Embed presentation
Download to read offline

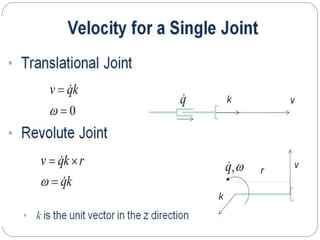
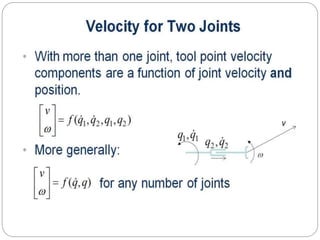
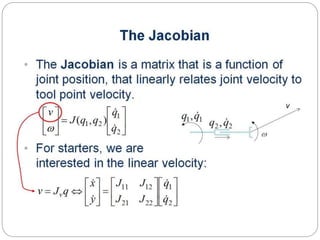
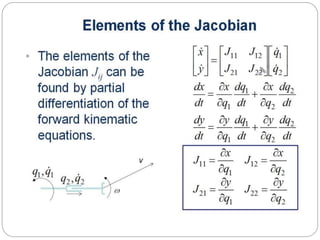
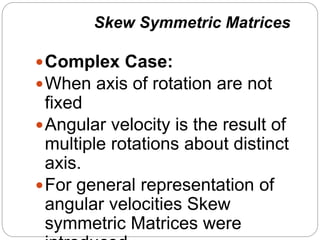
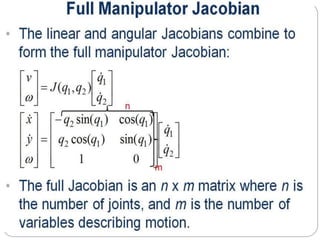


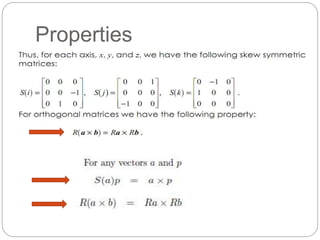
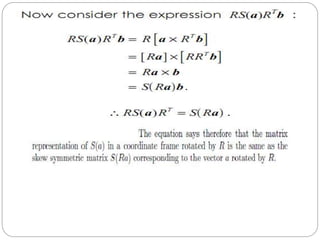
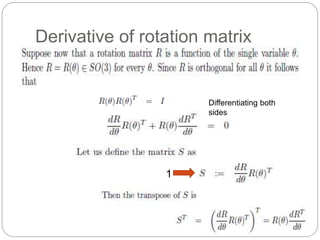

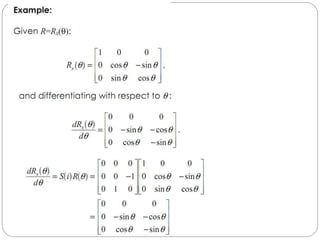
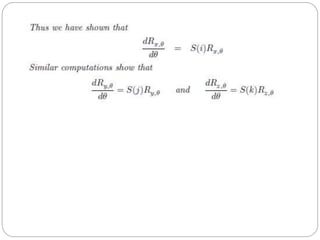
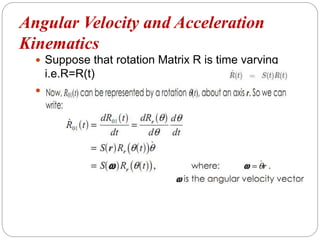


The document discusses differential kinematics involving skew symmetric matrices in complex cases where the axis of rotation is not fixed, leading to angular velocities from multiple distinct rotations. It defines skew symmetric matrices and explains their properties, along with the time-varying nature of rotation matrices and their derivatives. The content is centered on the mathematical representation and implications of rotation dynamics.

















