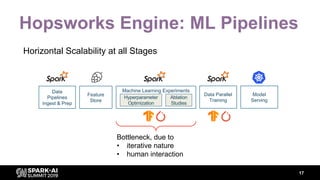
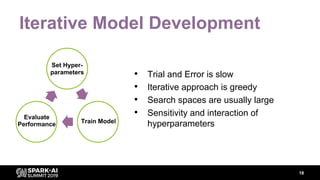
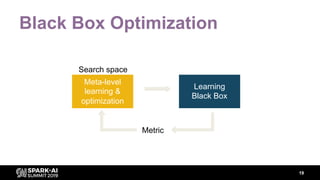
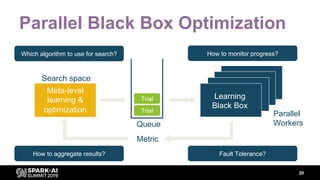
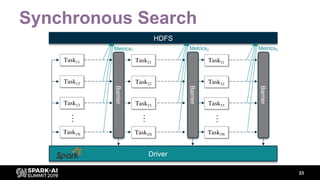
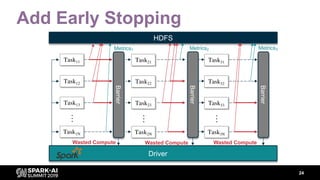
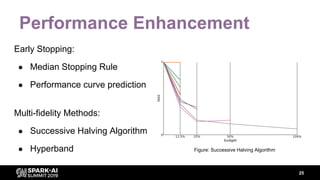
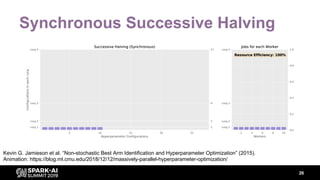
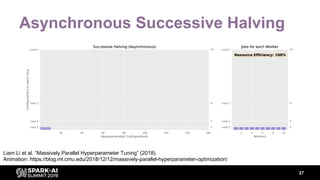
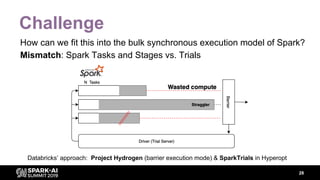
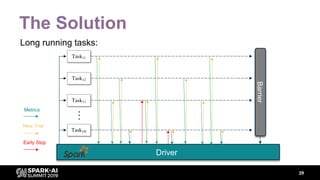
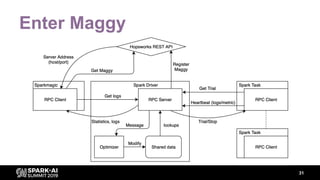
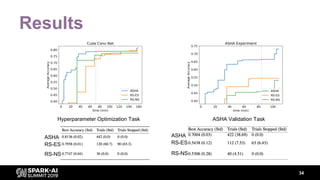
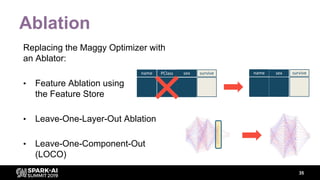
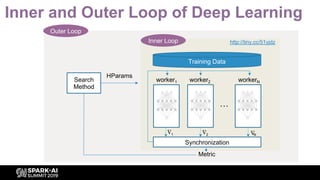
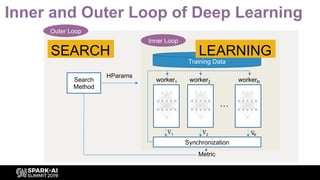
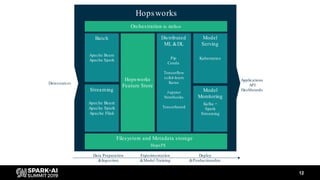
The document discusses asynchronous hyperparameter optimization using Apache Spark, focusing on making Spark more efficient for directed search tasks. It highlights the challenges of traditional bulk-synchronous methods and introduces Maggy, a framework for black-box optimization tailored for Spark. The presentation also outlines advancements in machine learning platforms and the need for support in automated hyperparameter tuning and ablation studies.



![The Complexity of Deep
Learning
8
Data validation
Distributed
Training
Model
Serving
A/B
Testing
Monitoring
Pipeline
Management
HyperParameter
Tuning
Feature Engineering
Data
Collection
Hardware
Management
Data Model Prediction
φ(x)
[Adapted from Schulley et al “Technical Debt of ML” ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/moritzmeisterjimdowling-191029231637/85/Asynchronous-Hyperparameter-Optimization-with-Apache-Spark-8-320.jpg)
![The Complexity of Deep
Learning
9
Data validation
Distributed
Training
Model
Serving
A/B
Testing
Monitoring
Pipeline
Management
HyperParameter
Tuning
Feature Engineering
Data
Collection
Hardware
Management
Data Model Prediction
φ(x)
Hopsworks
Feature Store
Hopsworks
REST API
[Adapted from Schulley et al “Technical Debt of ML” ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/moritzmeisterjimdowling-191029231637/85/Asynchronous-Hyperparameter-Optimization-with-Apache-Spark-9-320.jpg)


![Engines Matter!
15
[Image from https://twitter.com/_youhadonejob1/status/1143968337359187968?s=20]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/moritzmeisterjimdowling-191029231637/85/Asynchronous-Hyperparameter-Optimization-with-Apache-Spark-14-320.jpg)