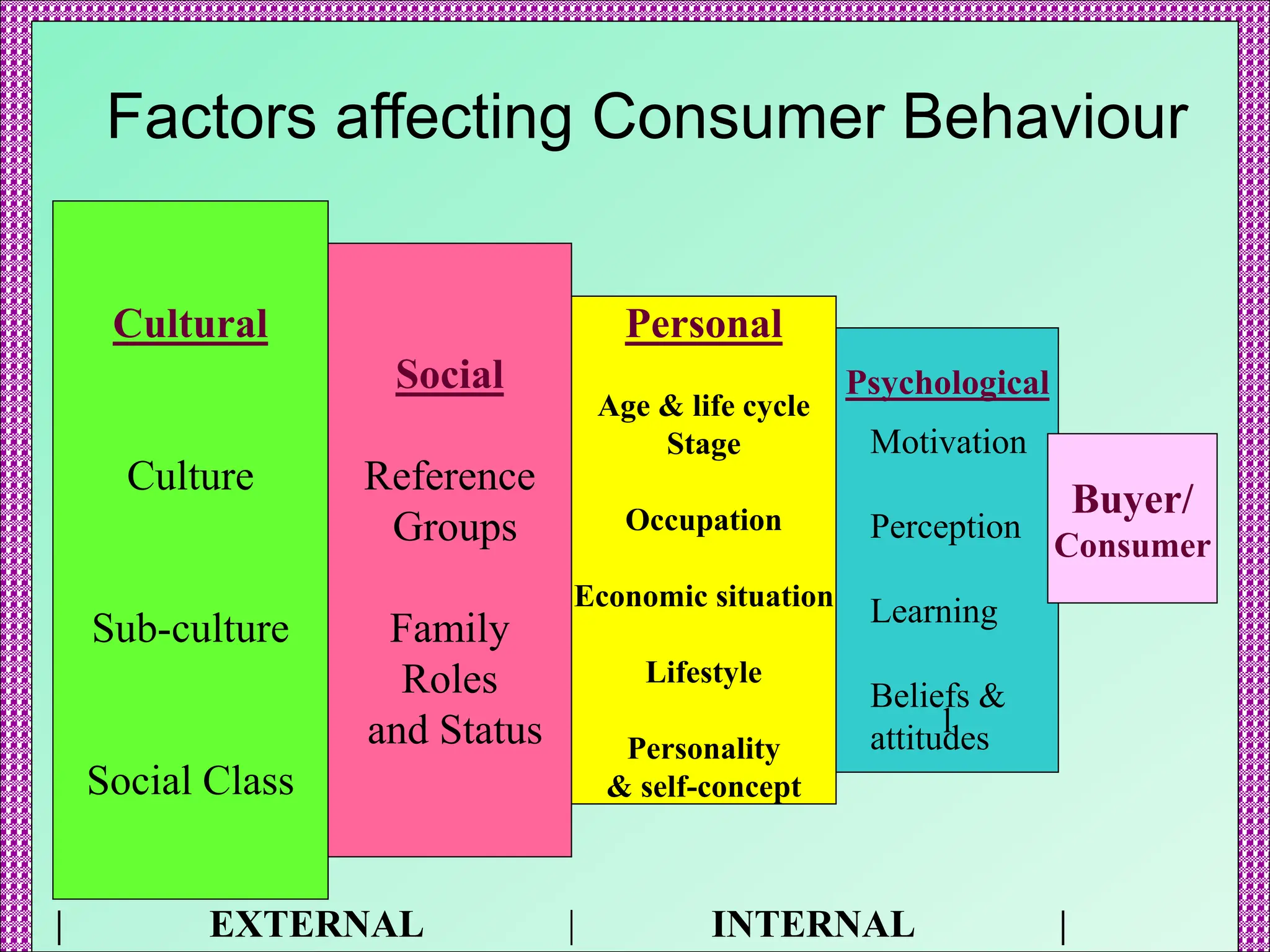
The document discusses the importance of understanding consumer behavior in marketing, emphasizing factors such as cultural, social, personal, and psychological influences on buyer decisions. It outlines the complexities of culture, including concepts like enculturation and globalization, and highlights different types of buying behaviors. Additionally, it references various resources for further reading on consumer behavior models and trends.



![1] Consumer Behaviour
by Batra and Kazmi
2] CONSUMER BEHAVIOUR
by Schiffman and Kanuk
3] CONSUMER BEHAVIOUR in the
Indian Context
by Srivastav and Khandai
4] CONSUMER BEHAVIOUR –
building marketing strategy
by Hawkins, Best and Cooney](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1-240204112327-1df5452a/75/Basics-of-Consumer-Behaviour-for-marketing-5-2048.jpg)




![Core Values
TERMINAL VALUES [ states of existence ]
INSTRUMENTAL VALUES [ modes of conduct ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1-240204112327-1df5452a/75/Basics-of-Consumer-Behaviour-for-marketing-10-2048.jpg)






