assignments:
• FORW[LOC]:=AVAIL and AVAIL:=LOC.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bcadatastructureslinkedlistmrs-220121094731/75/Bca-data-structures-linked-list-mrs-sowmya-jyothi-45-2048.jpg)