1) This study uses a deep learning model to estimate stratospheric gravity wave potential energy (GW Ep) averaged over 20-30 km using ERA5 reanalysis data and terrain data as inputs. The model is trained using GW Ep values calculated from COSMIC radio occultation data as labels.
2) The results show the model can effectively estimate the zonal trend of GW Ep but with larger errors in low latitudes than mid-latitudes. Seasonal variations are also seen in the estimated GW Ep.
3) The estimated GW Ep shows the effect of the quasi-biennial oscillation, though its amplitude may be less than that of the measured GW Ep from COSMIC data.





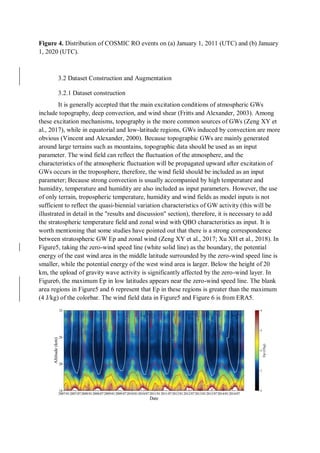
![Figure 5. The monthly average variation of GW Ep and zonal wind at each altitude in the
latitude range of 30°
N40°
N from 2007 to 2014 (the heat map is the GW Ep, the isoline is
the zonal wind, the negative zonal wind values [black dotted lines] represent east wind, and
the positive values (red solid lines] represent west wind).
Figure 6. Same as Figure 5, but for 10°
S10°
N.
The input data of the deep learning model have 22 layers, and the region of each layer
is 60°
S60°
N. A downsampling operation is performed to achieve a resolution of 1°
×
1°
,
which is the same as the resolution of the gridded GW Ep. All input layers are shown in
Table 1. The output of the model is the GW Ep grid data within the area of 60°
S60°
N.
Table 1. Input dataset of the deep learning model.
Layer Parameter name
Pressure levels
(hPa)
Resolution Latitude range
1 Terrain / 1°
×
1° 60°
S60°
N
24 Relative humidity 500, 700, 850 1°
×
1° 60°
S60°
N
57 Temperature 500, 700, 850 1°
×
1° 60°
S60°
N
810 Zonal wind 500, 700, 850 1°
×
1° 60°
S60°
N
1113 Meridional wind 500, 700, 850 1°
×
1° 60°
S60°
N
1416 Vertical velocity 500, 700, 850 1°
×
1° 60°
S60°
N
1719 Temperature 50, 100, 200 1°
×
1° 60°
S60°
N
2022 Zonal wind 50, 100, 200 1°
×
1° 60°
S60°
N
To accelerate the convergence of the model, it is necessary to normalize the data of
each layer. For the input/output layer 𝐴, its maximum and minimum values, Max and Min,](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/applicationofdeeplearningtoestimatestratosphericgravitywavepotentialenergy-231014173827-fdd8ae19/85/Application-of-deep-learning-to-estimate-stratospheric-gravity-wave-potential-energy-pdf-9-320.jpg)
![in the global range over the years examined can be determined, and the normalization
operation for 𝐴 can be expressed as [𝐴 − (Min − 𝜀1)]/[(Max + 𝜀2) − (Min − 𝜀1)], where
(Min − 𝜀1) and (Max + 𝜀2) represent an appropriate expansion of the value range to ensure
that the normalization operation always has an input/output data value between 0 and 1 when
new data are input in the model.
To verify the seasonal variation in the estimated Ep, datasets from three years (June
2009 to May 2010, June 2010 to May 2011, and June 2011 to May 2012) were used as test
sets to evaluate three models separately. For each model, 5% of the data outside the test set
were randomly selected as the validation set and the other data were used as the training set.
The date range of the training set, validation set and test set of the three models are shown in
Table 2. This study uses three models is to verify that the seasonality of GW Ep is not the
result typical of other years, because the intensity of GW Ep is different in these three years.
Table 2. Date range of the training set, validation set and test set.
Model Training and validation set Test set
Model 1
2006.122009.05
&
2010.062020.12
2009.062010.05
Model 2
2006.122010.05
&
2011.062020.12
2010.062011.05
Model 3
2006.122011.05
&
2012.06~2020.12
2011.062012.05
3.2.2 Dataset augmentation
Since the calculation of the measured values of GW Ep requires all the temperature
profile data from each day, only one global distribution of GW Ep can be obtained for each
day. The time span of COSMIC RO data in this paper is from January 2007 to December
2020, and the quantities of daily profiles on many days are not enough to calculate the global
distribution of GW Ep, so there are only approximately 3300 valid days, which is far from
enough for deep learning. Hence, it is necessary to augment the dataset.
This study develops a "cut-swap" dataset augmentation method for global
meteorological data. Taking terrain data as an example, the specific steps for dataset
augmentation are as follows:
(a) Select an integer longitude within the longitude range of 180°
W180°
E and cut
the dataset along that longitude (Figure 7a).
(b) Swap the left and right parts of the split dataset and then re-splice them together
(Figure 7b).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/applicationofdeeplearningtoestimatestratosphericgravitywavepotentialenergy-231014173827-fdd8ae19/85/Application-of-deep-learning-to-estimate-stratospheric-gravity-wave-potential-energy-pdf-10-320.jpg)














