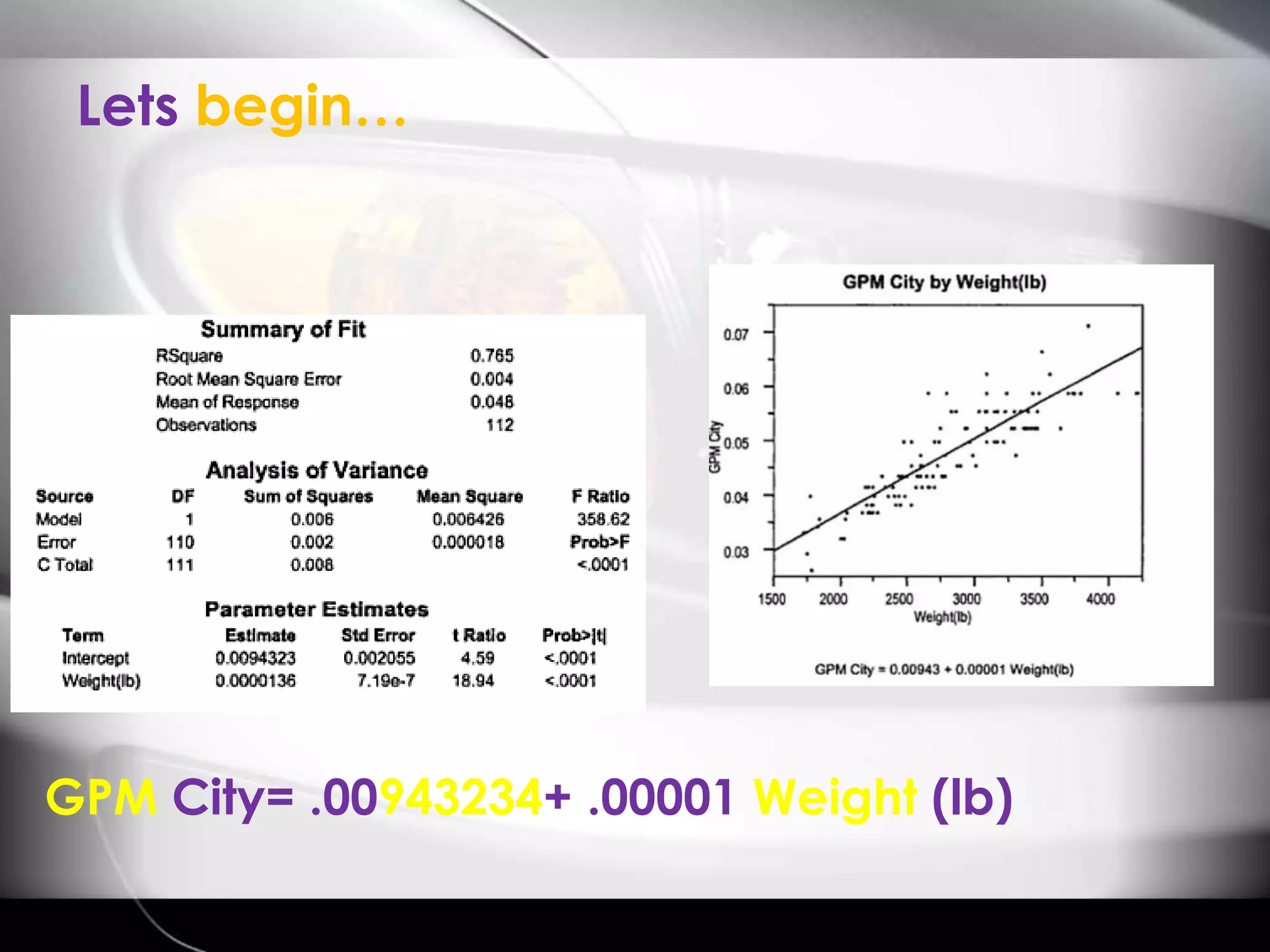
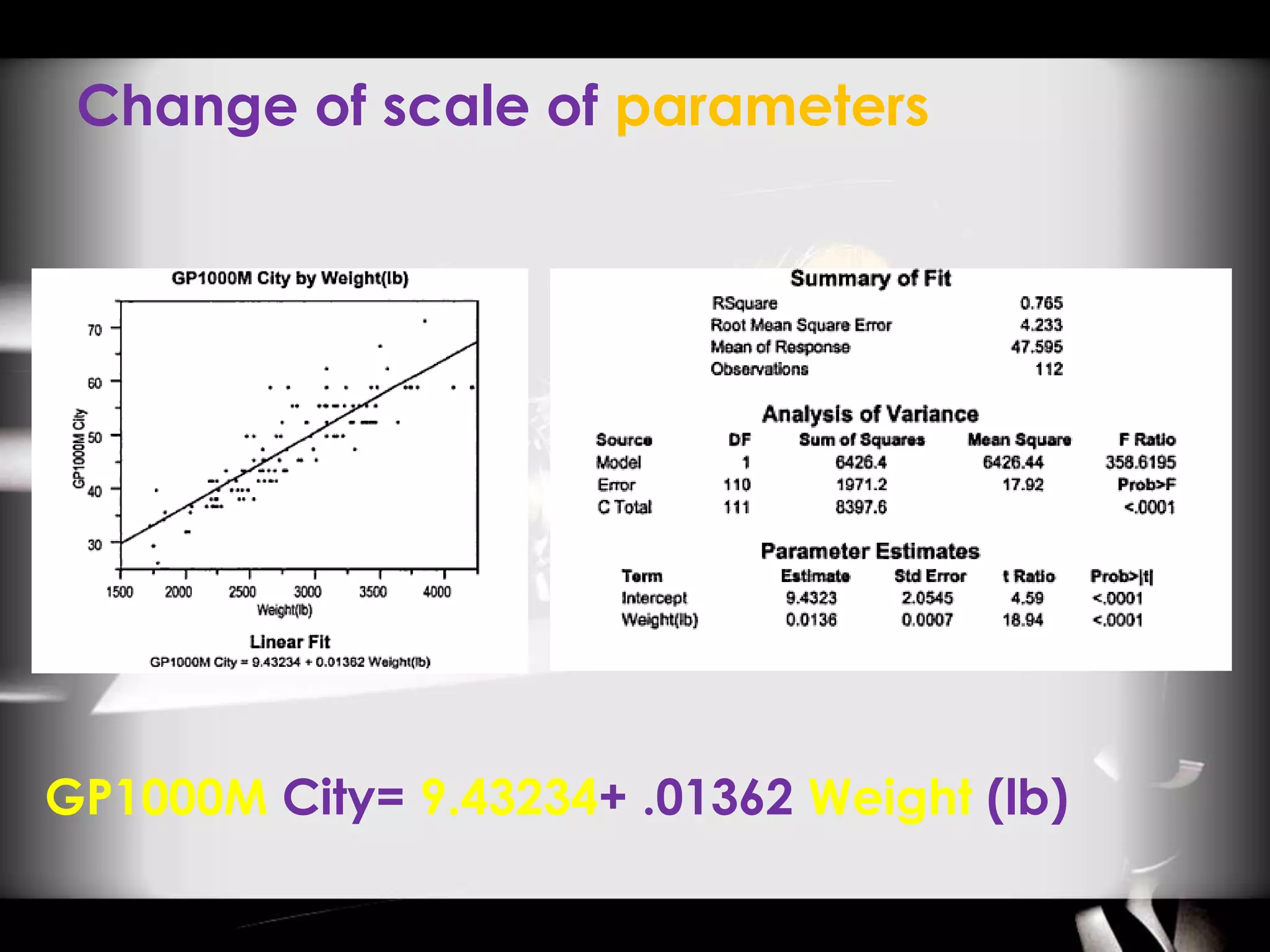
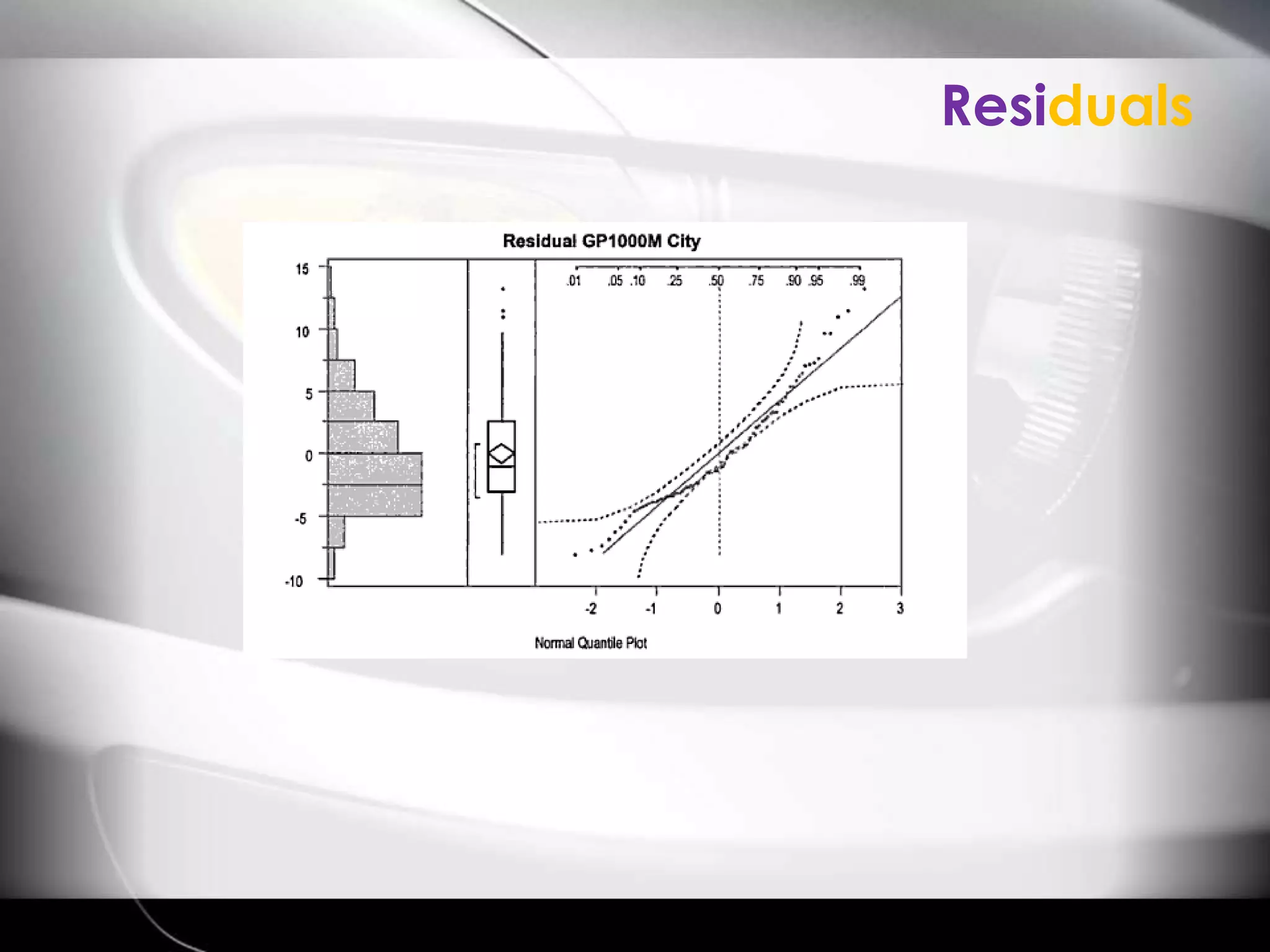
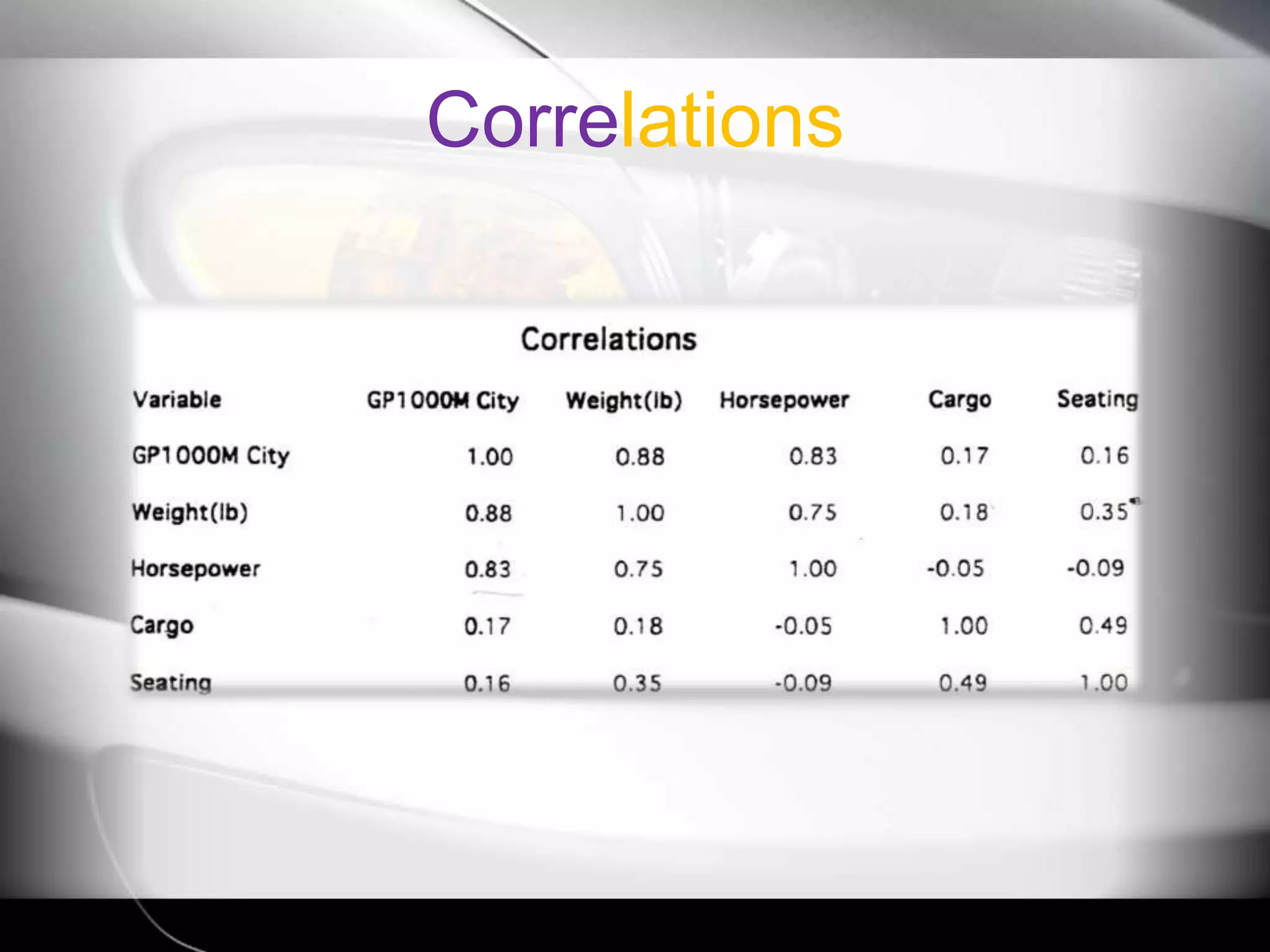
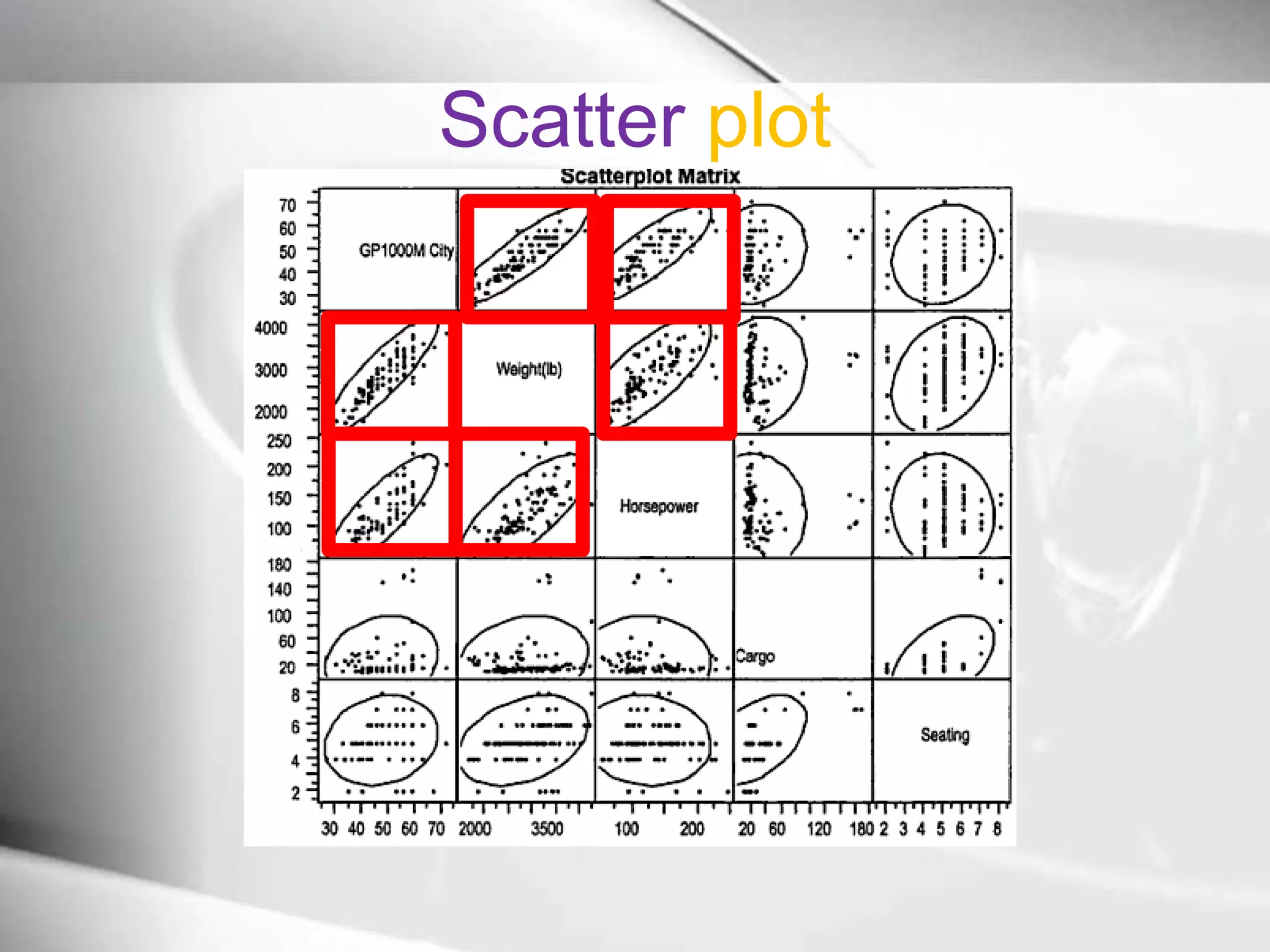
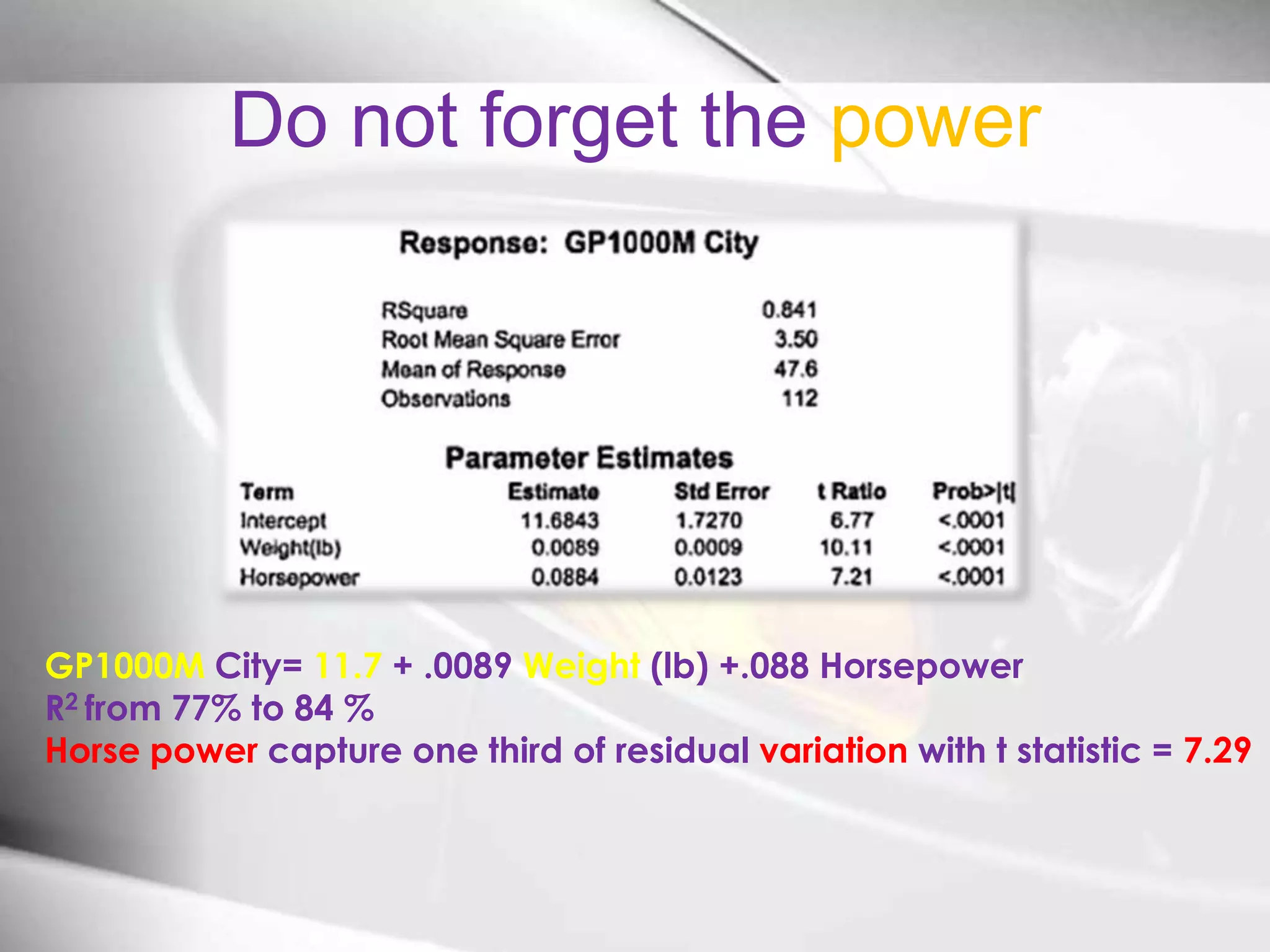
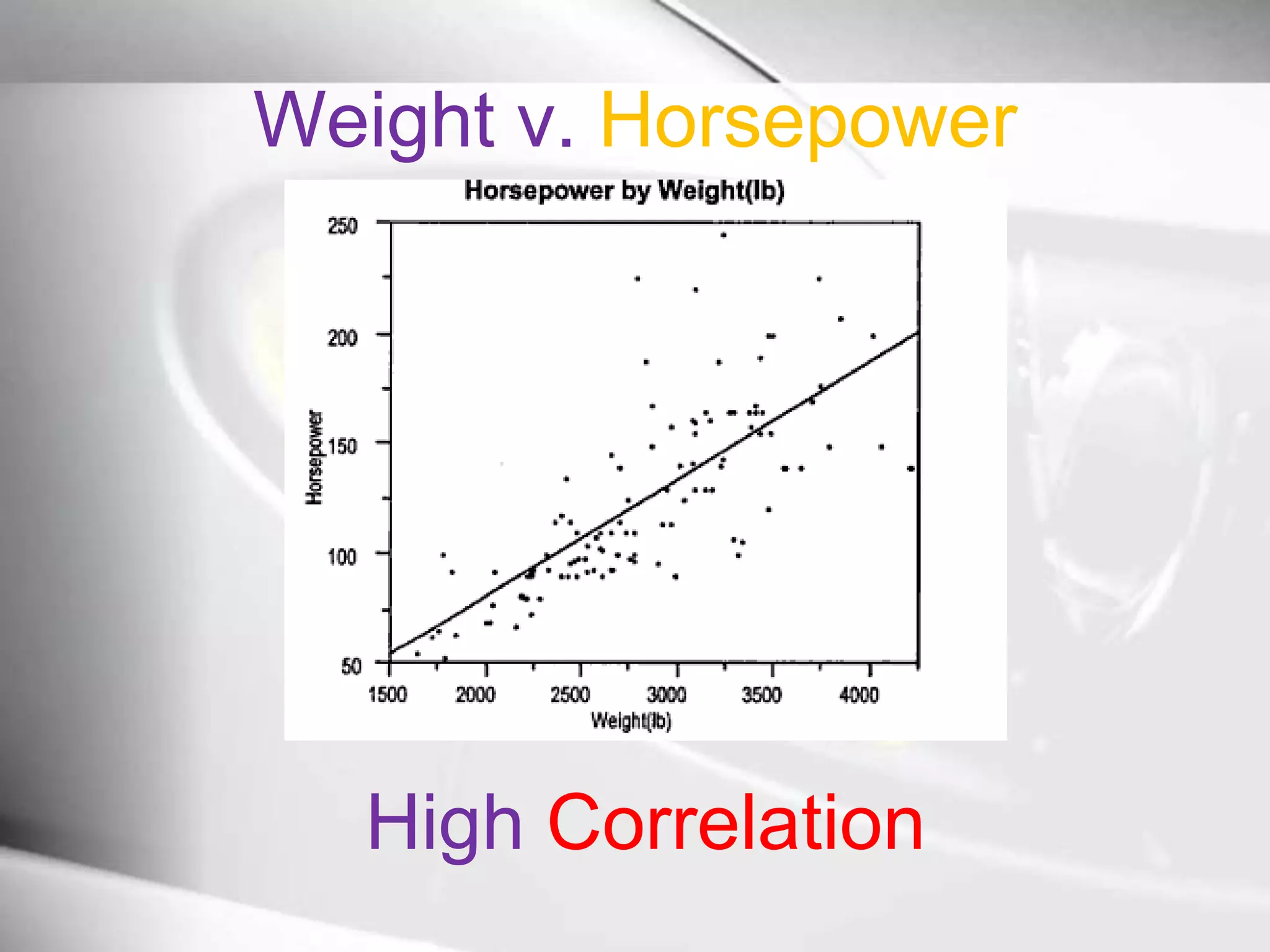
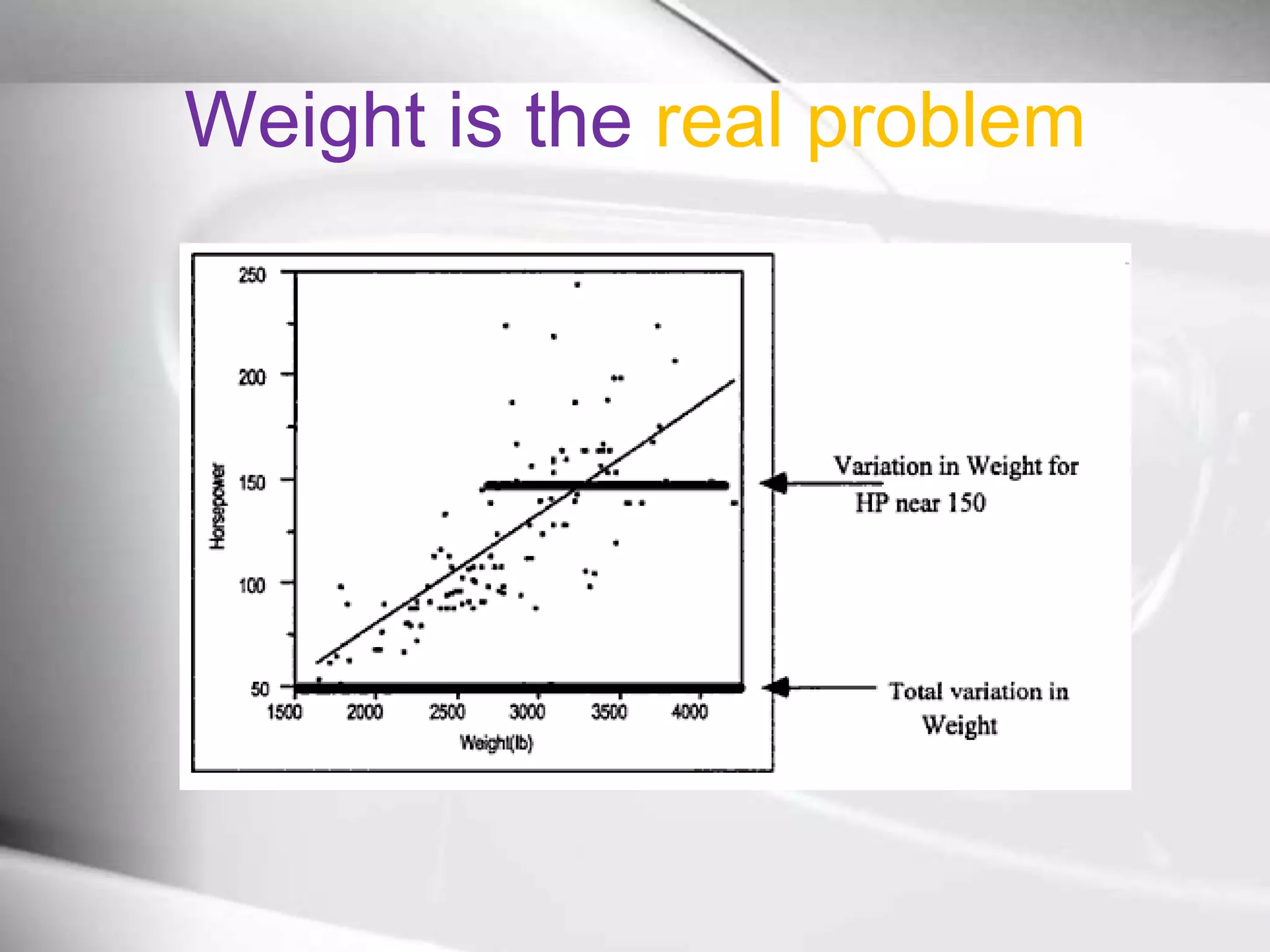
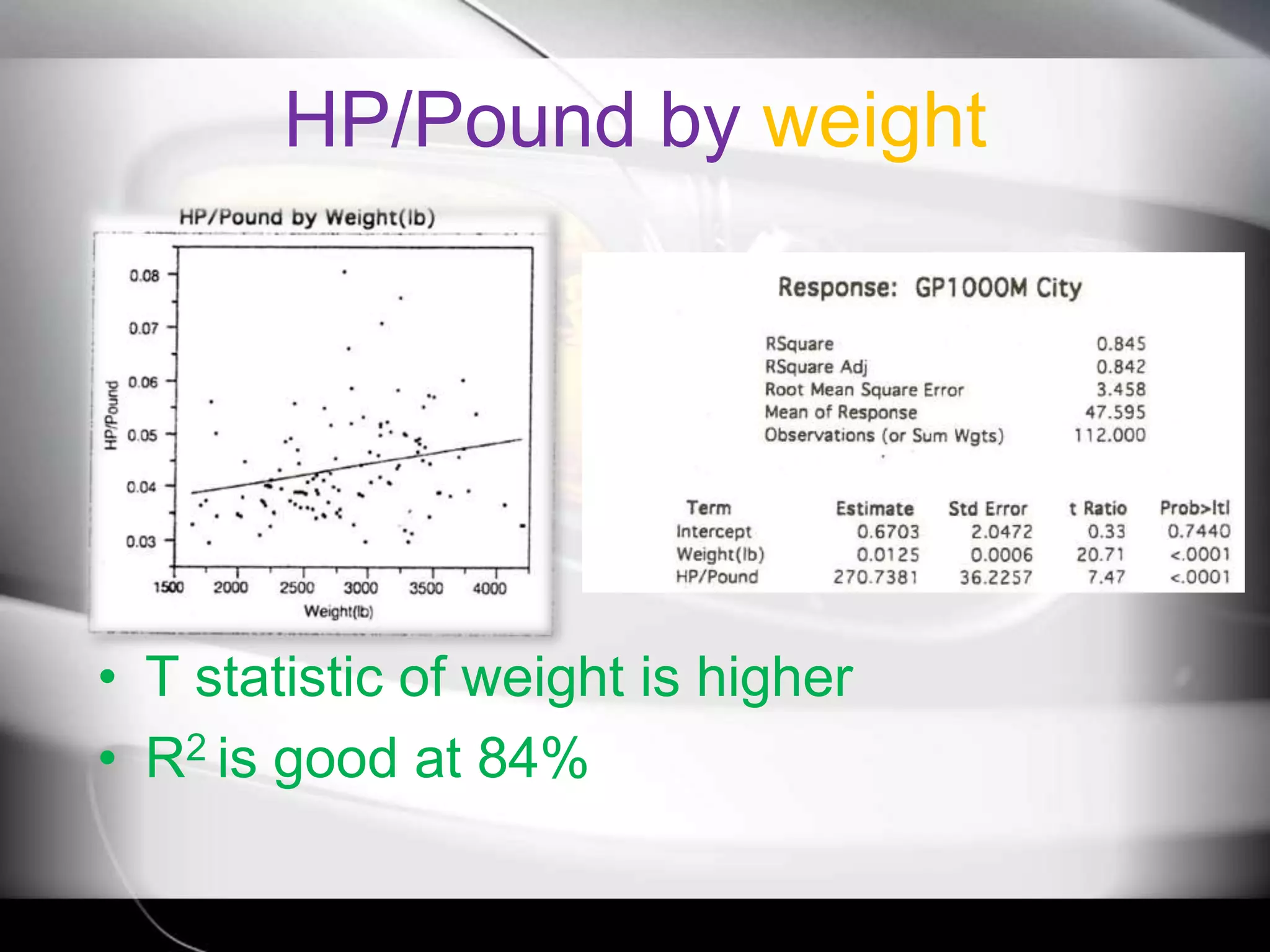
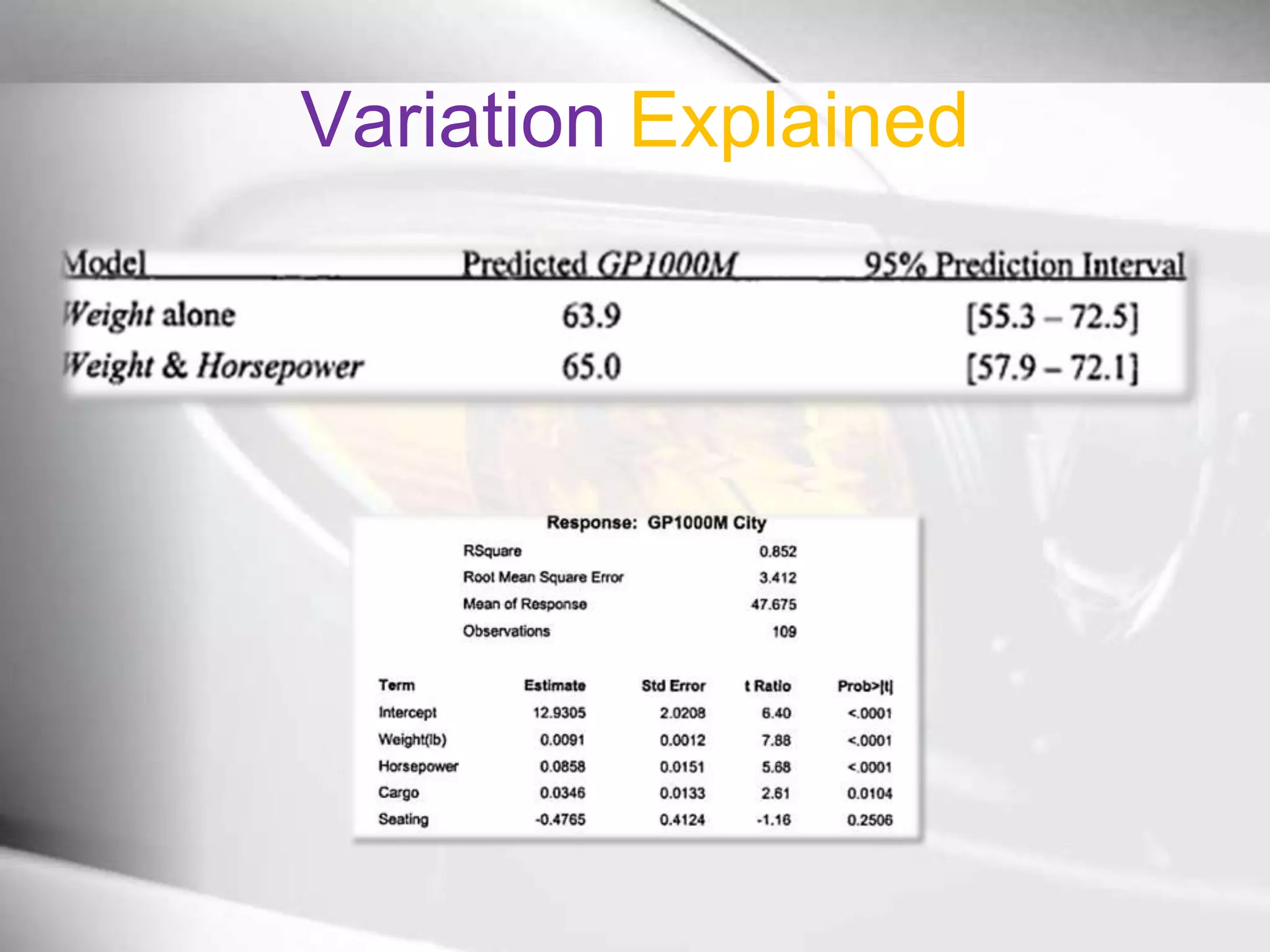
The document discusses automobile designers wanting to predict a car's gasoline mileage based on its weight. It presents a linear regression model that found mileage (GP1000M City) can be estimated as 9.43234 + .01362 * weight (in pounds). This predicts 63.8 GP1000M for a 4000 pound car, with a 95% confidence interval of 55.3-72.5 GP1000M. A second model adds horsepower as a variable, improving the R2 from 77% to 84%, showing weight and horsepower are important factors for predicting mileage.




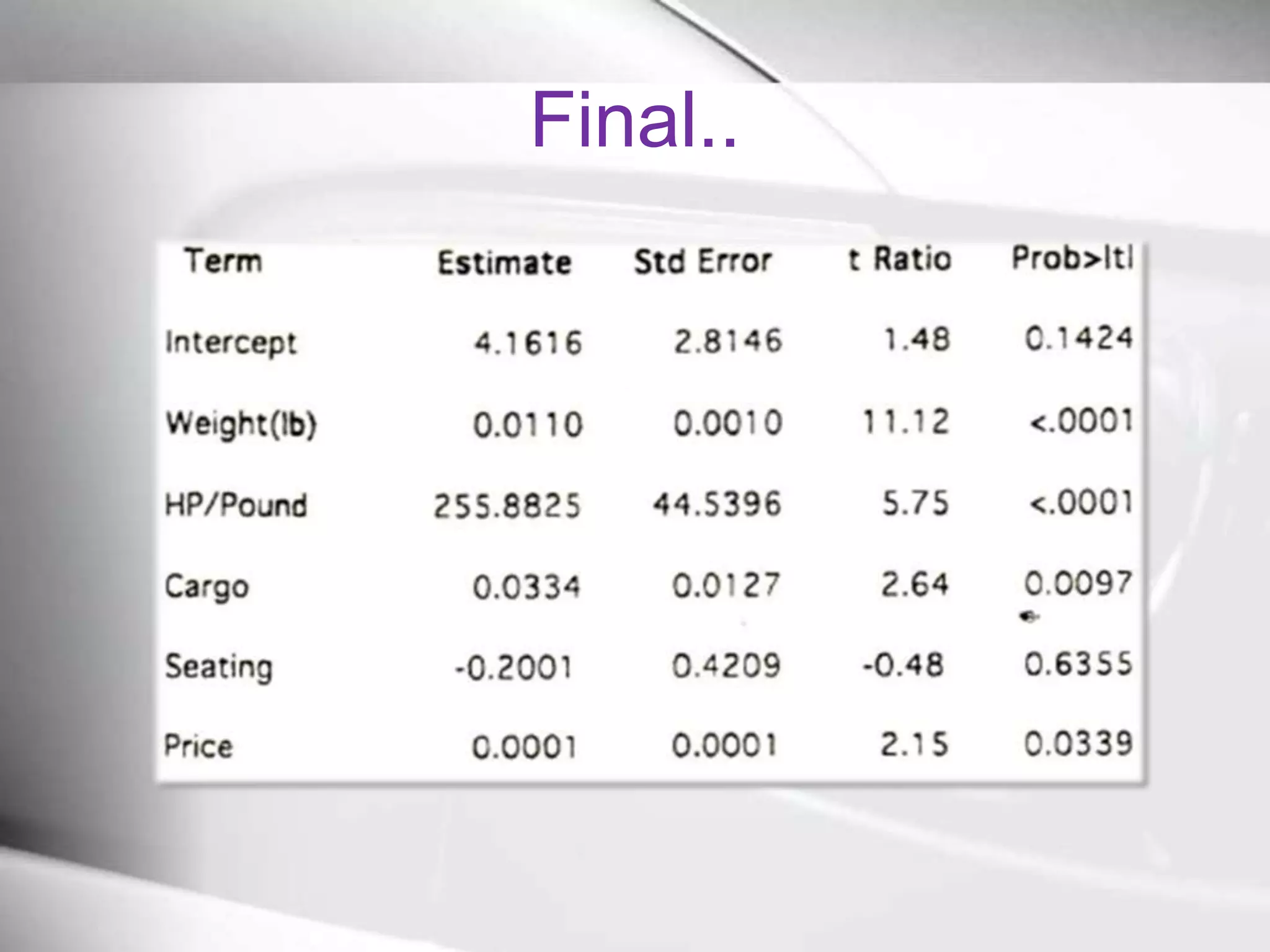
![ConclusionWeightand Horsepower are the important factorsPowerto weight gives the better equationPrediction Interval[57.3-71.3]GP1000M=> [14.0-17.5] MPG](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/automobiledesign-100926140328-phpapp01/75/Automobile-design-17-2048.jpg)
