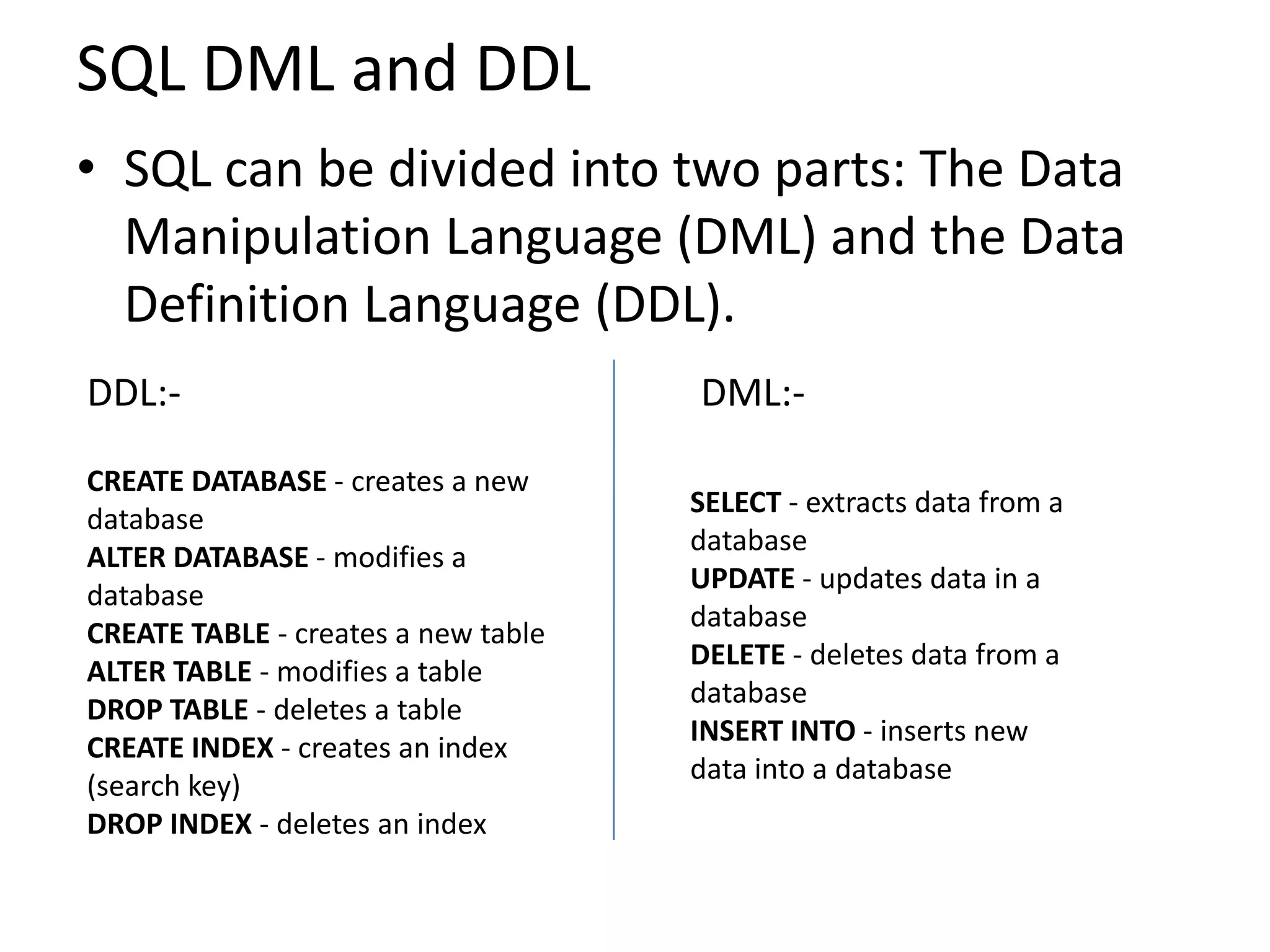
1) SQL is a language used to manage data in relational database management systems. It allows users to define, manipulate, and control access to data.
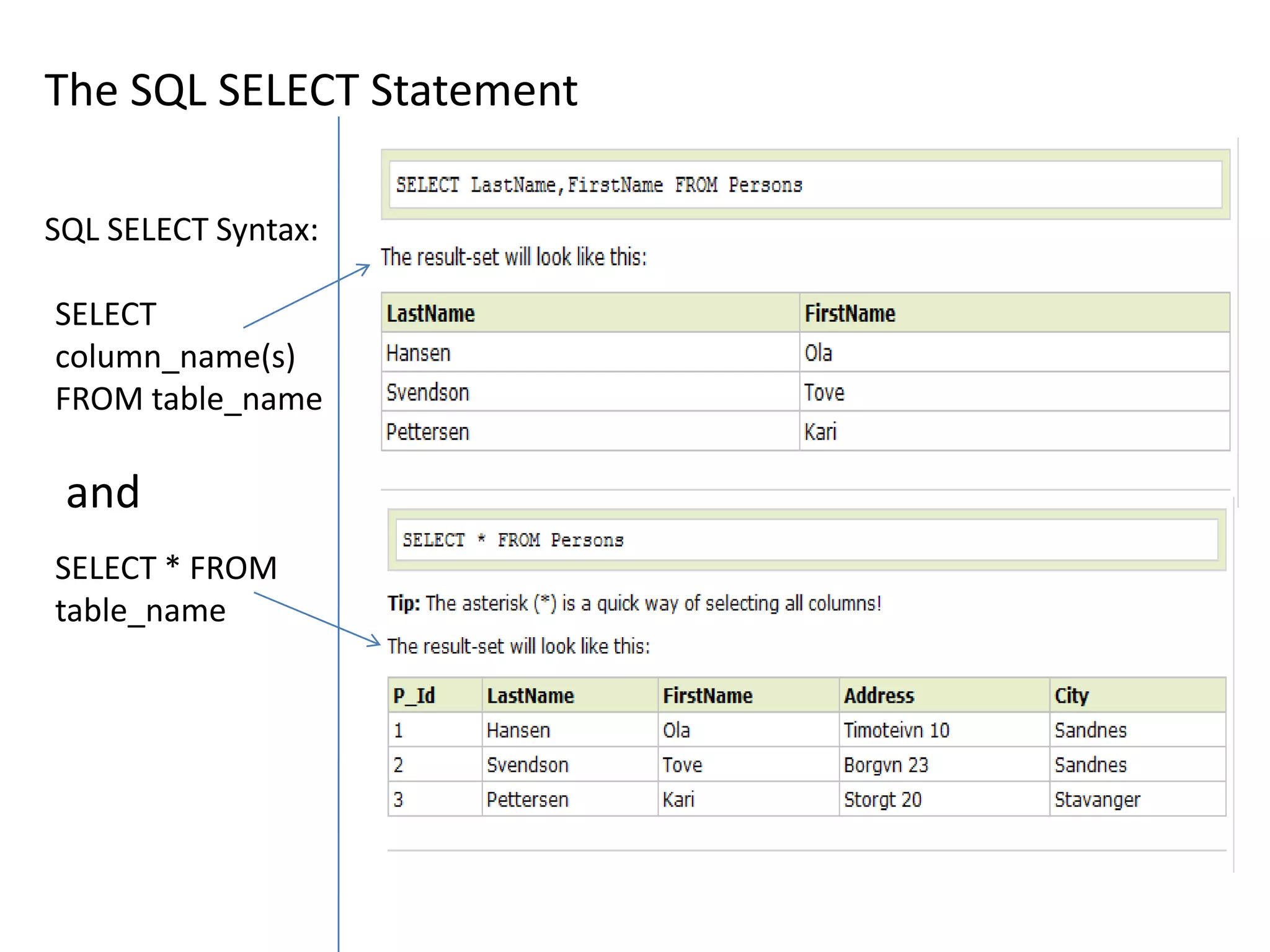
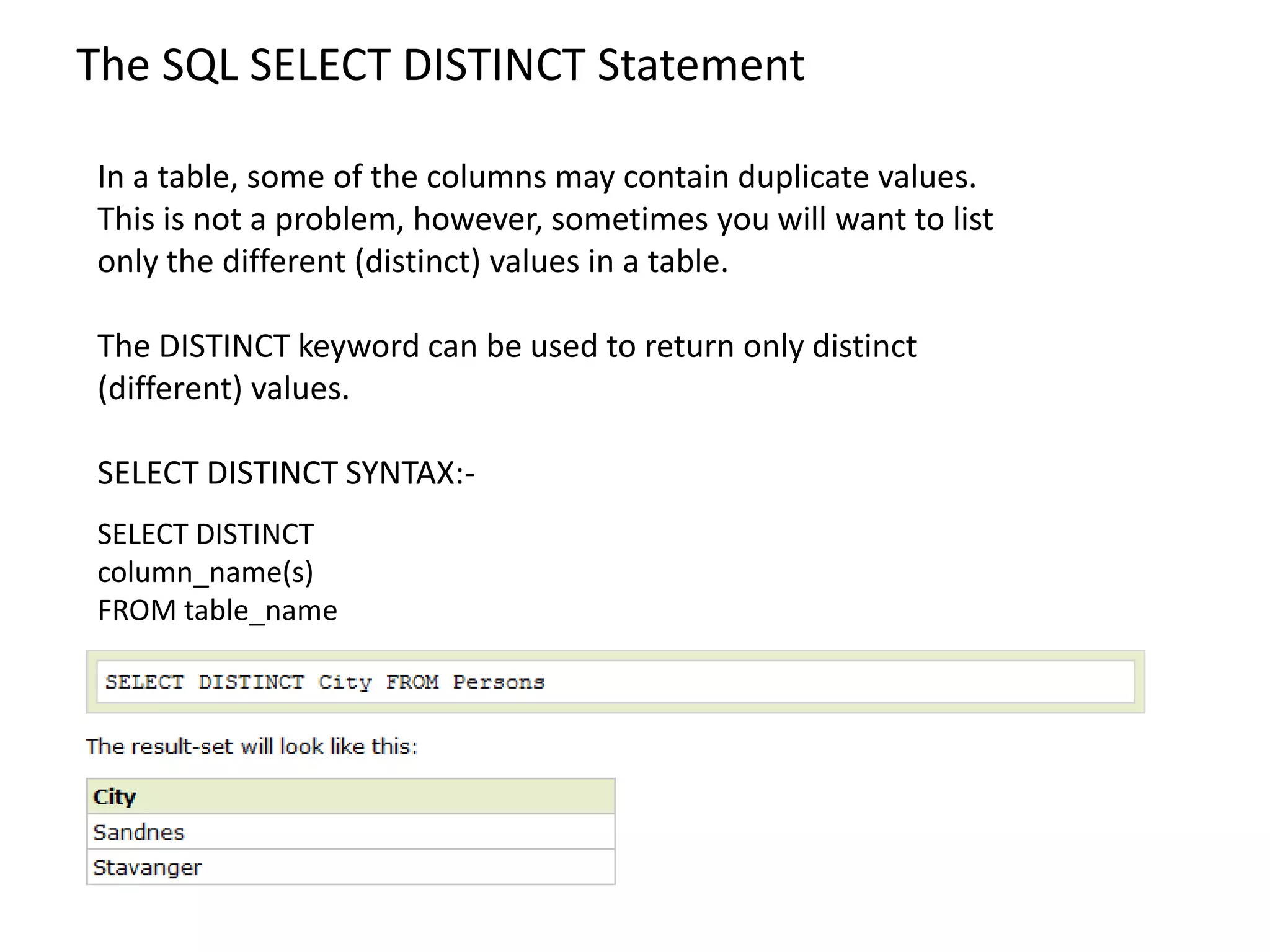
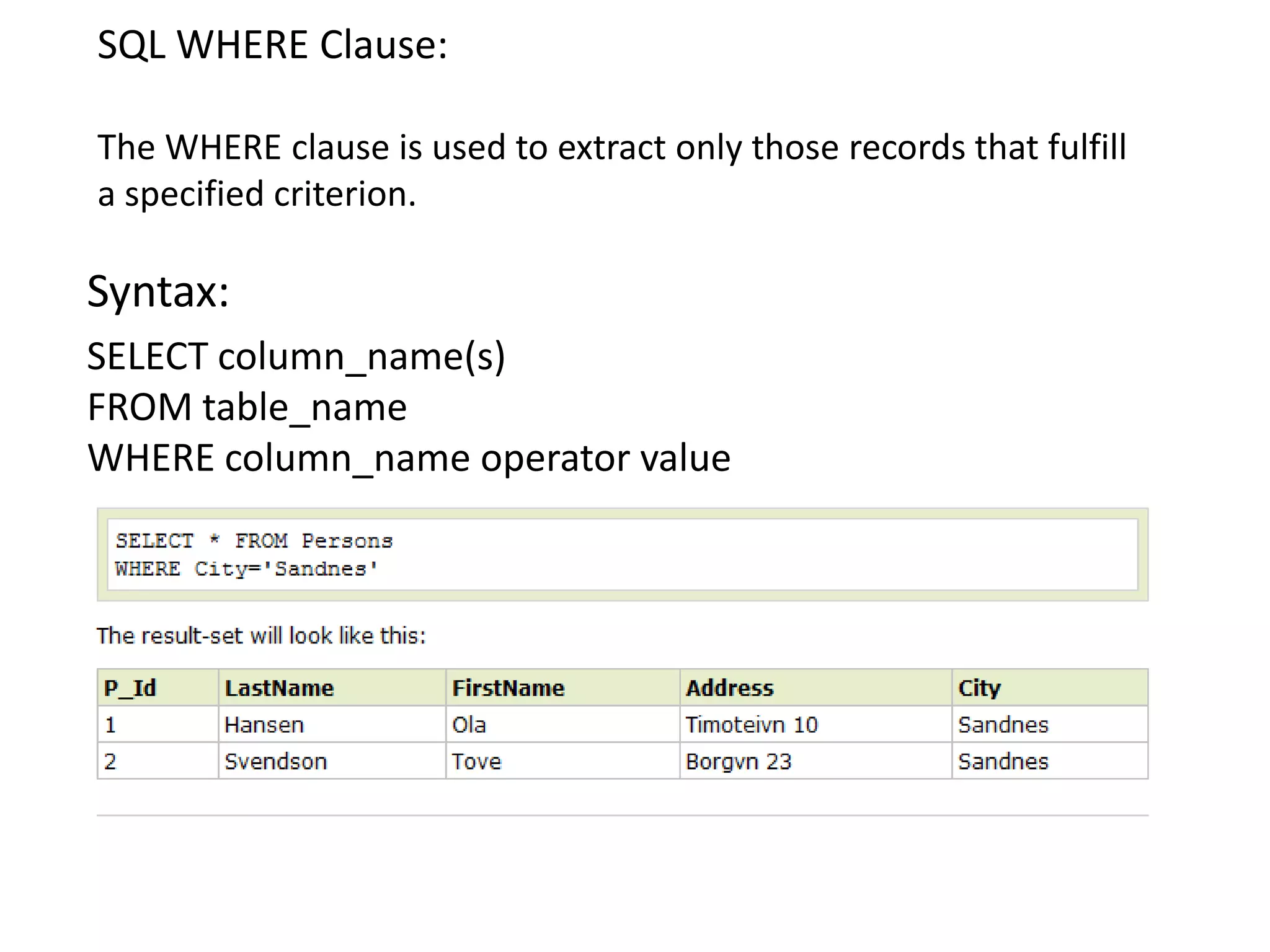
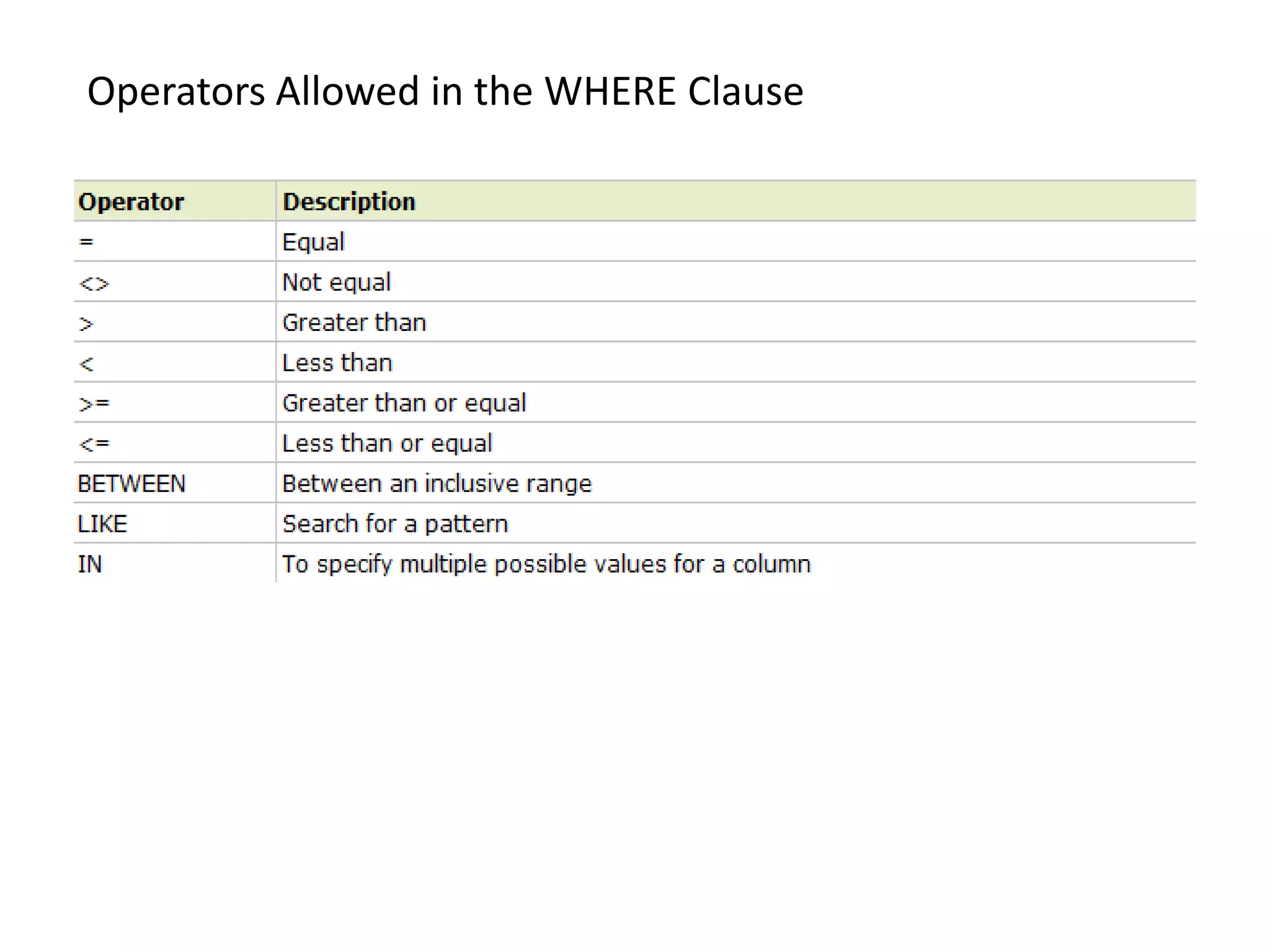
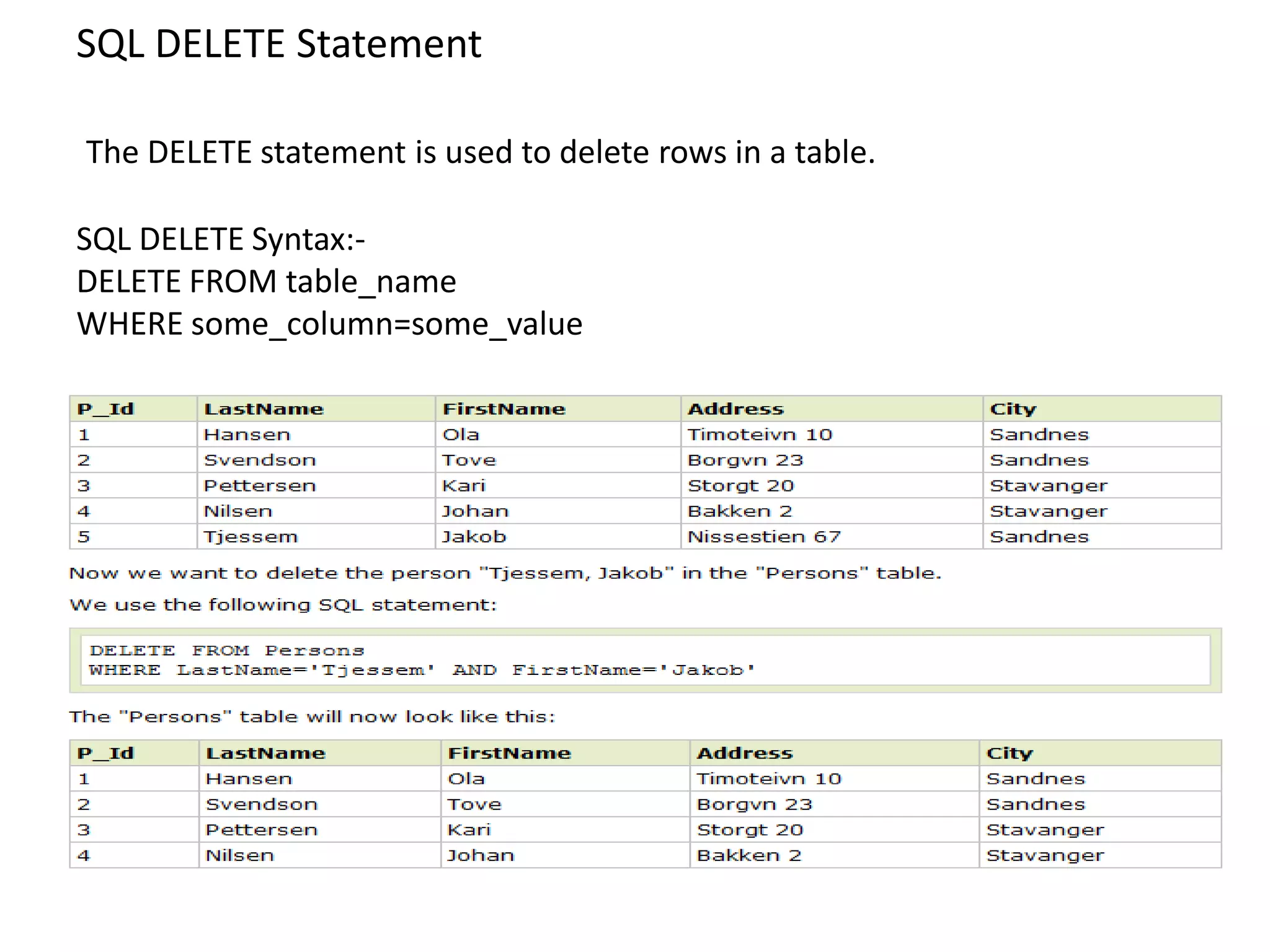
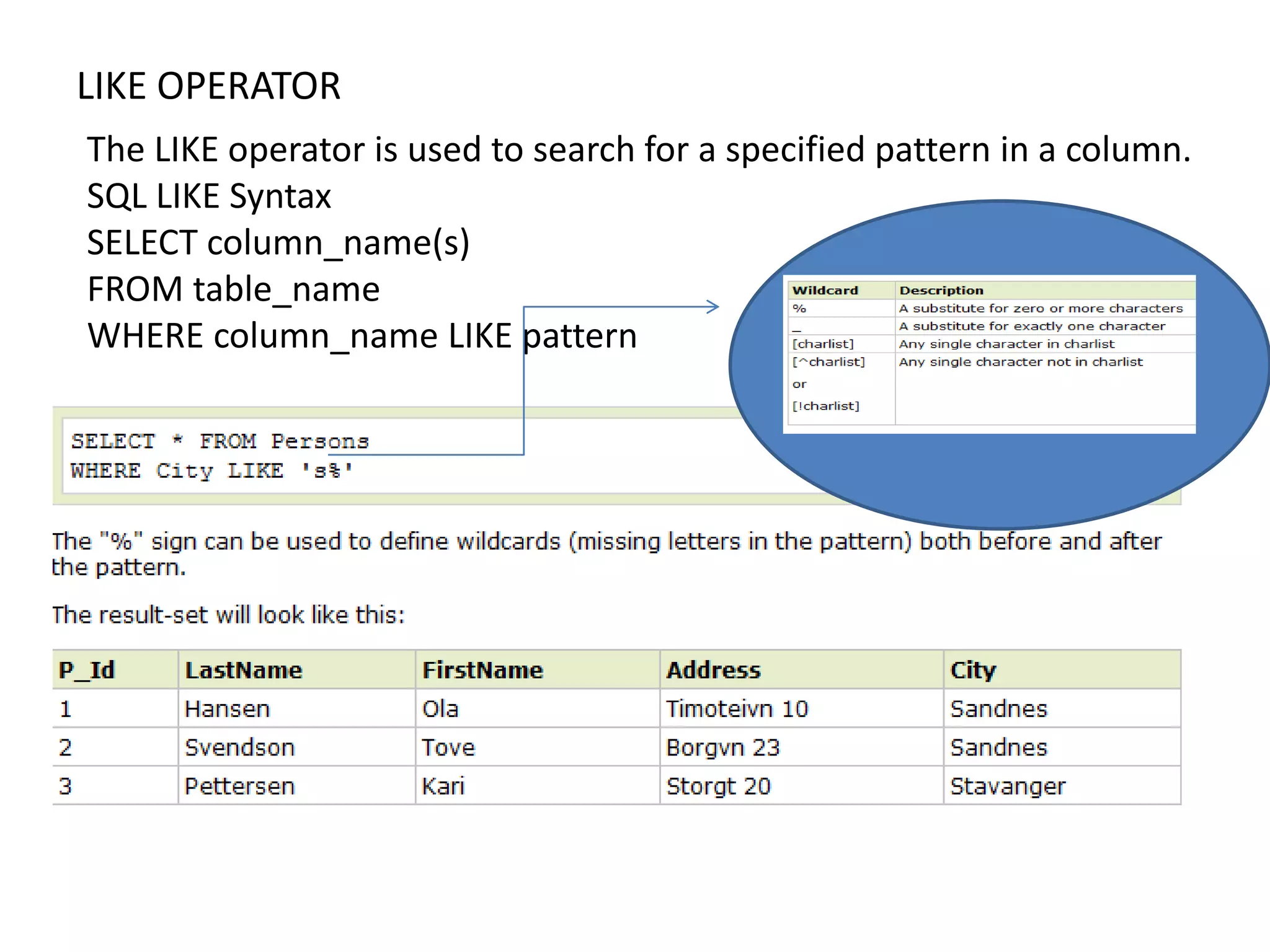
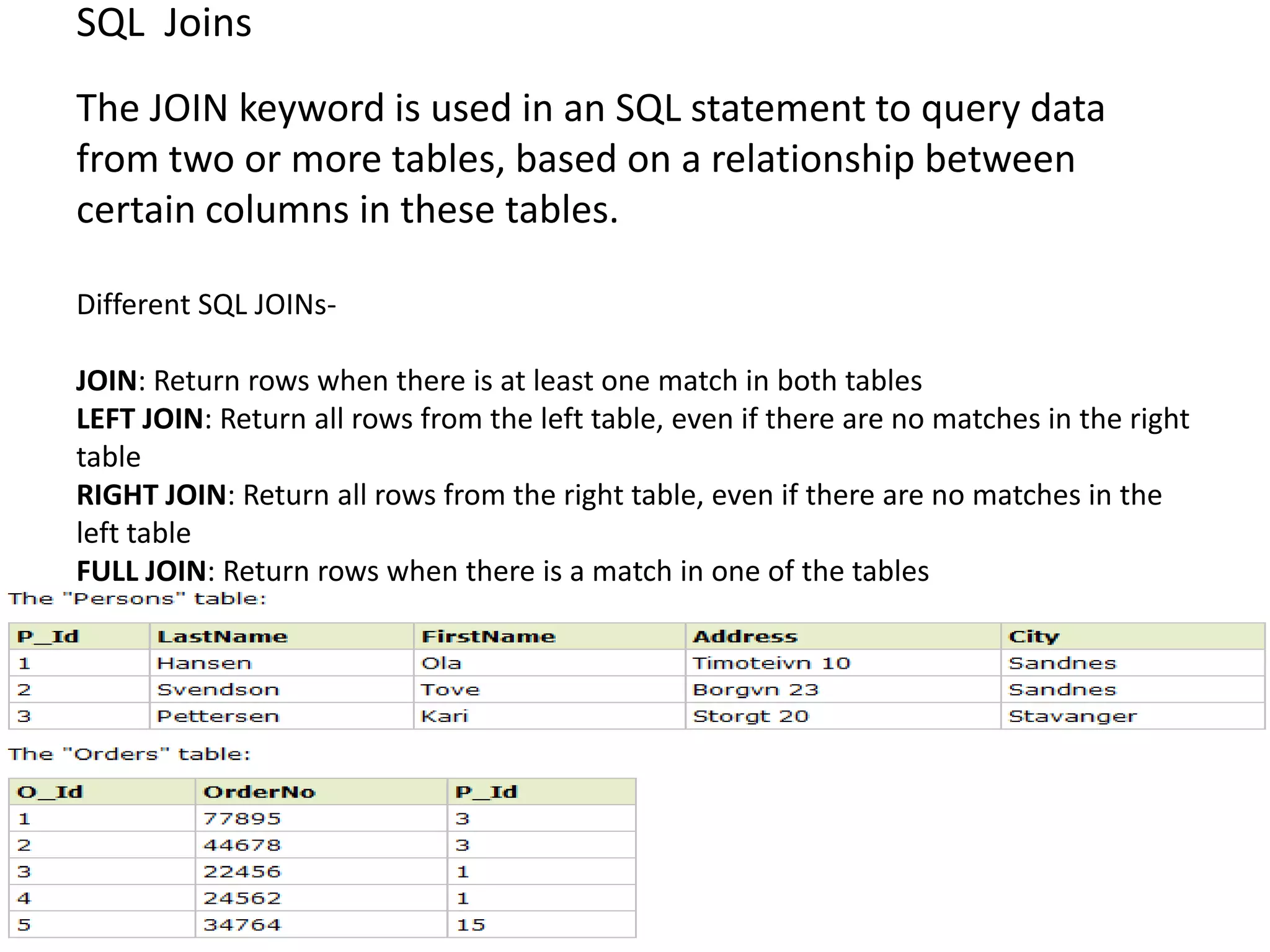
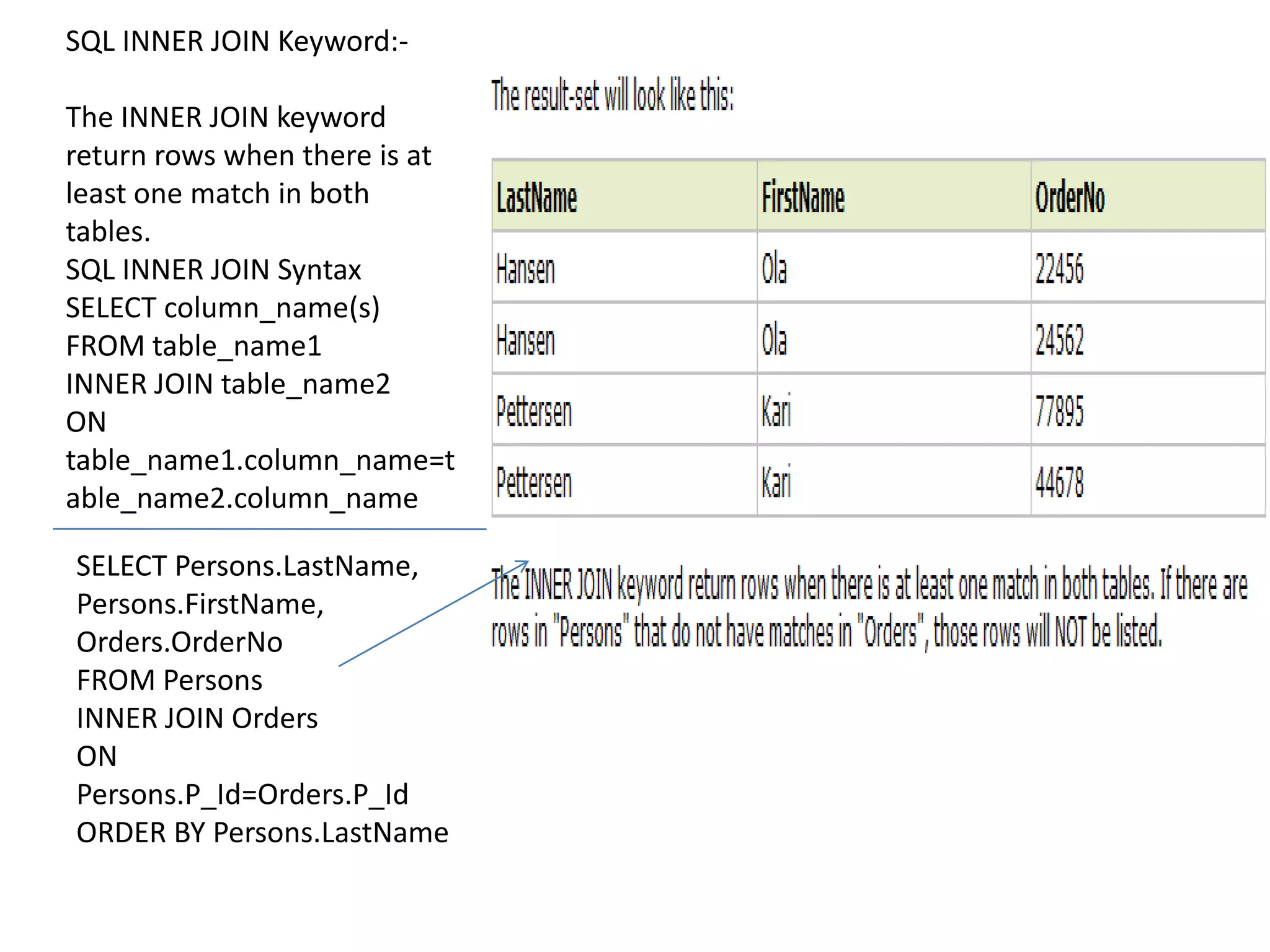
2) SQL statements like SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE allow users to retrieve, add, modify and remove data from database tables.
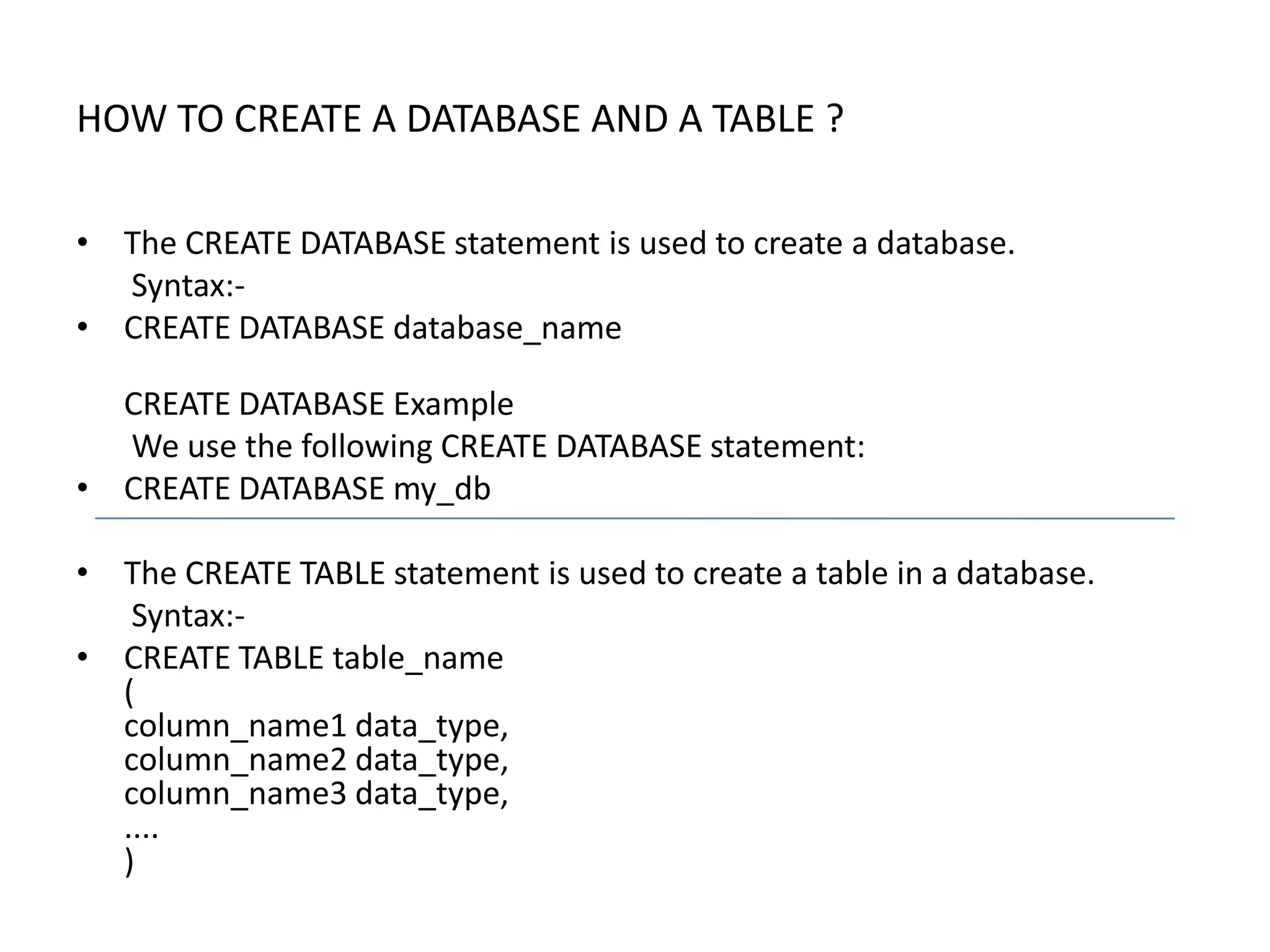
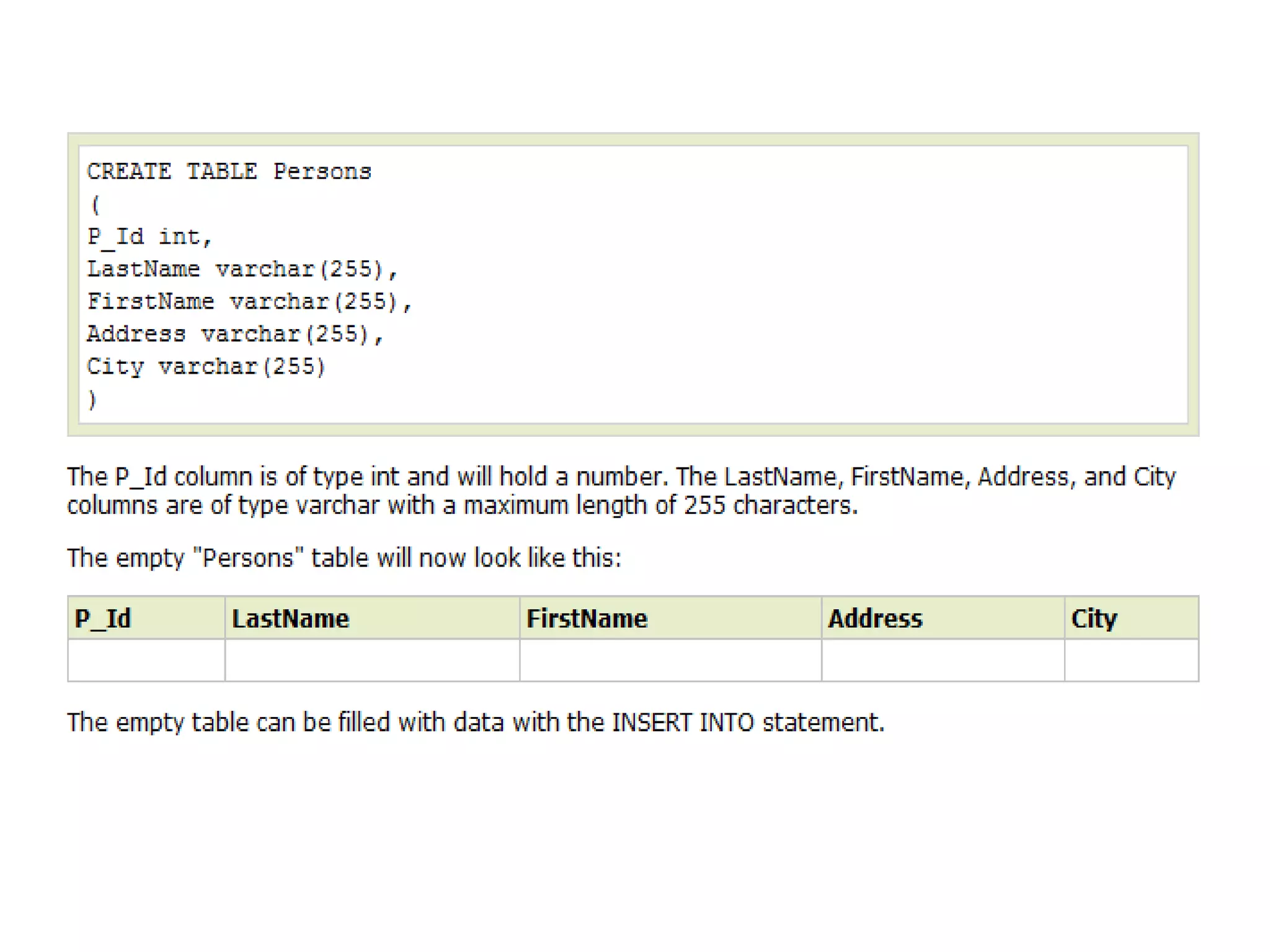
3) SQL also includes statements for defining the structure of a database through data definition language commands like CREATE DATABASE, CREATE TABLE.





![SQL Creating a View SQL Updating a View SQL Dropping a View
In SQL, a view is a virtual table You can update a view by You can delete a view with the
based on the result-set of an using the following syntax: DROP VIEW command.
SQL statement.
SQL CREATE OR REPLACE VIEW SQL DROP VIEW Syntax:-
SQL CREATE VIEW Syntax:- Syntax:-
DROP VIEW view_name
CREATE VIEW view_name AS CREATE OR REPLACE VIEW
SELECT column_name(s) view_name AS
FROM table_name SELECT column_name(s)
WHERE condition FROM table_name
WHERE condition
For example,
CREATE VIEW [Current Product
CREATE VIEW [Current Product List] AS
List] AS SELECT
SELECT ProductID,ProductName,Categ
ProductID,ProductName ory
FROM Products FROM Products
WHERE Discontinued=No WHERE Discontinued=No](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/avinashdatabase-121117064010-phpapp01/75/Avinash-database-25-2048.jpg)