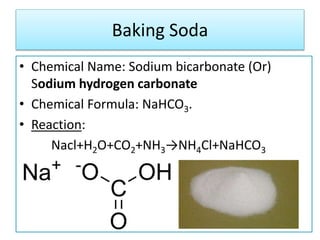
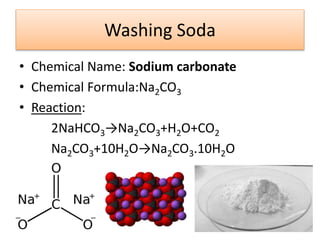
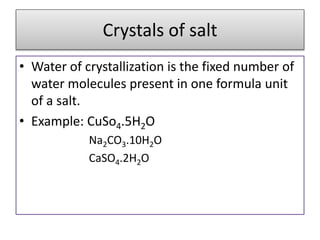
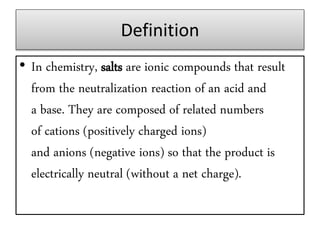
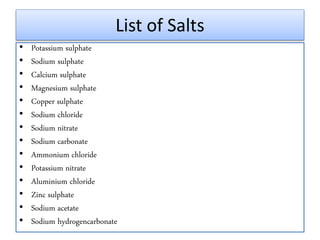
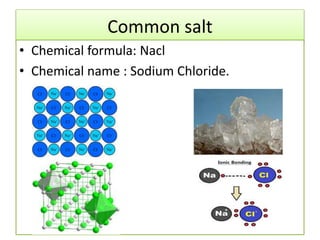
This document discusses various types of salts and their properties and applications. It defines salts as ionic compounds that result from acid-base neutralization reactions. It provides examples of common salts like sodium chloride, potassium sulfate and lists their properties such as being crystalline solids with high melting/boiling points that dissolve in water and conduct electricity. It then describes specific applications of salts like sodium chloride in the Chlor-alkali process, baking soda in baking and antacids, and plaster of paris in supporting fractured bones.




![Bleaching Power
Chemical Name: Calcium oxychloride
Chemical Formula: CaOCl2
Process:
• Electrolysis of aqueous sodium chloride(Brine);
• Chloride on dry slake lime [Ca(OH)2] gives
bleaching power [CaOCl2]
Reaction:
Ca(OH)2+Cl2→CaOCl2+H2O](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/applicationsofsalts-150730193750-lva1-app6892/85/Applications-of-salts-8-320.jpg)