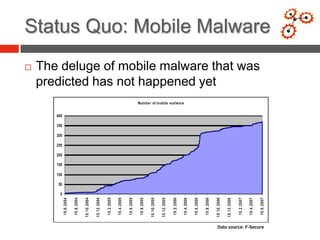
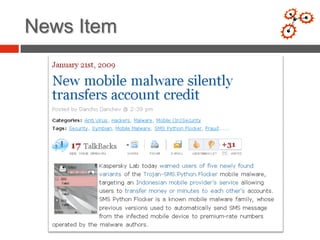
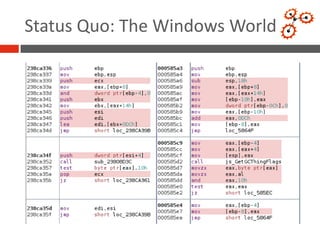
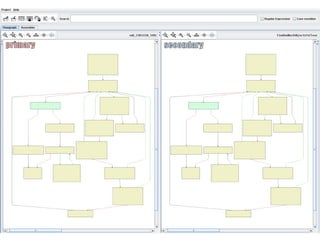
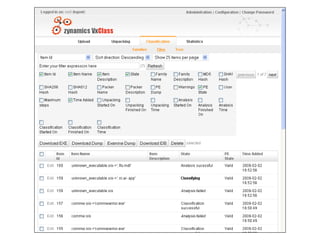
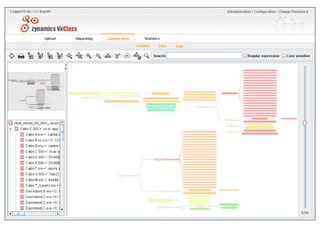
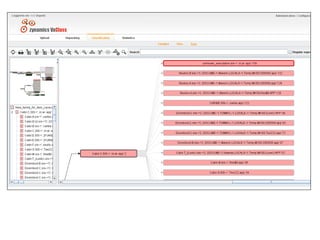
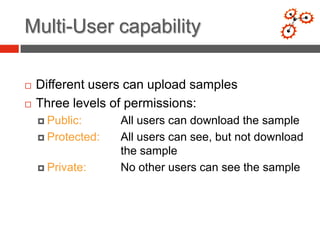
This document discusses developing an automated system called VxClass for classifying mobile malware. It summarizes the current state of mobile malware, the problem of variant detection, and proposes using program comparison tools to analyze malware variants at scale. The system would allow users to upload files to check against a malware database, identify variants, and optionally share samples. Pricing models and a roadmap are proposed to adapt the system to emerging mobile platforms and file types.