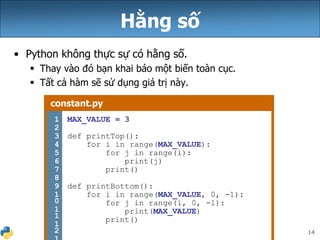
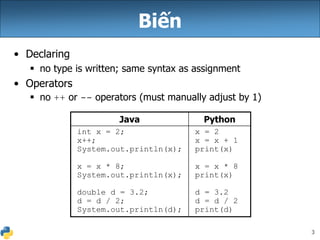
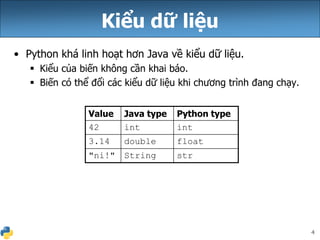
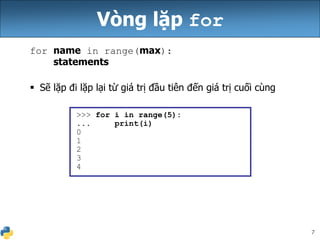
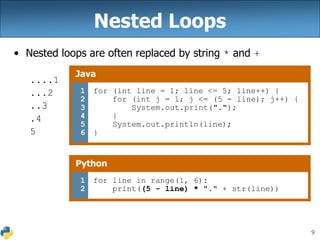
Tài liệu này giải thích về biểu thức, biến và vòng lặp for trong Python, cho thấy cú pháp khai báo biến mà không cần kiểu dữ liệu. Nó cũng mô tả cách nhân chuỗi và cách xử lý chuỗi với số, cùng với các ví dụ cụ thể về vòng lặp for và cách nối các chuỗi. Cuối cùng, nó đề cập đến việc sử dụng biến toàn cục để giả lập hằng số trong Python.






![12
Kết nối các khoảng
• Các khoảng dữ liệu có thể kết nối bằng dấu +
Có thể sử dụng vòng vặp trên một phạm vi để nối các dãy số
>>> range(1, 5) + range(10, 15)
[1, 2, 3, 4, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14]
>>> for i in range(4) + range(10, 7, -1):
... print(i)
0
1
2
3
10
9
8](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bai2-pythonvietnam-140513061822-phpapp02/85/Slide-Python-Bai-2-pythonvietnam-info-12-320.jpg)