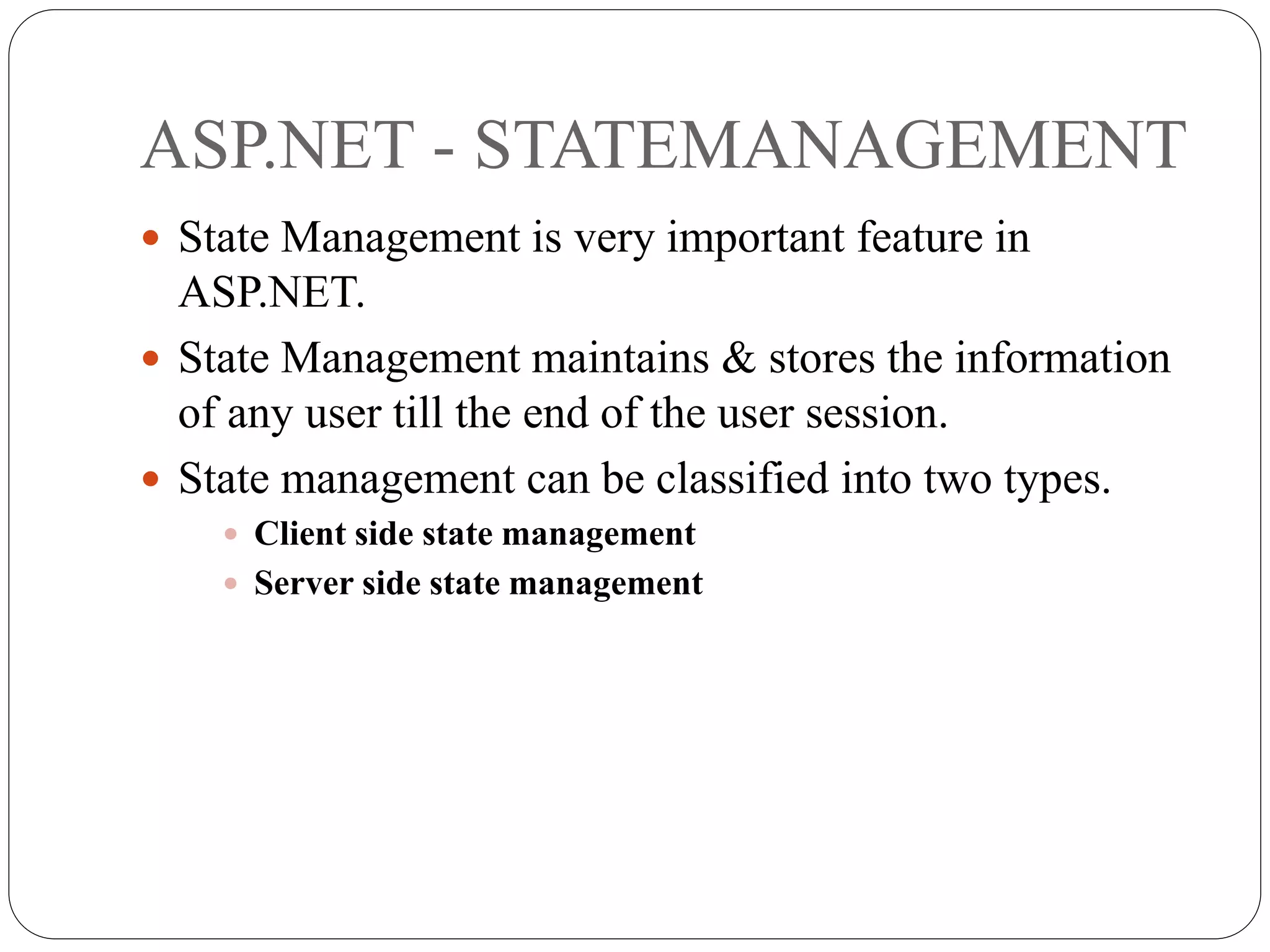
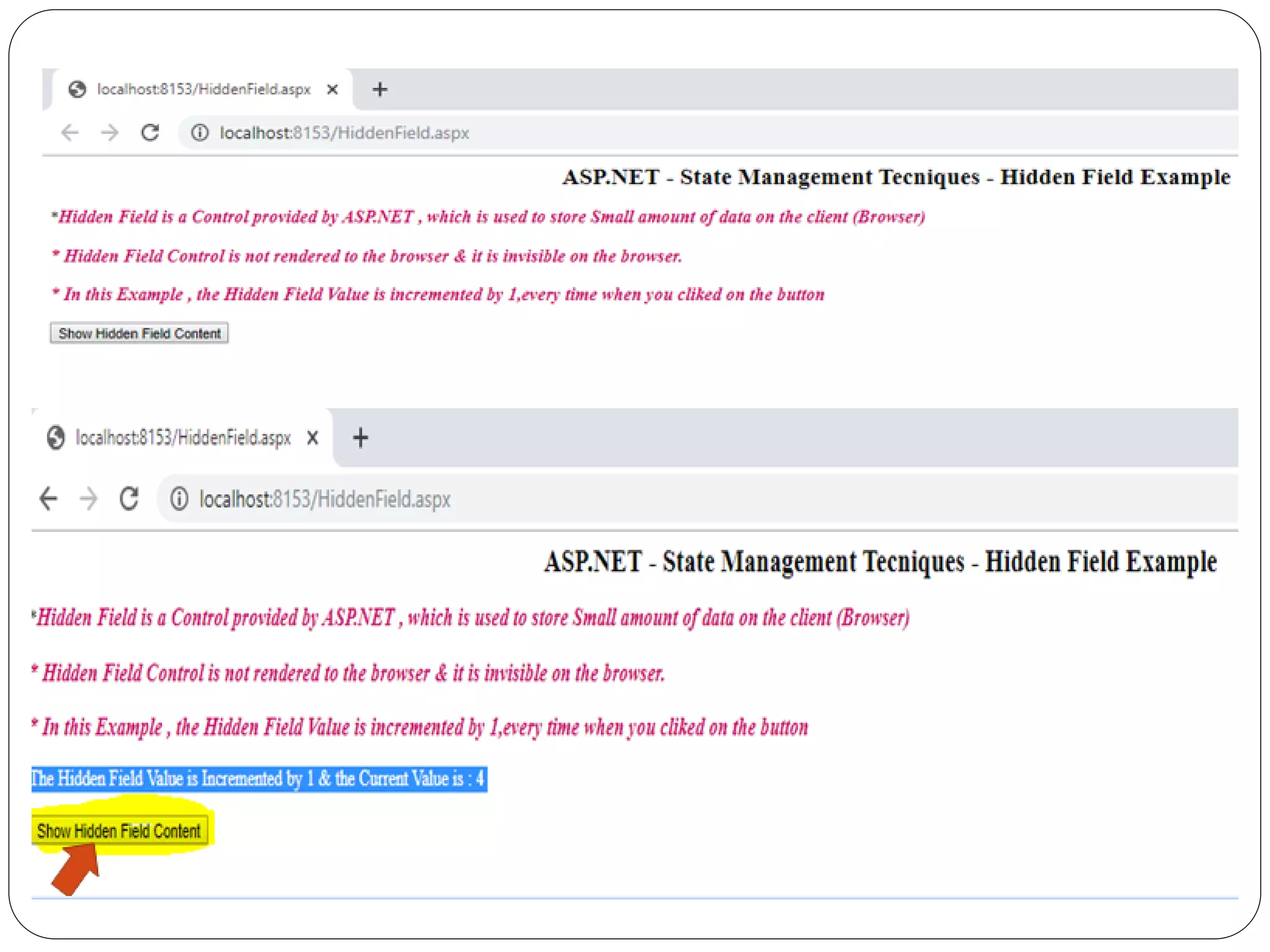
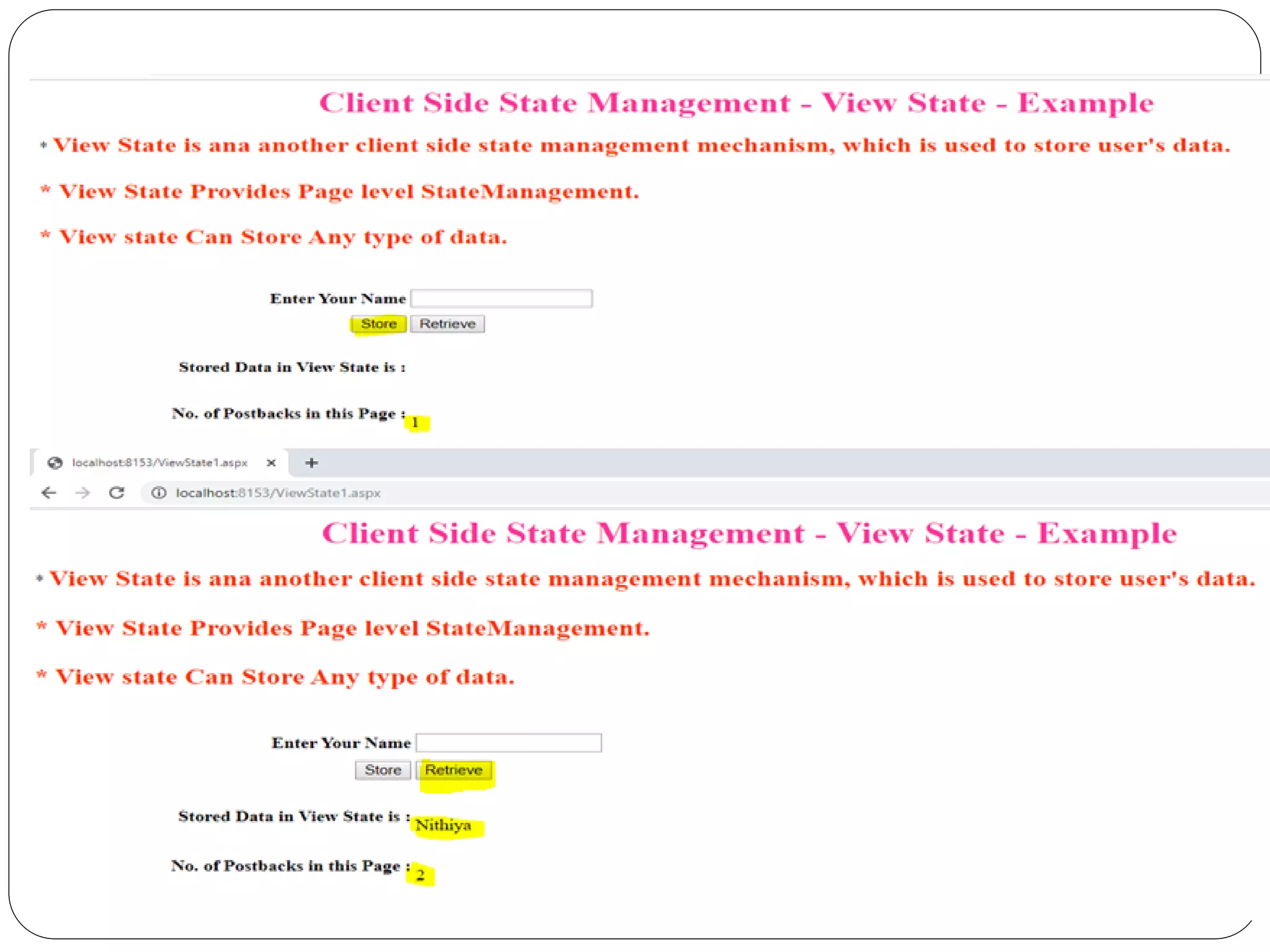
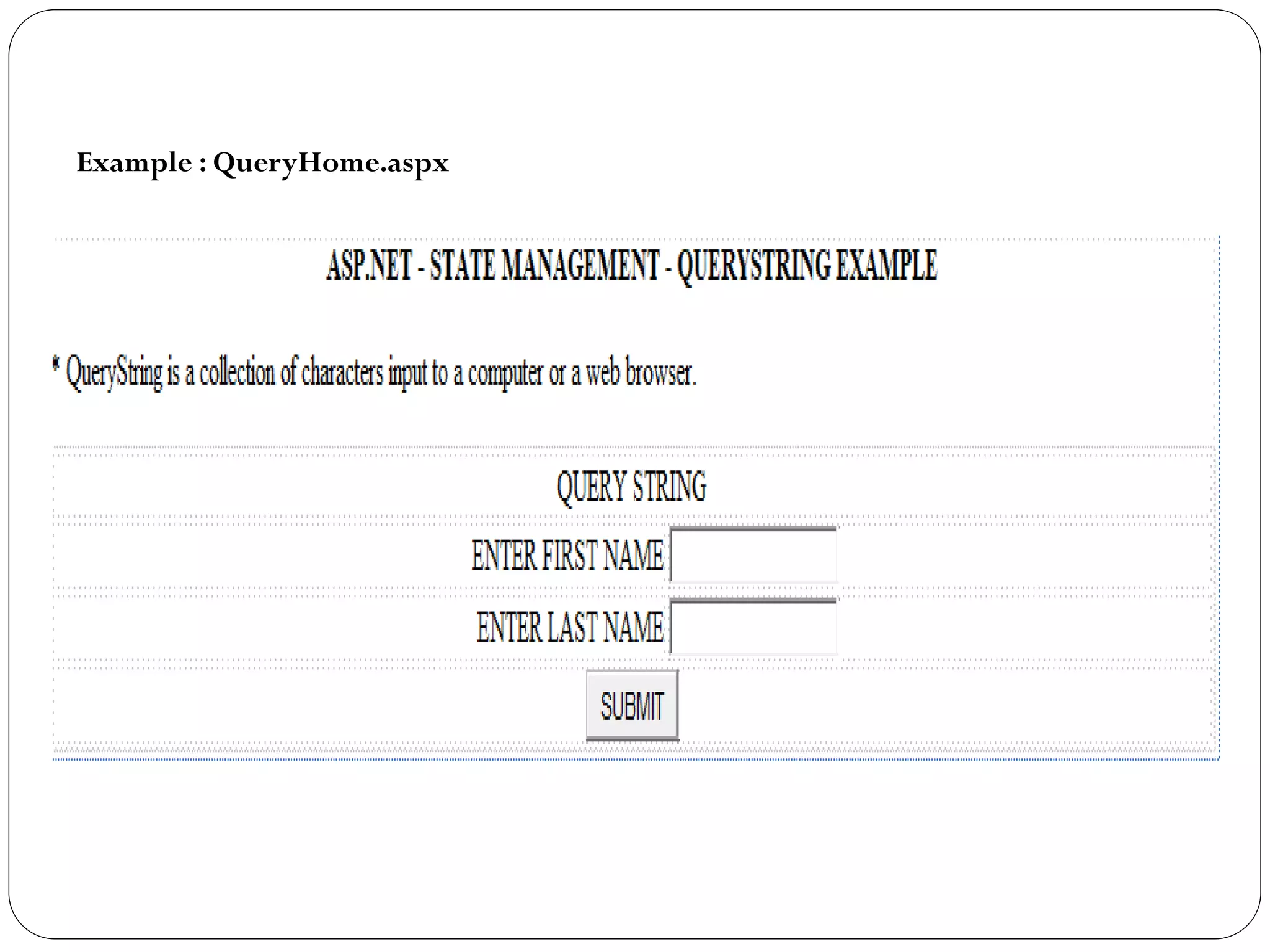
The document discusses different state management techniques in ASP.NET. It describes client-side techniques like hidden fields, view state, cookies, query strings, and control state. It also describes server-side techniques like session state and application state. Session state stores and retrieves data for each user session while application state stores data accessible to all users. Examples are provided for hidden fields, view state, cookies, query strings, session state, and application state.







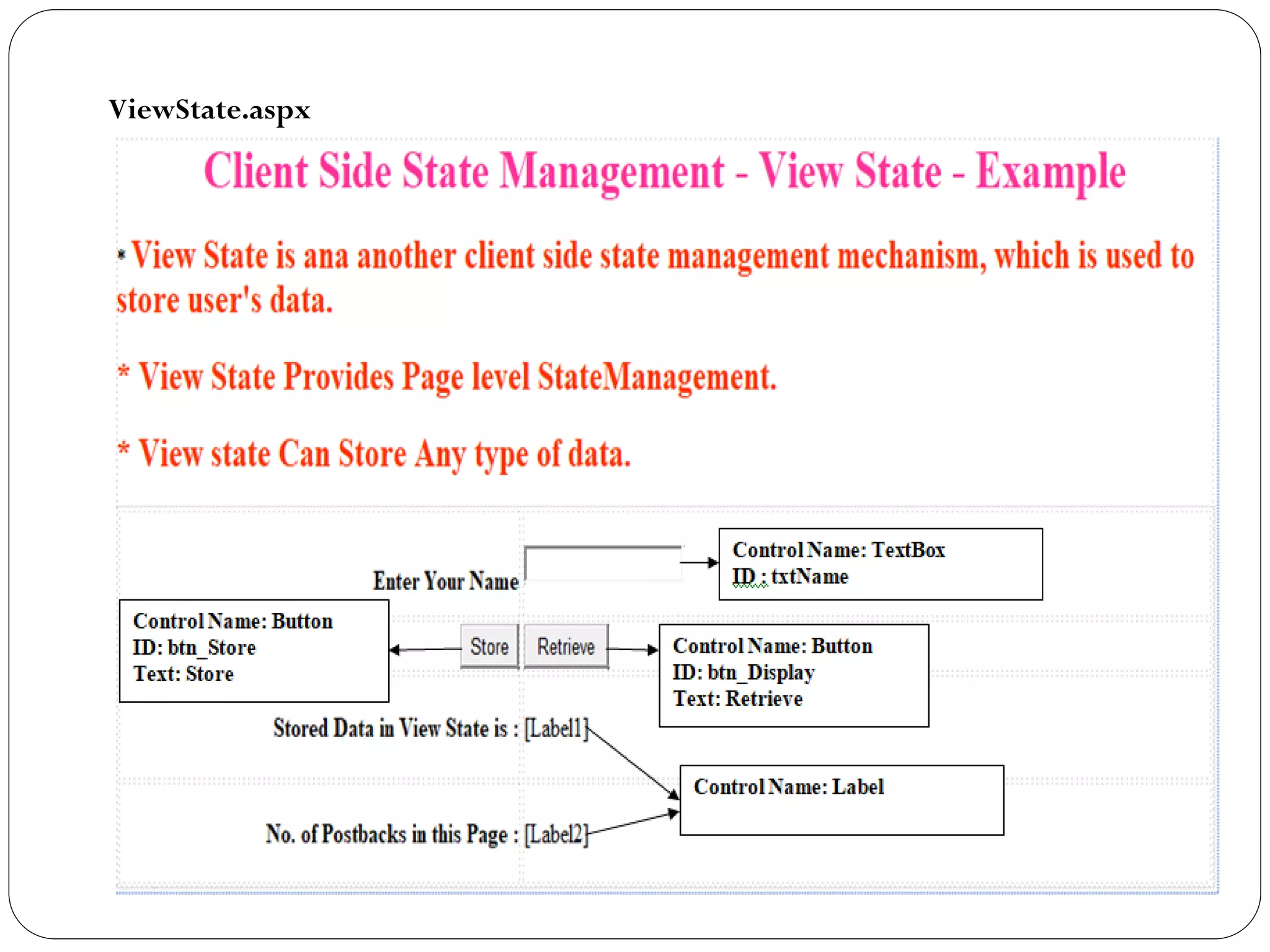
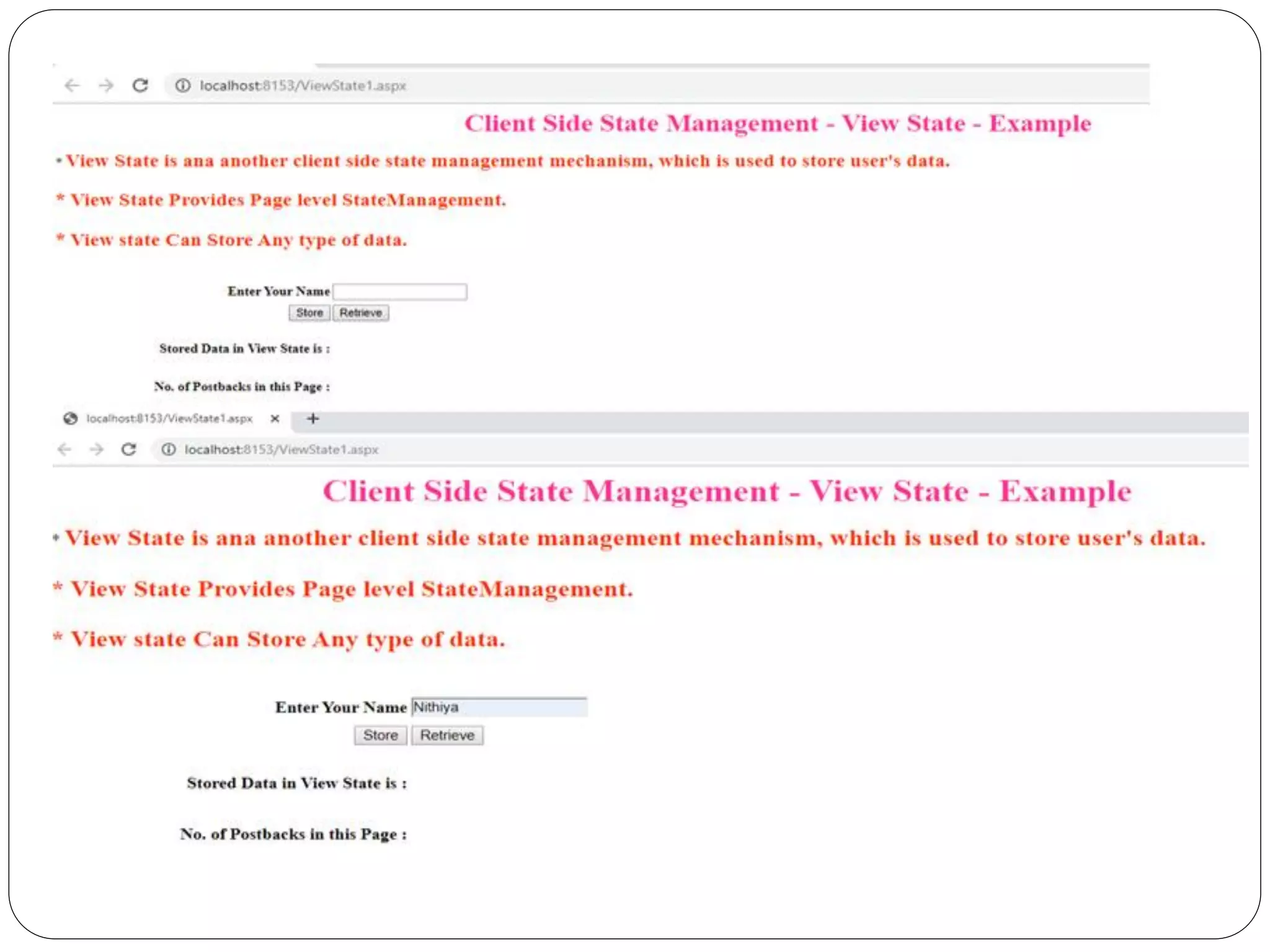
![Viewstate.aspx.cs
protected void Page_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (IsPostBack)
{
if (ViewState["count"] != null)
{
int viewstatecount = Convert.ToInt32(ViewState["count"]) + 1;
Label2.Text = viewstatecount.ToString();
ViewState["count"] = viewstatecount.ToString();
}
else
{
ViewState["count"] = "1";
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aspnetstatemanagement-191121101222/75/Asp-net-state-management-11-2048.jpg)
![protected void btn_Store_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
ViewState["name"] = txtName.Text;
txtName.Text = "";
Label2.Text=ViewState["count"].ToString();
}
protected void btn_Display_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Label1.Text =ViewState["name"].ToString();
Label2.Text =ViewState["count"].ToString();
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aspnetstatemanagement-191121101222/75/Asp-net-state-management-12-2048.jpg)


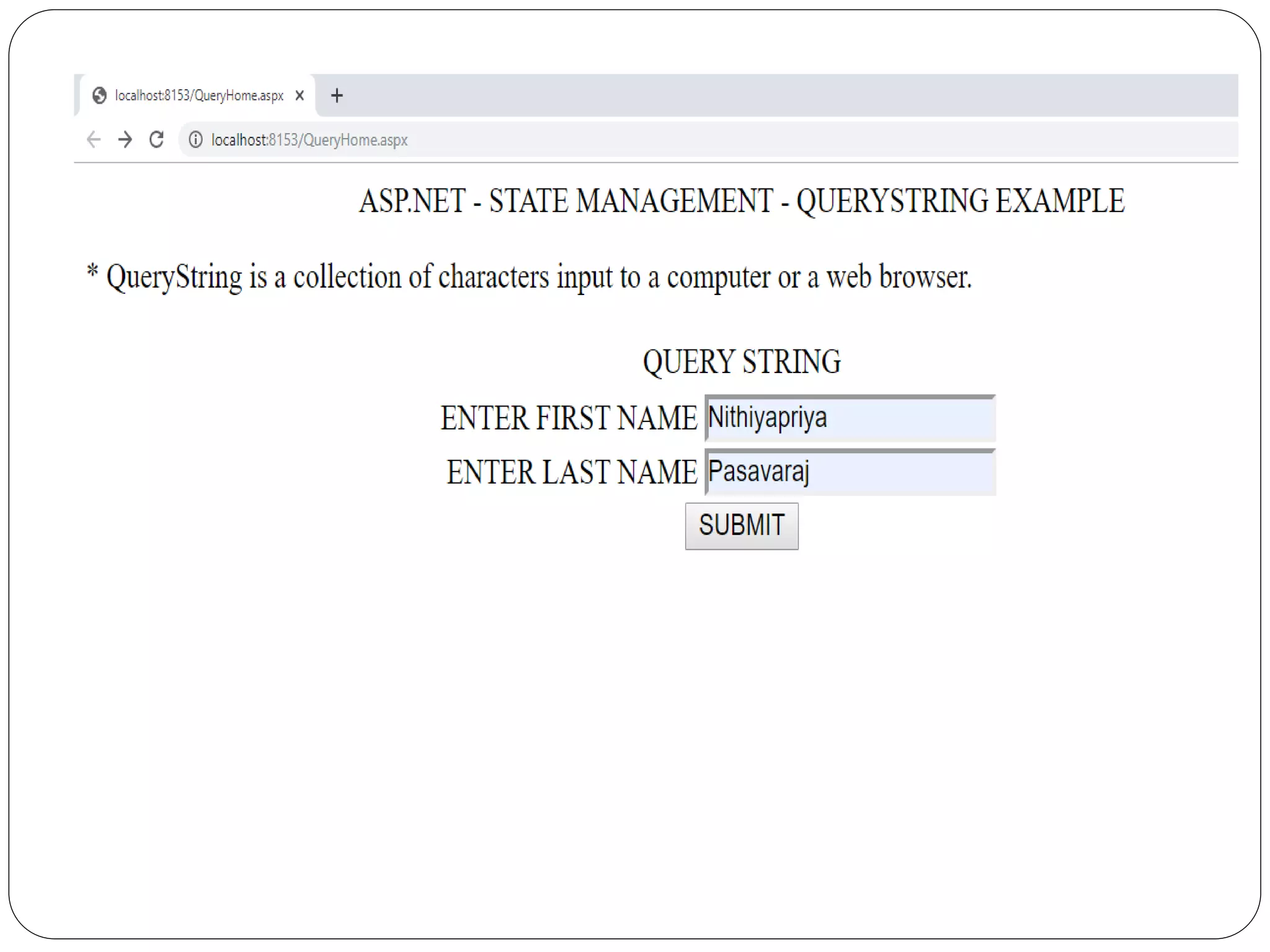
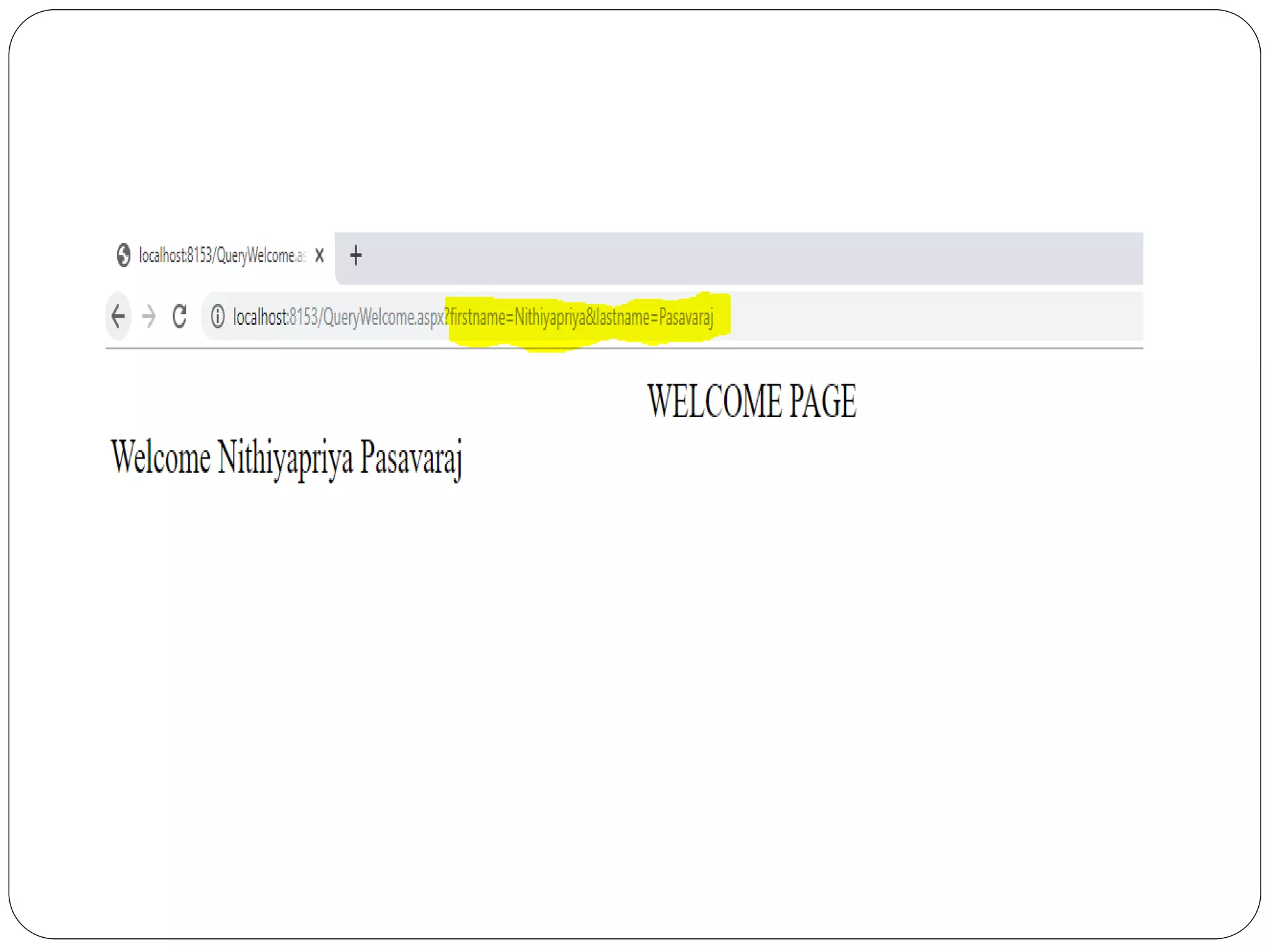
![QueryWelcome.aspx
QueryWelcome.aspx.cs
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Web;
using System.Web.UI;
using System.Web.UI.WebControls;
public partial class QueryWelcome : System.Web.UI.Page
{
protected void Page_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
String firstname = Request.QueryString["firstname"];
String lastname= Request.QueryString["lastname"];
Label1.Text = "Welcome " + firstname + " " + lastname;
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aspnetstatemanagement-191121101222/75/Asp-net-state-management-18-2048.jpg)

![1. Persistence Cookie
This types of cookies are permanently stored on user hard drive.
Cookies which have an expiry date time are called persistence cookies.
This types of cookies stored user hard drive permanently till the date time we
set.
To create persistence cookie:
Response.Cookies[“name”].Value = “Nithiyapriya”;
Response.Cookies[“Nithiyapriya”].Expires = DateTime.Now.AddMinutes(2);
(or)
HttpCookie strname = new HttpCookie(“name”);
strname.Value = “Nithiyapriya”;
strname.Expires = DateTime.Now.AddMinutes(2);
Response.Cookies.Add(strname);
Here, the Cookie Expire time is set as 2 minutes; so that we can access the
cookie values up to 2 minutes, after 2 minutes the cookies automatically
expires.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aspnetstatemanagement-191121101222/75/Asp-net-state-management-22-2048.jpg)
![2. Non-Persistence Cookie
This types of cookies are not permanently stored on user hard
drive.
It stores the information up the user accessing the same browser.
When user close the browser the cookies will be automatically
deleted.
To create non-persistence cookie:
Response.Cookies[“name”].Value = “Nithiyapriya”;
(OR)
HttpCookie strname = new HttpCookie(“name”);
strname.Value = “Nithiyapriya”;
Response.Cookies.Add(strname);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aspnetstatemanagement-191121101222/75/Asp-net-state-management-23-2048.jpg)
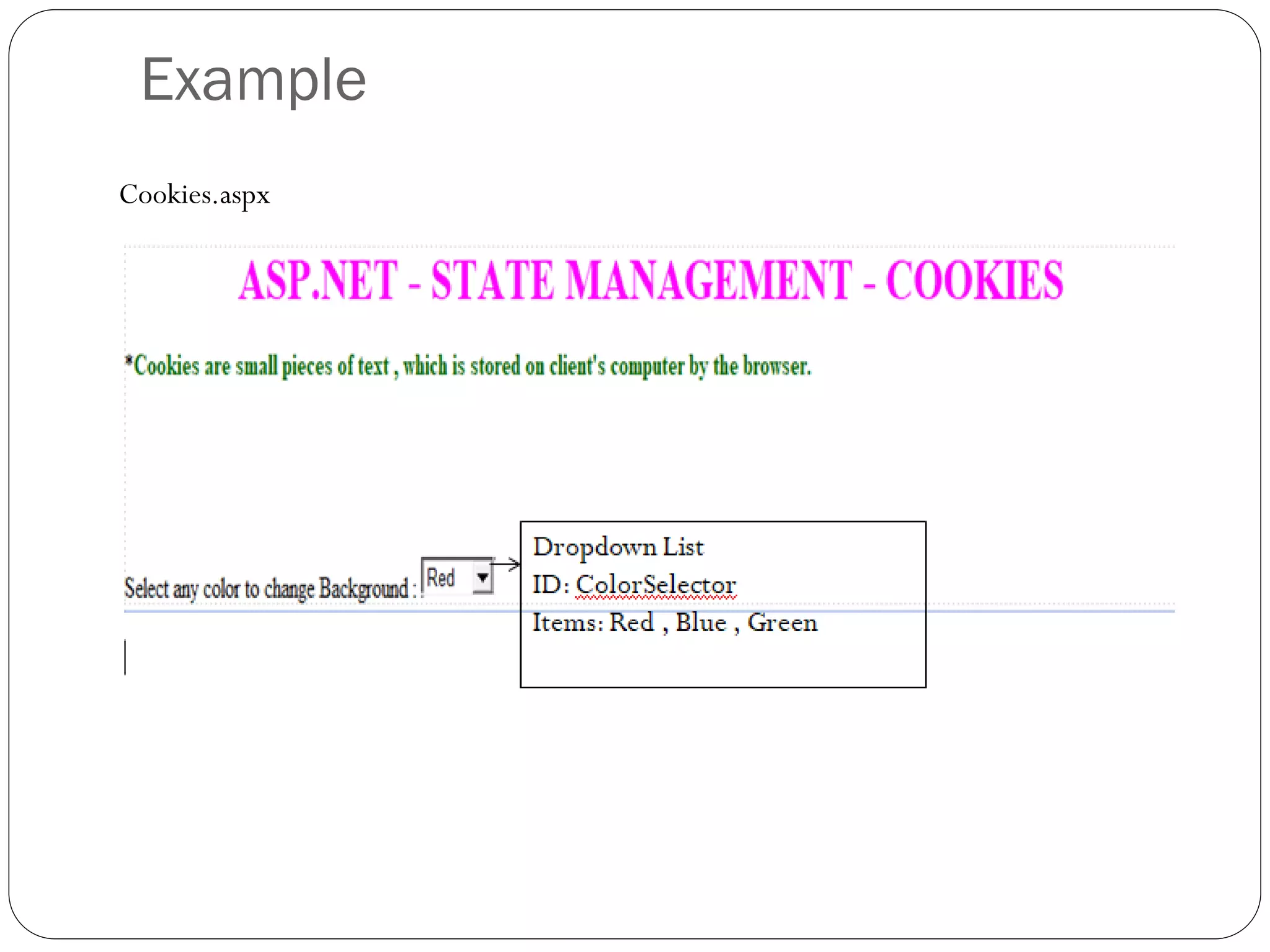
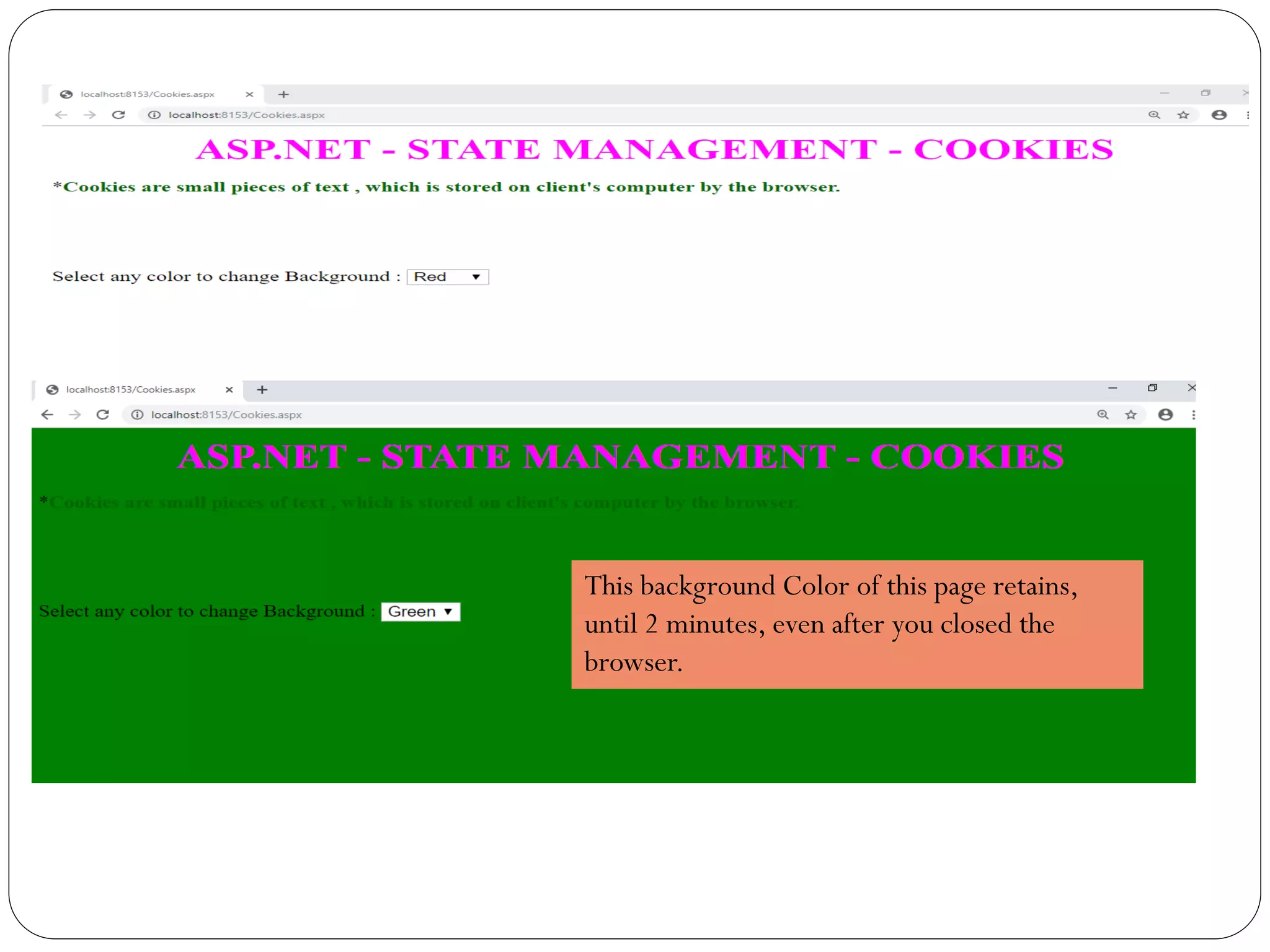
![Cookies.aspx.cs
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Web;
using System.Web.UI;
using System.Web.UI.WebControls;
public partial class Cookies : System.Web.UI.Page
{
protected void Page_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (Request.Cookies["BackgroundColor"] != null)
{
ColorSelector.SelectedValue=Request.Cookies["BackgroundColor"].Value;
BodyTag.Style["background-color"] = ColorSelector.SelectedValue;
}
}
protected void ColorSelector_SelectedIndexChanged(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
BodyTag.Style["background-color"] = ColorSelector.SelectedValue;
HttpCookie cookie = new HttpCookie("BackgroundColor");
cookie.Value = ColorSelector.SelectedValue;
cookie.Expires = DateTime.Now.AddMinutes(2);
Response.SetCookie(cookie);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aspnetstatemanagement-191121101222/75/Asp-net-state-management-25-2048.jpg)

![Syntax :
Session[“session_name”] = “session value”;
To Declare session in asp.net
Session[“name”]=”Nithiyapriya”;
Response.Redirect(“Welcomepage.aspx”);
To Retrieve session value onWelcomepage
string myvalue= Session[“name”].ToString();
Response.Write(“Name = ” + myvalue);
Example:
To set SessionTimeout add this code toWeb.config
<system.web>
<compilation debug="true" targetFramework="4.5" />
<httpRuntime targetFramework="4.5" />
<sessionState timeout="1"></sessionState>
</system.web>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aspnetstatemanagement-191121101222/75/Asp-net-state-management-28-2048.jpg)
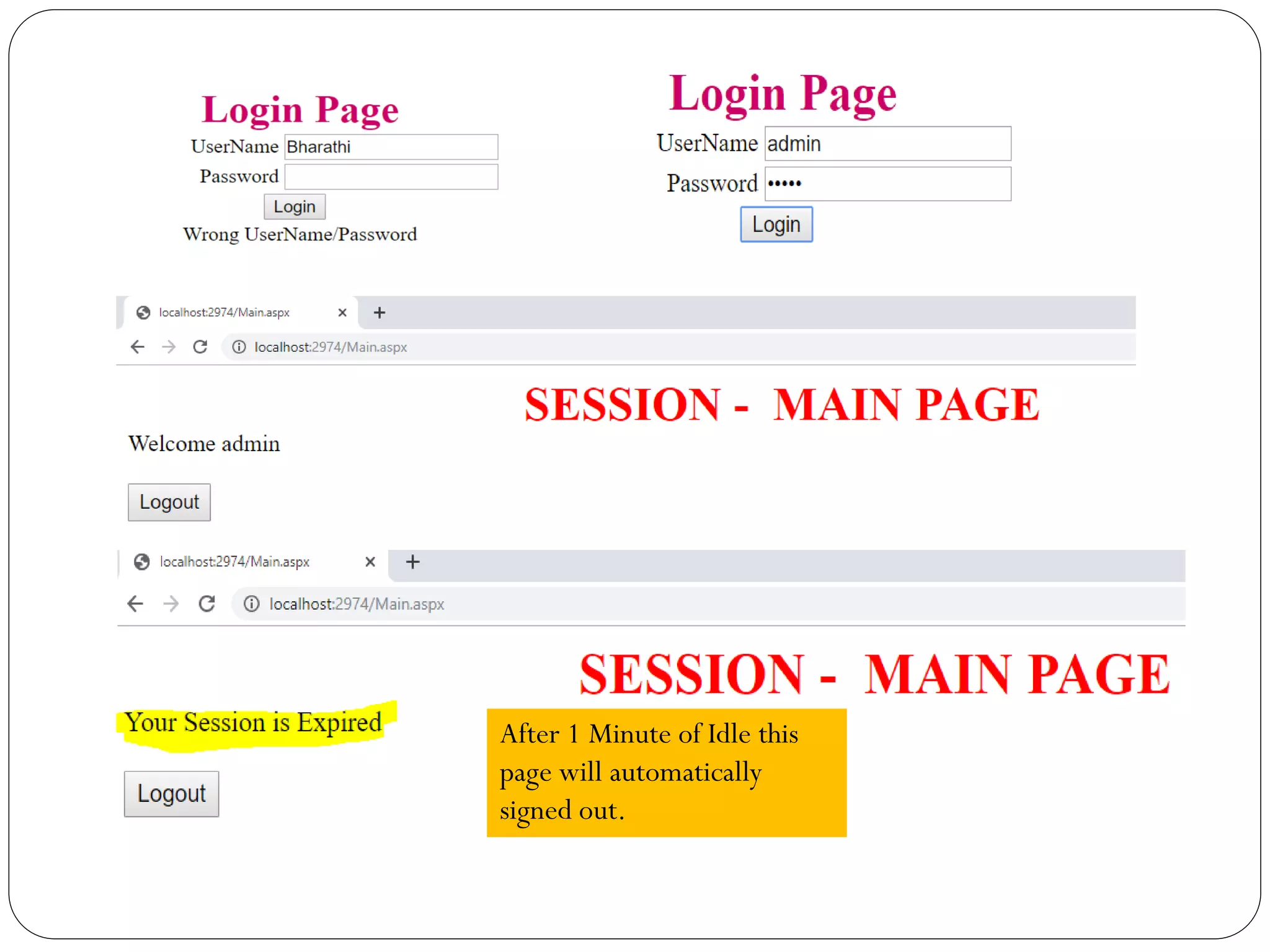
![Login.aspx
Login.aspx.cs
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Web;
using System.Web.UI;
using System.Web.UI.WebControls;
public partial class Login : System.Web.UI.Page
{
protected void Page_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
}
protected void Button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (txtusername.Text == "admin" && txtpassword.Text == "admin")
{
Session["uname"] = txtusername.Text;
Response.Redirect("Main.aspx");
} else
{
Label1.Text = "Wrong UserName/Password";
} } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aspnetstatemanagement-191121101222/75/Asp-net-state-management-29-2048.jpg)
![Main.aspx
Main.aspx.cs
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Web;
using System.Web.UI;
using System.Web.UI.WebControls;
public partial class Main : System.Web.UI.Page
{
protected void Page_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (Session["uname"] == null)
{
// Response.Redirect("Login.aspx");
Label1.Text = "Your Session is Expired";
} else
{
Label1.Text = "Welcome " + Session["uname"].ToString();
} }
protected void btn_logout_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Session["uname"] = null;
Response.Redirect("Login.aspx");
} }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aspnetstatemanagement-191121101222/75/Asp-net-state-management-30-2048.jpg)
![To Store value in application state
Application[“name”] = “Nithiyapriya”;
To get value from application state
string str = Application[“name”].ToString();
Example:
Here we are going to calculate how many times a given page has
been visited by various clients.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aspnetstatemanagement-191121101222/75/Asp-net-state-management-33-2048.jpg)

![ApplicationState.aspx.cs
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Web;
using System.Web.UI;
using System.Web.UI.WebControls;
public partial class ApplicationState : System.Web.UI.Page
{
protected void Page_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
}
protected void Button1_Click1(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
int count = 0;
if (Application["visit"] != null)
{
count = Convert.ToInt32(Application["visit"].ToString());
}
count = count + 1;
Application["visit"] = count;
Label1.Text = "This page is been visited for <b> " + count.ToString() + " </b>times";
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aspnetstatemanagement-191121101222/75/Asp-net-state-management-35-2048.jpg)
