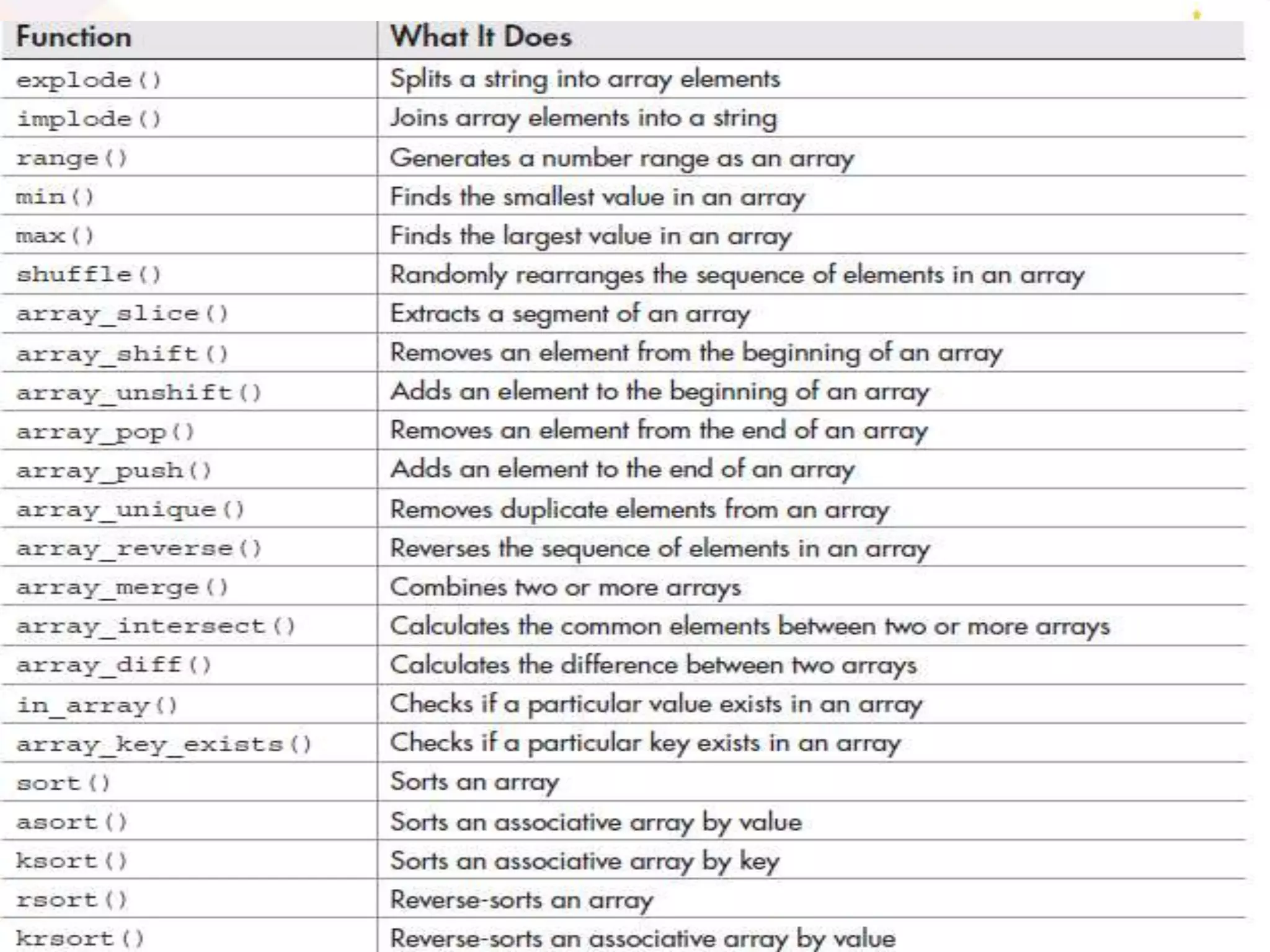
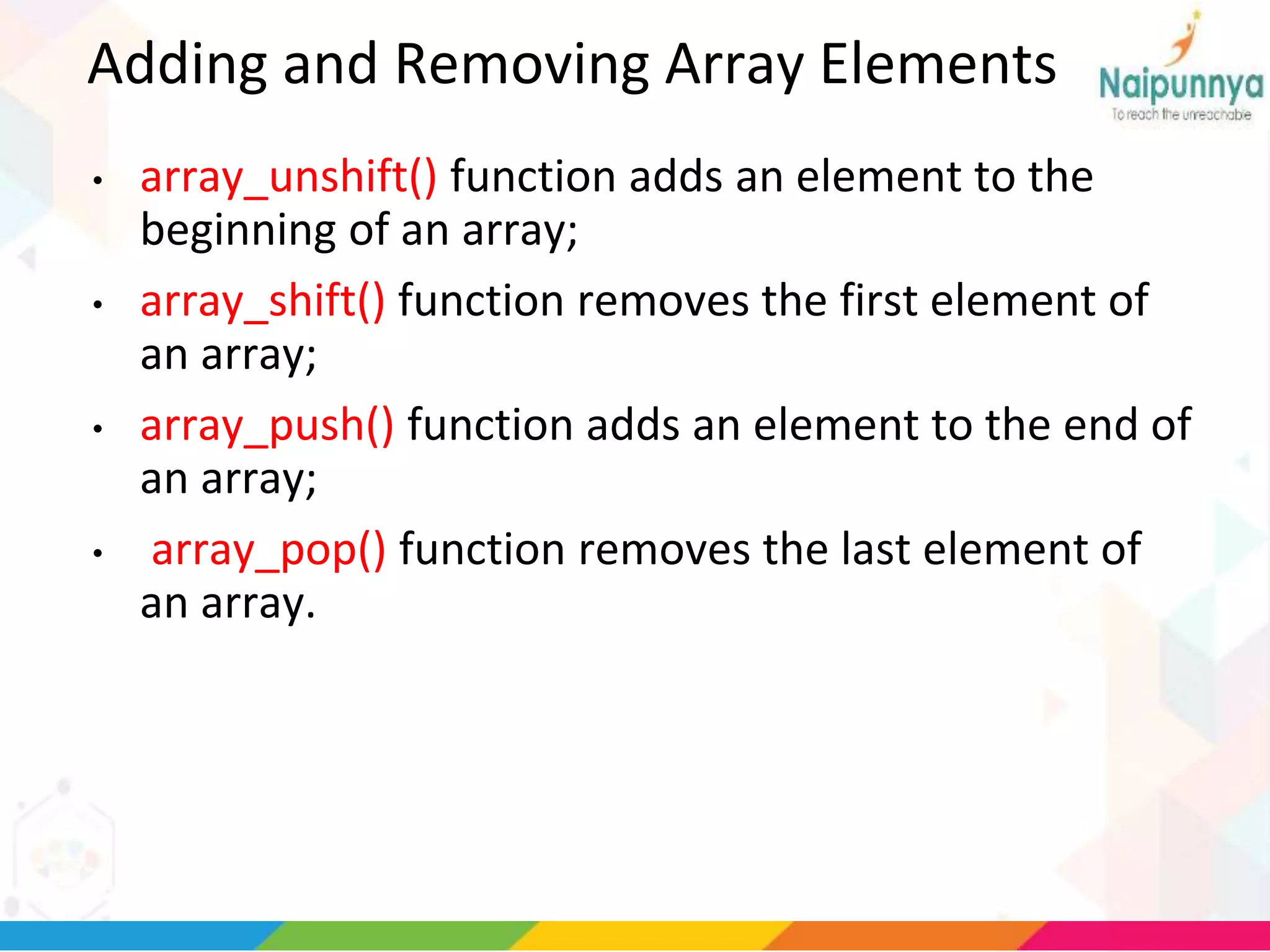
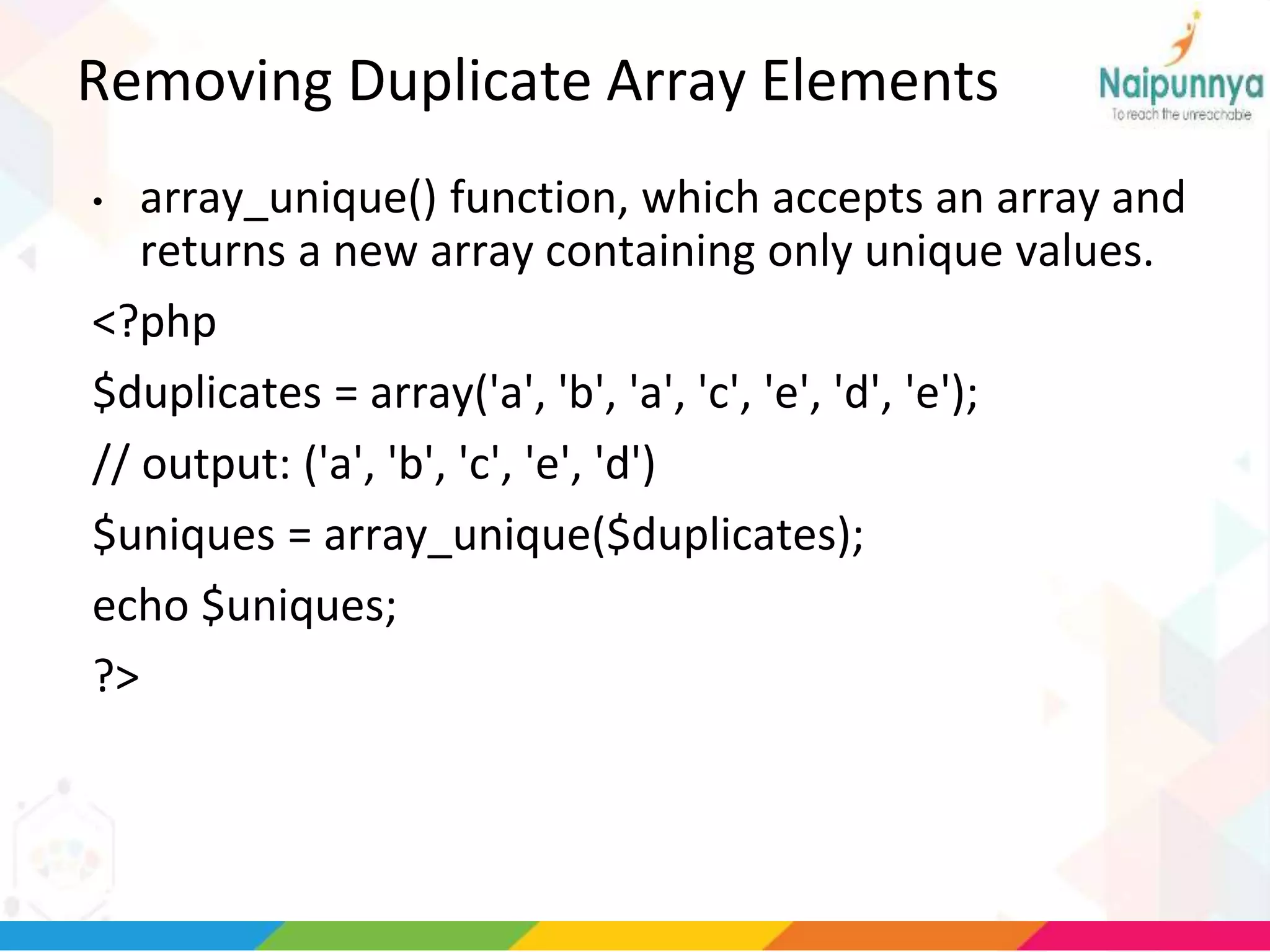
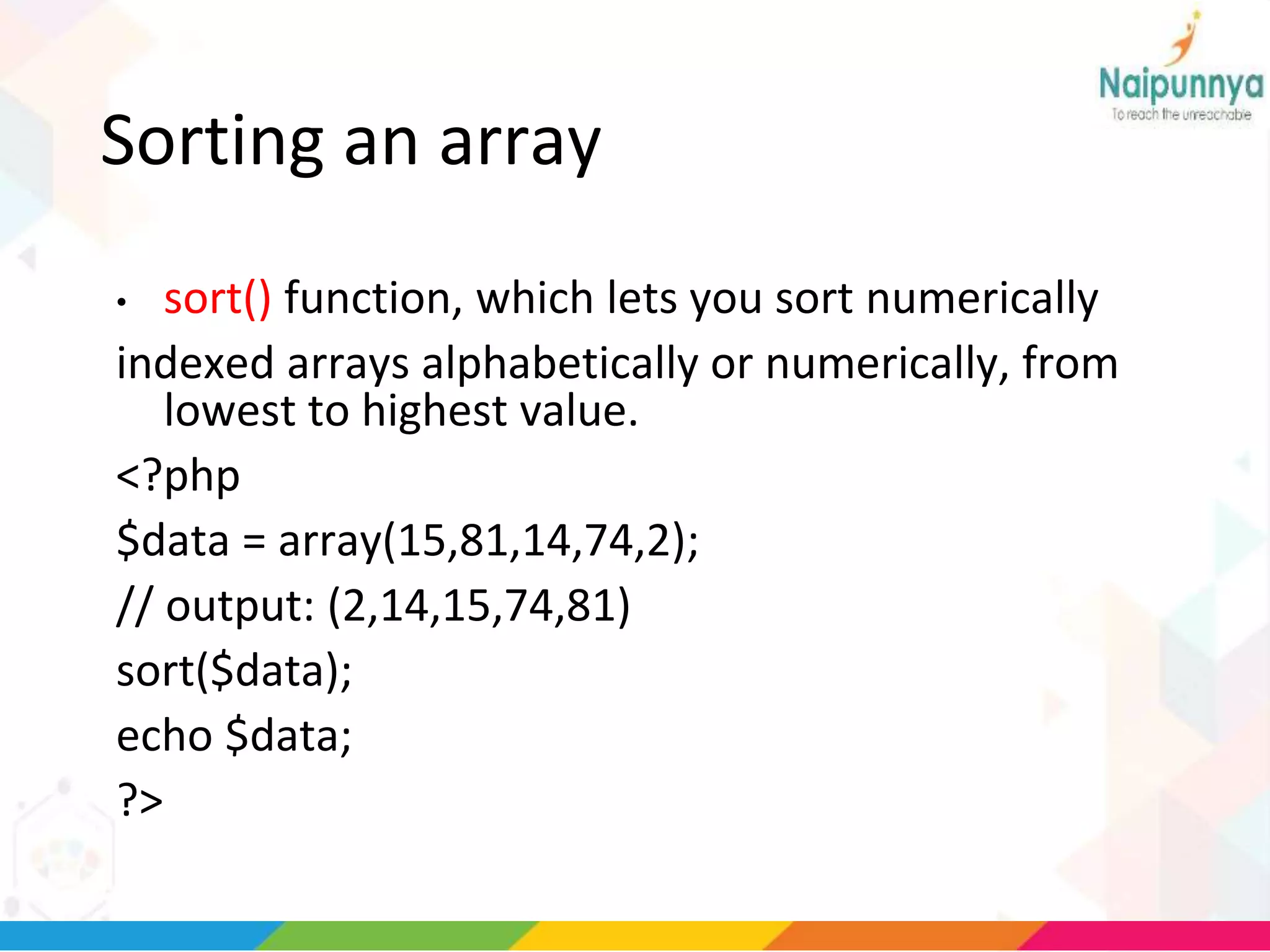
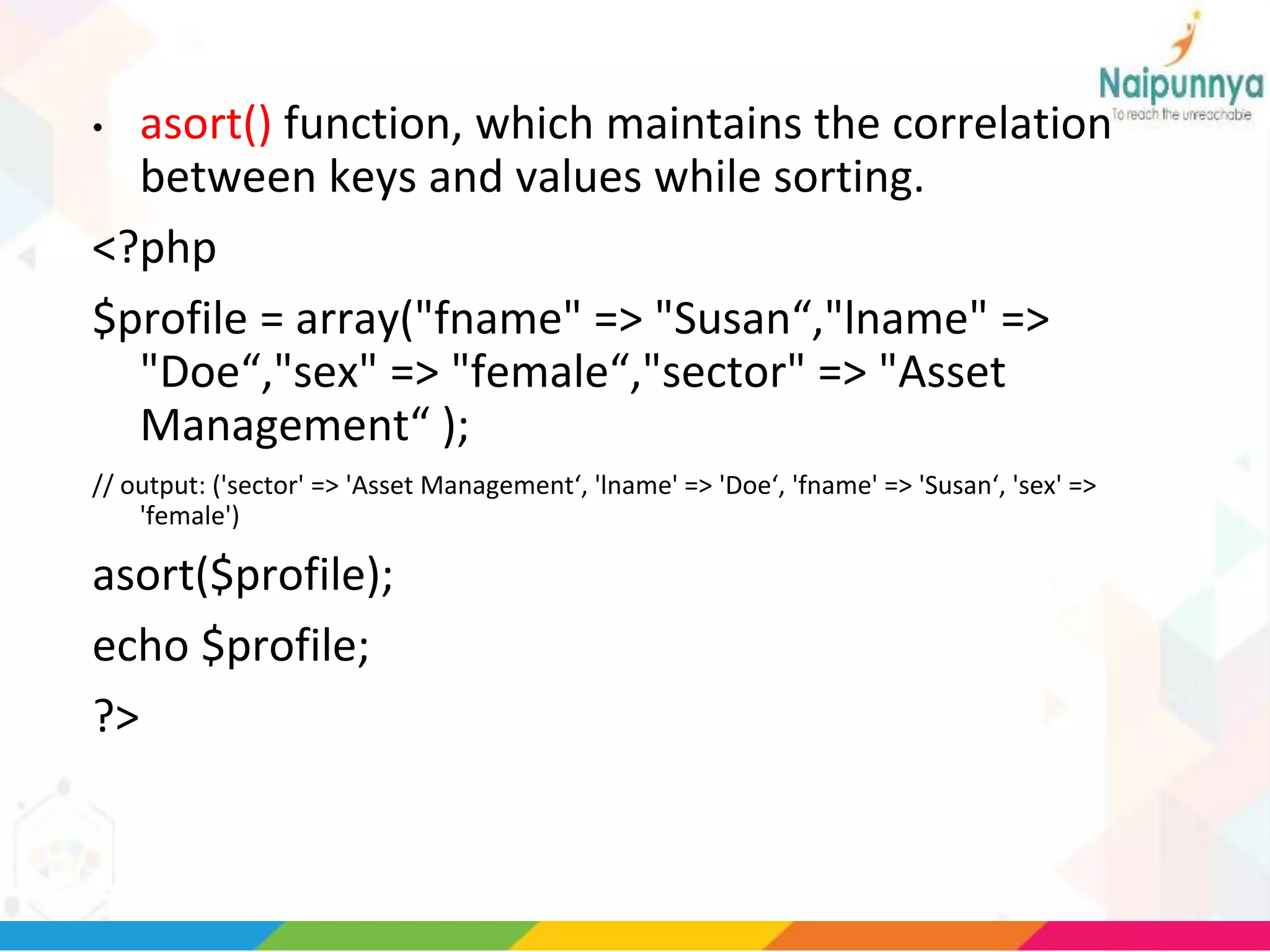
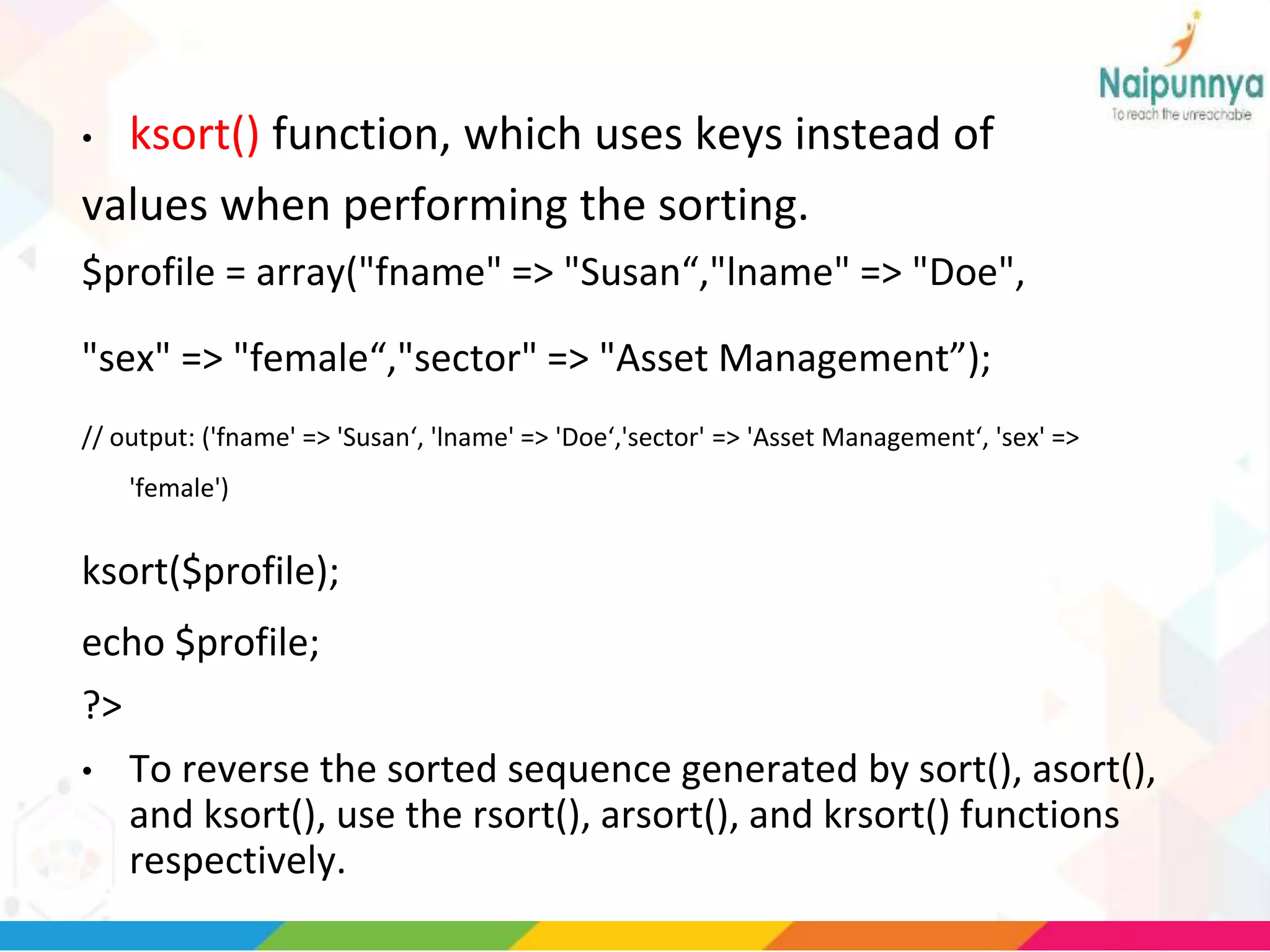
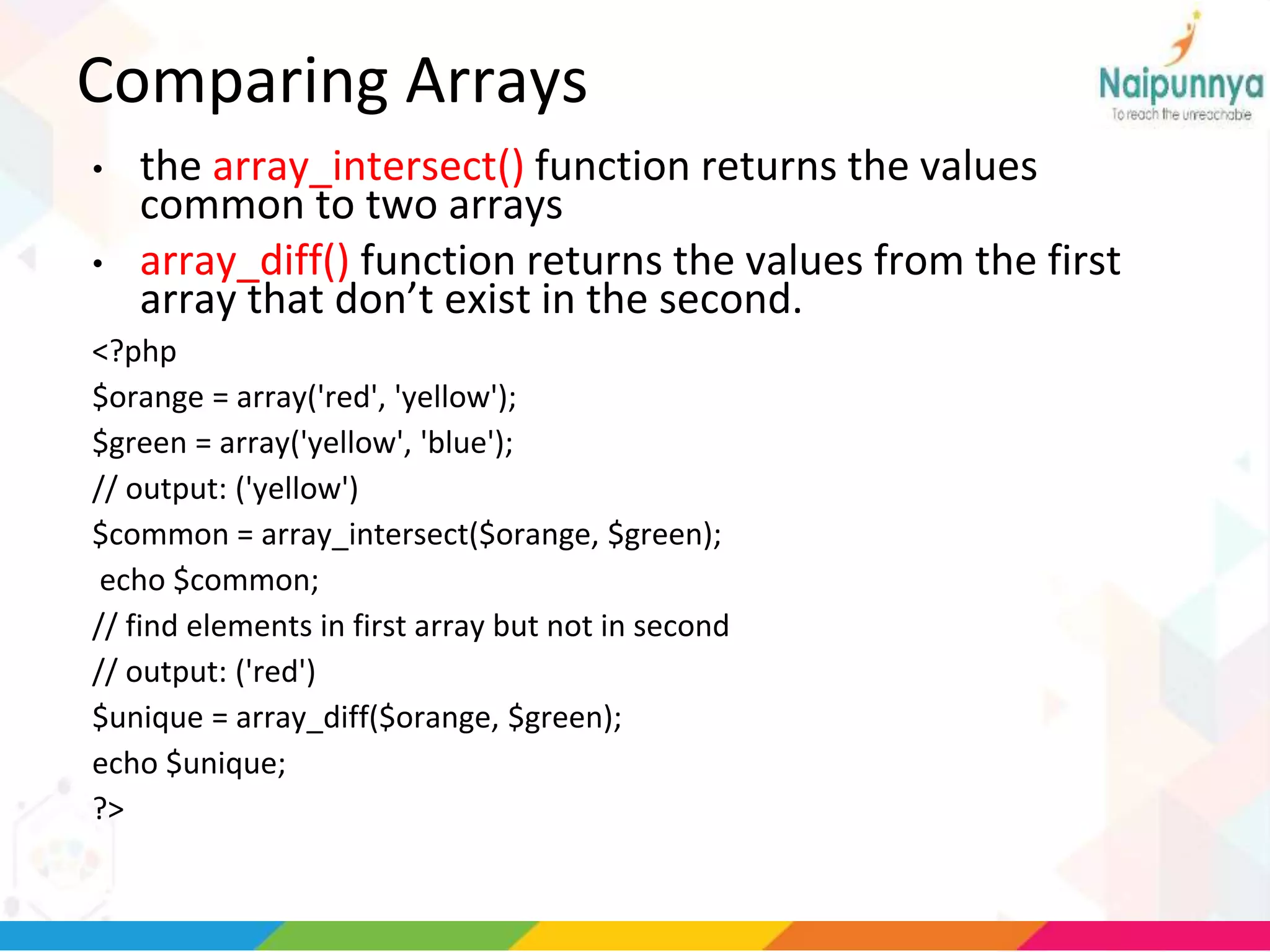
The document discusses arrays in PHP, including the three types of arrays (indexed, associative, and multidimensional), how to create and access array elements, functions for manipulating arrays like sort(), merge(), search(), and more. Key array functions covered are sort(), asort(), ksort(), array_merge(), array_intersect(), array_diff(), and the list() function for assigning array values to variables.


![PHP Indexed Arrays
• two ways to create indexed arrays:
$cars=array("Volvo","BMW","Toyota");
Or :
• $cars[0]="Volvo";
$cars[1]="BMW";
$cars[2]="Toyota";](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arraysinphp-210912165258/75/Arrays-in-php-3-2048.jpg)
![EXAMPLE
<?php
$cars=array("Volvo","BMW","Toyota");
echo "I like " . $cars[0] . ", " . $cars[1] . " and " . $cars[2] .
".";
?>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arraysinphp-210912165258/75/Arrays-in-php-4-2048.jpg)

![Loop Through an Indexed Array
<?php
$cars=array("Volvo","BMW","Toyota");
$arrlength=count($cars);
for($x=0;$x<$arrlength;$x++)
{
echo $cars[$x];
echo "<br>";
}
?>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arraysinphp-210912165258/75/Arrays-in-php-6-2048.jpg)
![PHP Associative Arrays
• Associative arrays are arrays that use named keys that you
assign to them.
$age=array("Peter"=>"35","Ben"=>"37","Joe"=>"43");
or:
$age['Peter']="35";
$age['Ben']="37";
$age['Joe']="43";
• The named keys can then be used in a script:
Example
<?php
$age=array("Peter"=>"35","Ben"=>"37","Joe"=>"43");
echo "Peter is " . $age['Peter'] . " years old.";
?>
•](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arraysinphp-210912165258/75/Arrays-in-php-7-2048.jpg)



![Array
(
[Griffin] => Array
(
[0] => Peter
[1] => Lois
[2] => Megan
)
[Quagmire] => Array
(
[0] => Glenn
)
[Brown] => Array
(
[0] => Cleveland
[1] => Loretta
[2] => Junior
)
)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arraysinphp-210912165258/75/Arrays-in-php-11-2048.jpg)
![echo "Is " . $families['Griffin'][2] .
" a part of the Griffin family?";
• Output
• Is Megan a part of the Griffin family?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arraysinphp-210912165258/75/Arrays-in-php-12-2048.jpg)