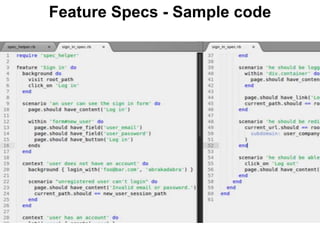
The document provides an overview of RSpec testing framework. It discusses test-driven development (TDD) and behavior-driven development (BDD), then introduces RSpec as a BDD framework for Ruby. It covers key RSpec concepts like expectations and matchers, mocking and stubbing, controller and model specs. It also compares RSpec and Cucumber testing frameworks and provides sample feature spec code using Capybara.





















![Controller specs
•Check rendering
oCorrect template
response.should render_template
oRedirect
response.should redirect_to (url or hash)
o Status code
response.code.should eq(200)
•Verify variable assignments
o Instance variables assigned in the controller to be
shared with the view
o Cookies sent back with the response
cookies['key']
cookies['key']](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation-rspec1-130416180210-phpapp02/85/Basic-RSpec-2-25-320.jpg)