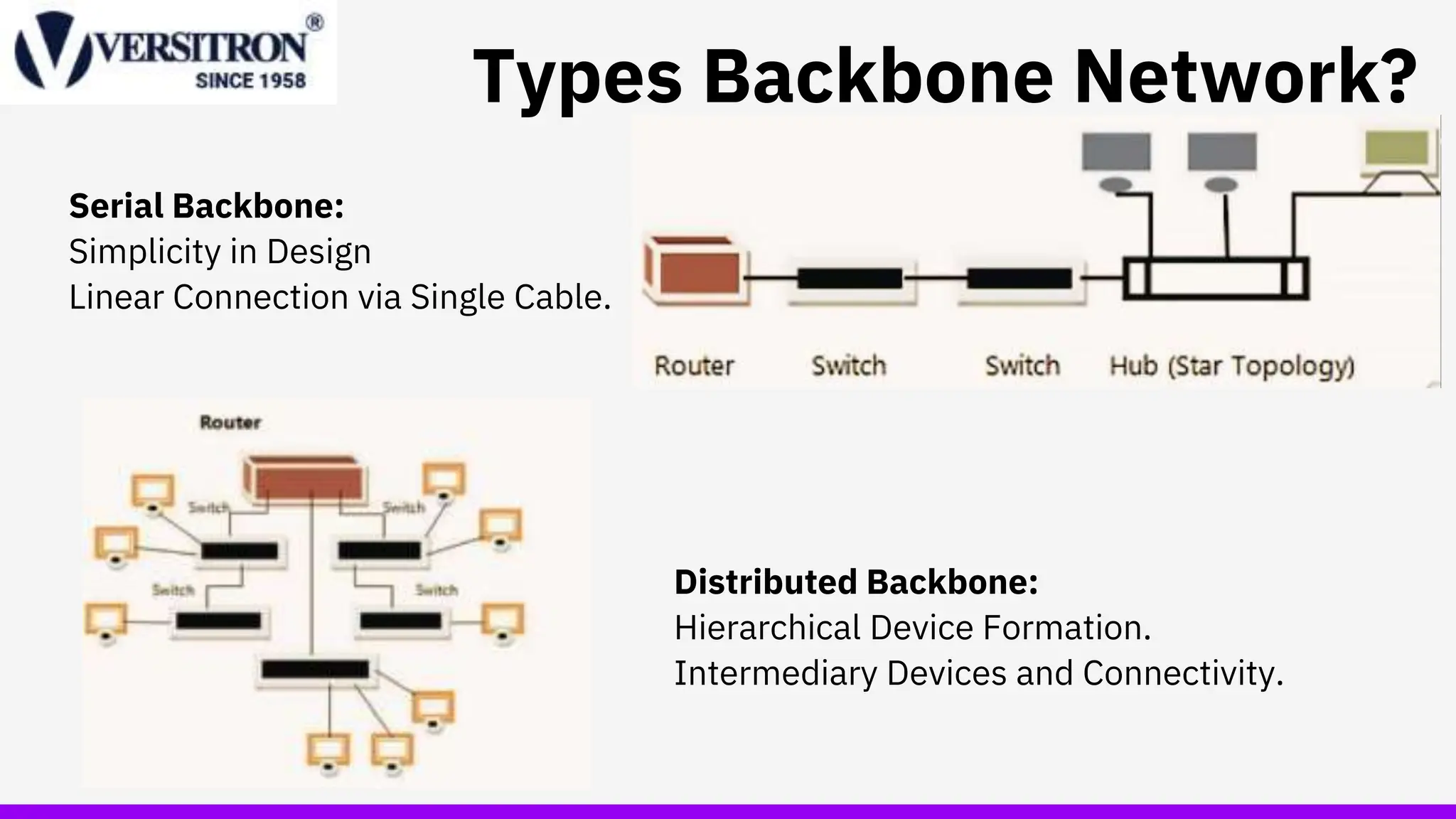
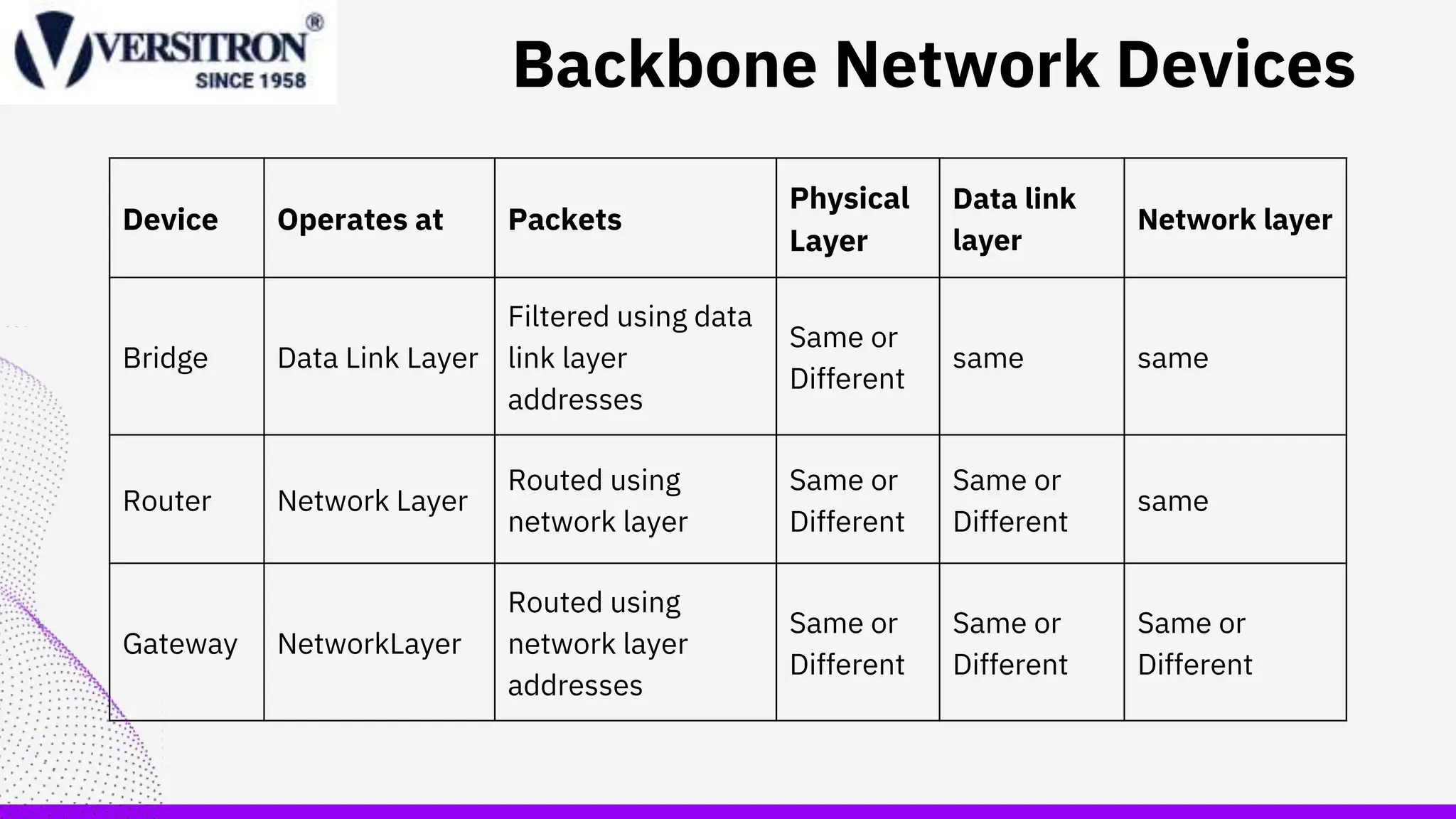
A backbone network is a high-capacity infrastructure that connects multiple networks to facilitate seamless data flow, serving as the foundation for larger networks like WANs and MANs. It consists of components such as network cables, routers, switches, and hubs, each playing a role in communication efficiency. Best practices for improving backbone network performance include upgrading devices, optimizing routing protocols, and reducing overall network demand.