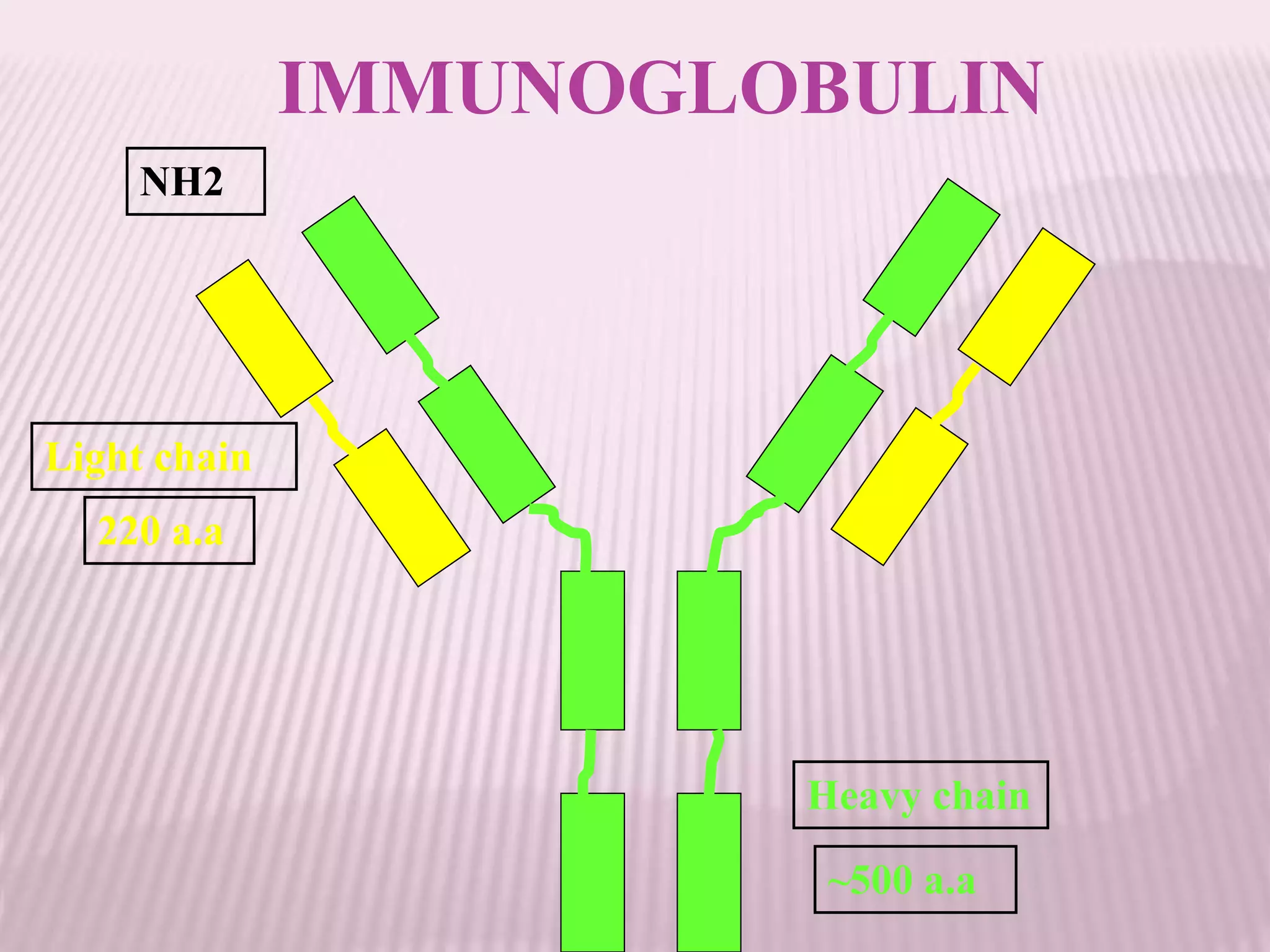
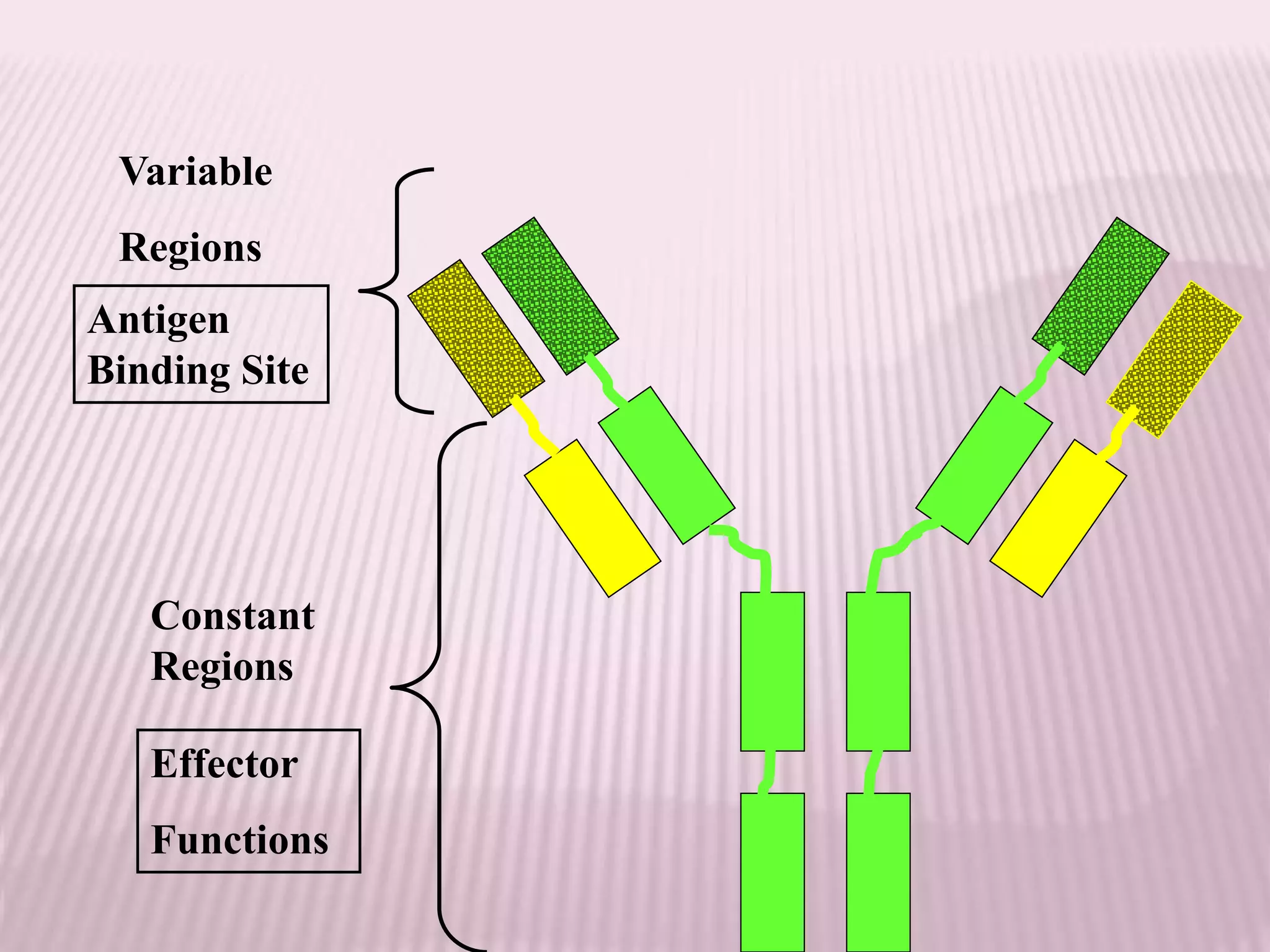
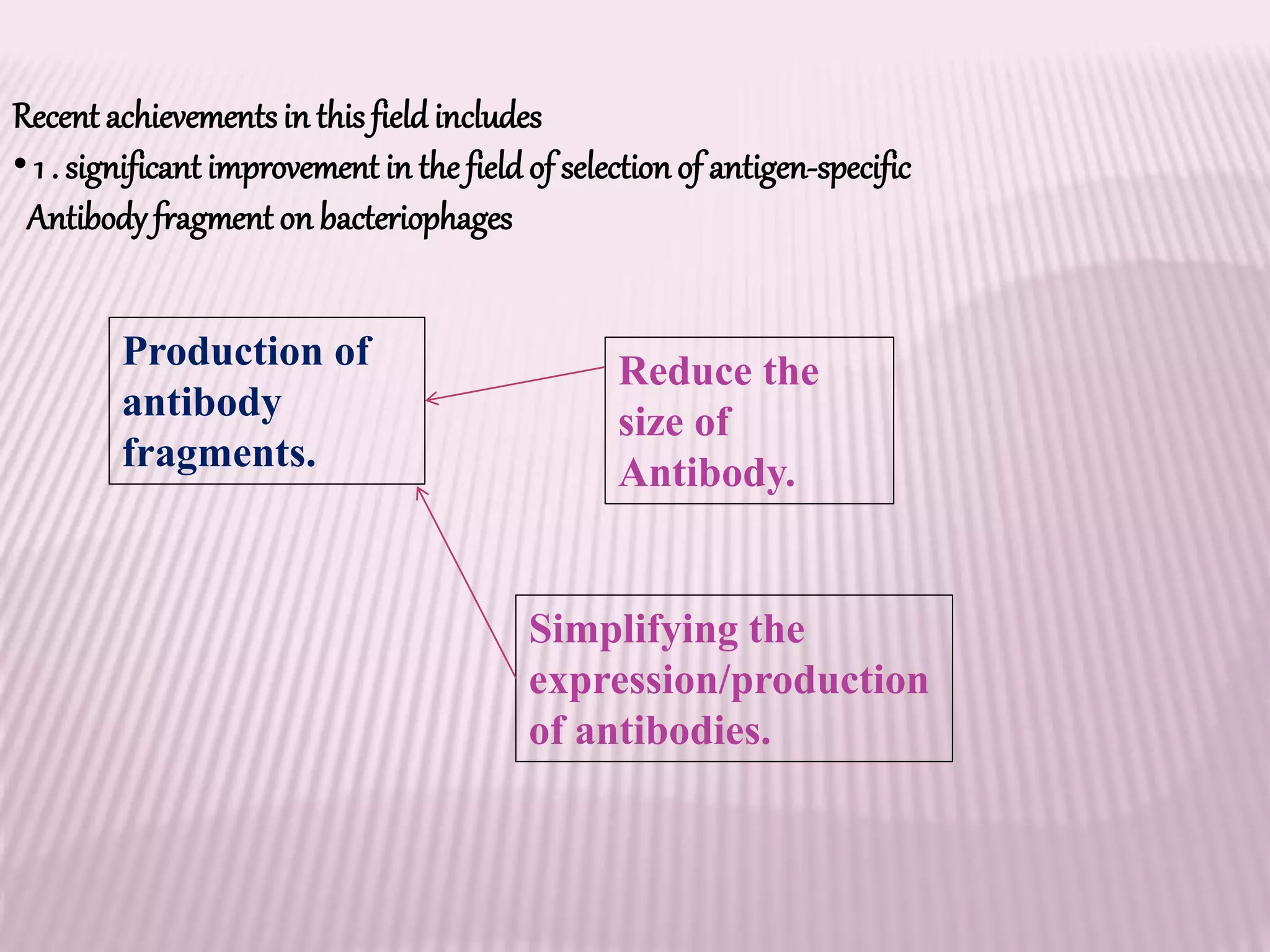
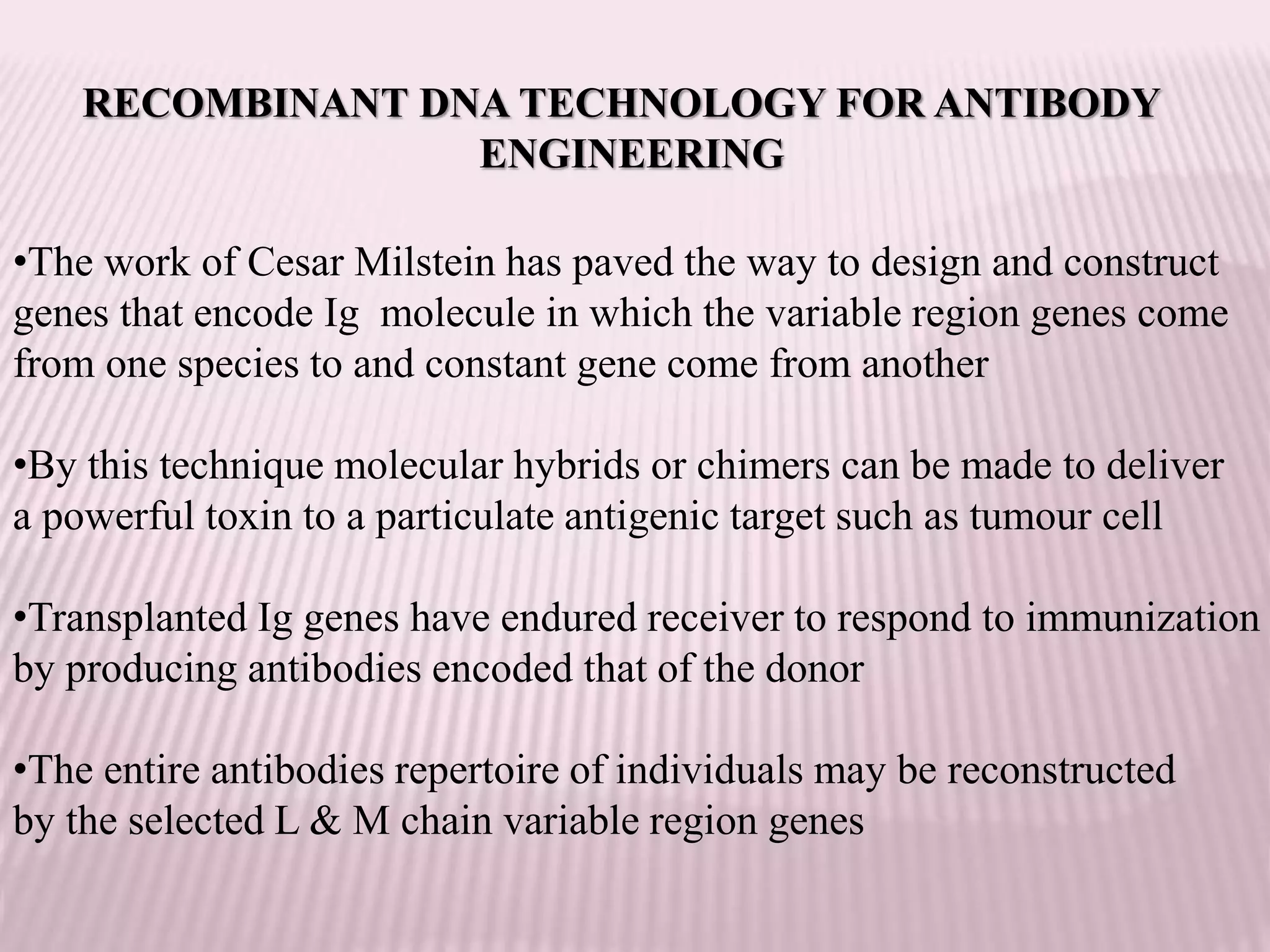
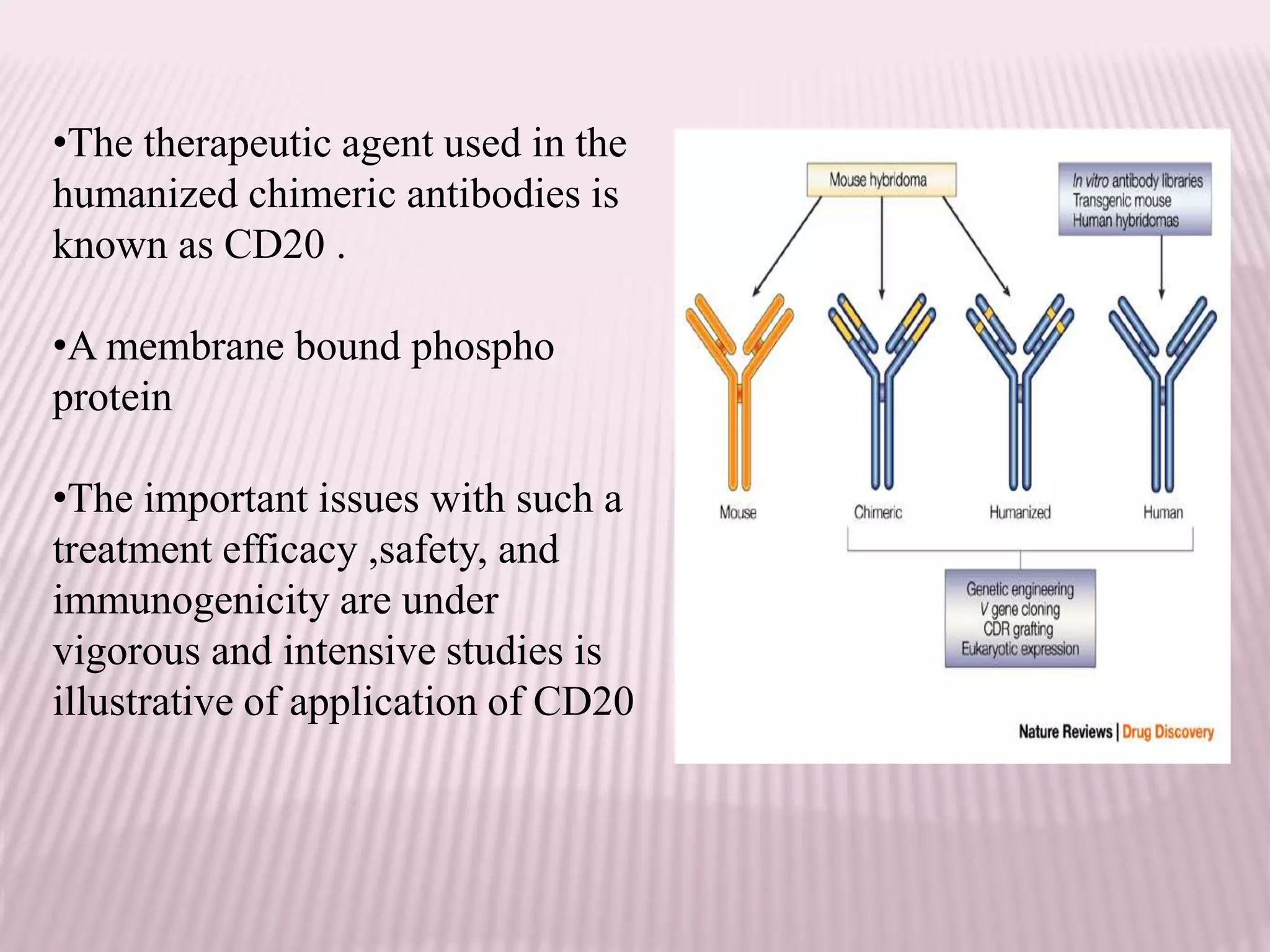
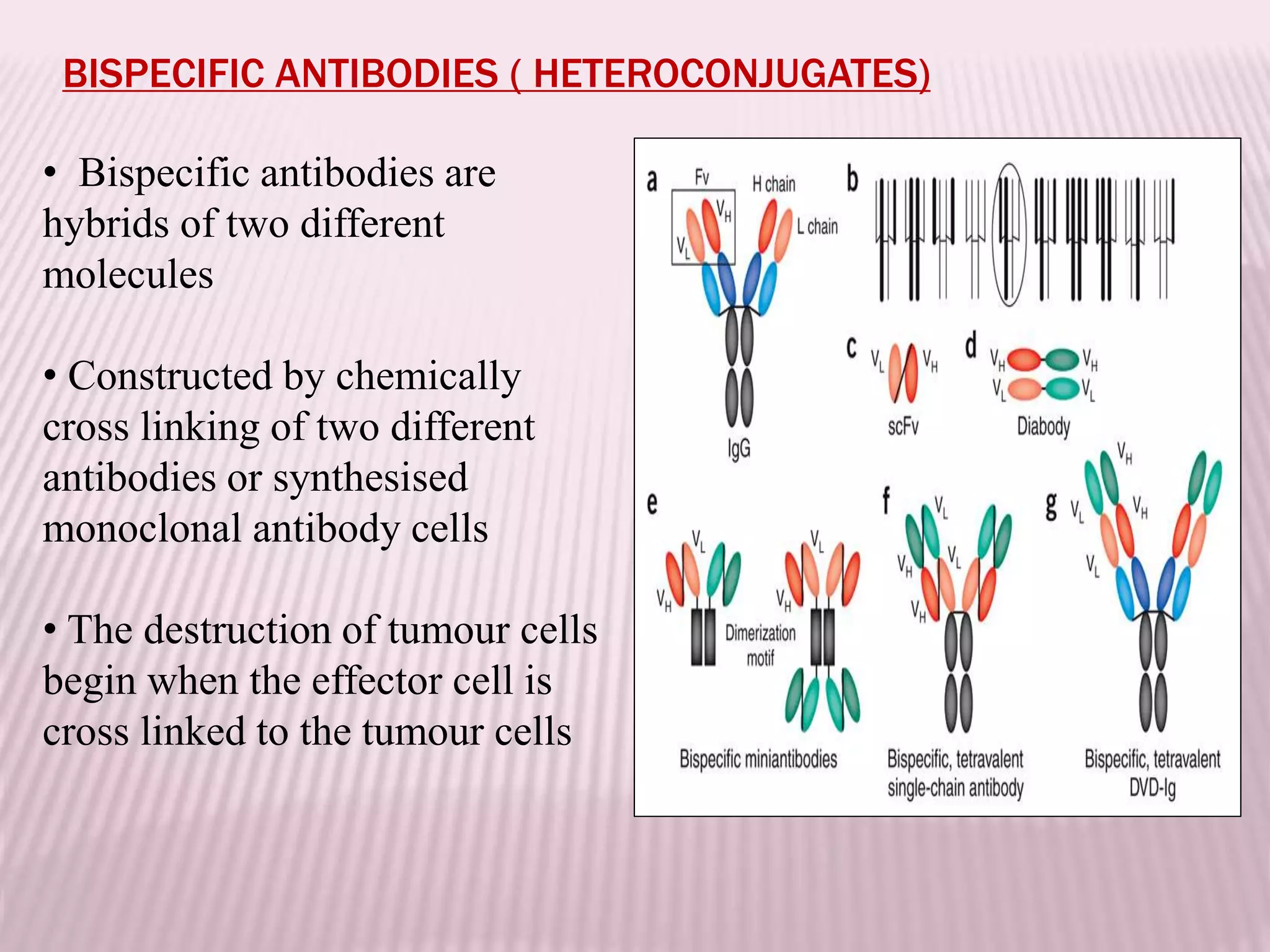
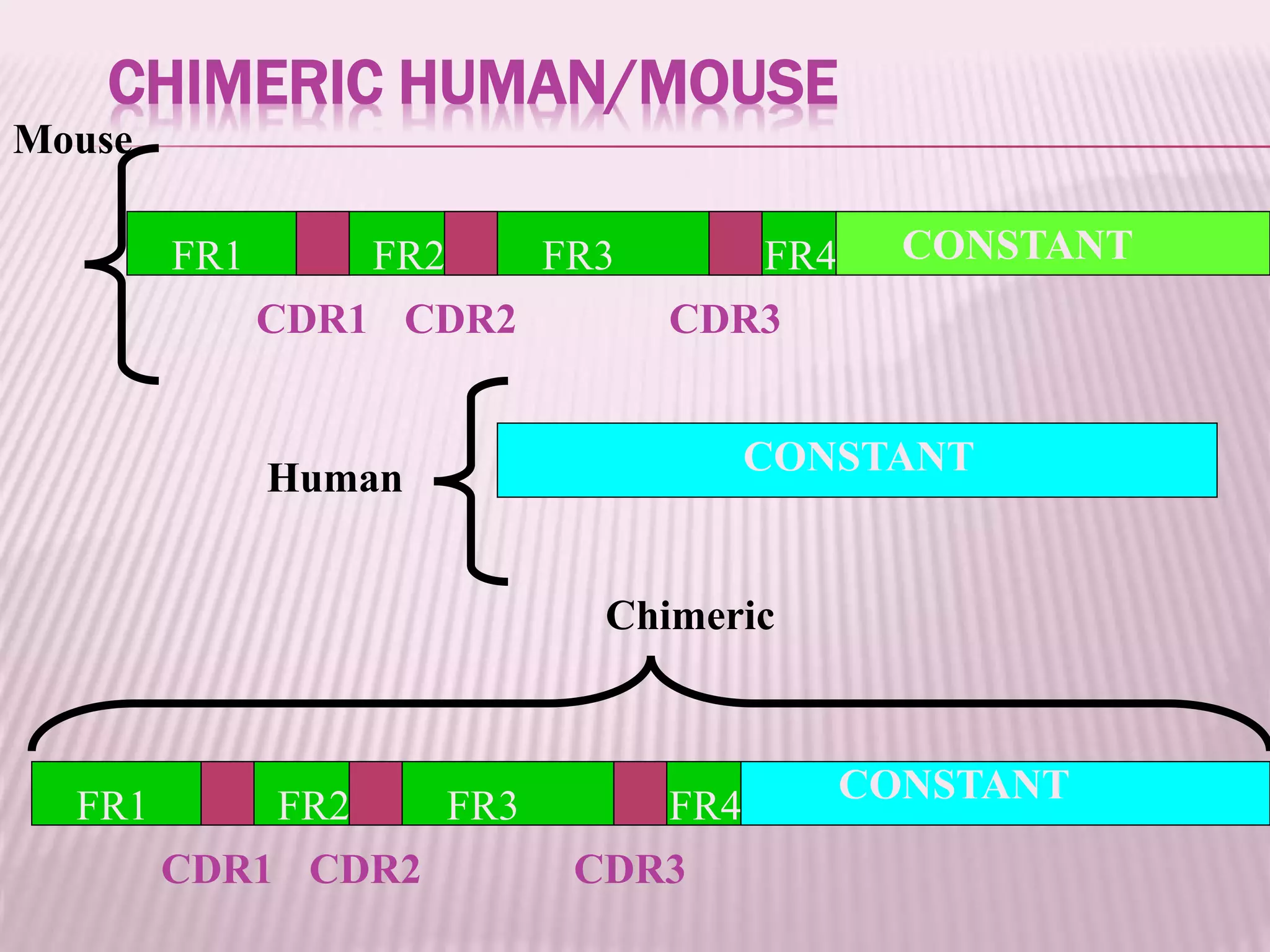
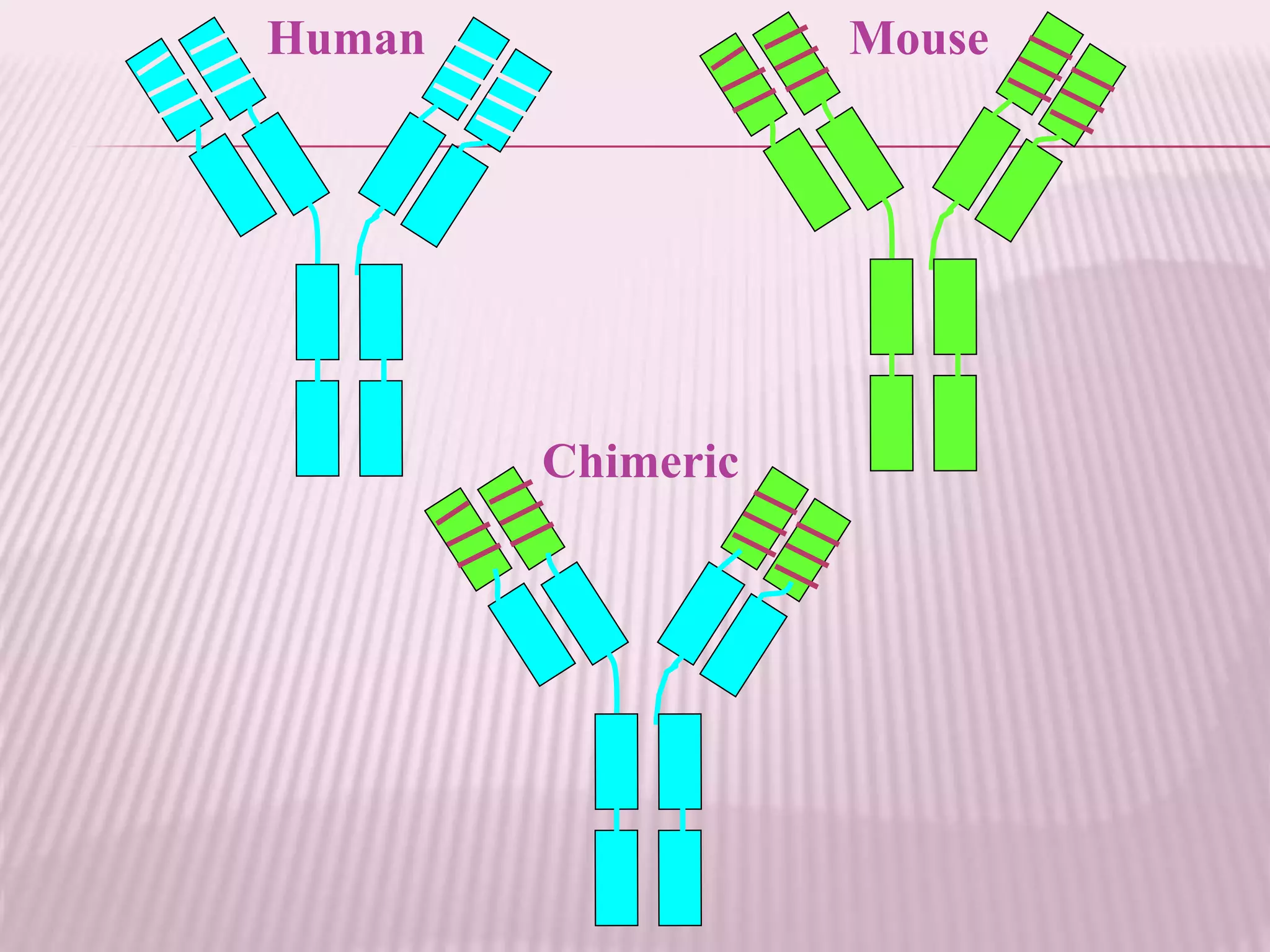
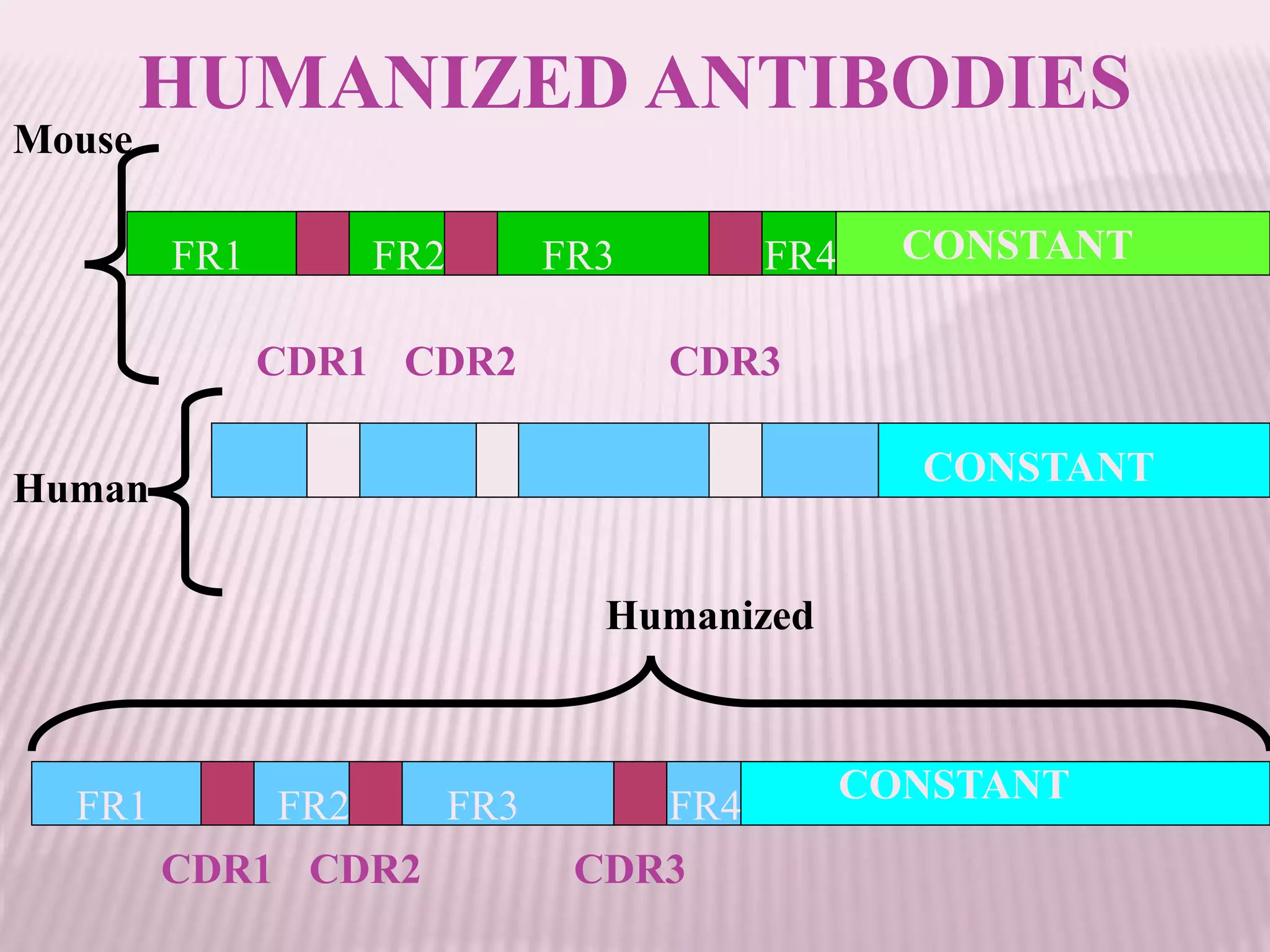
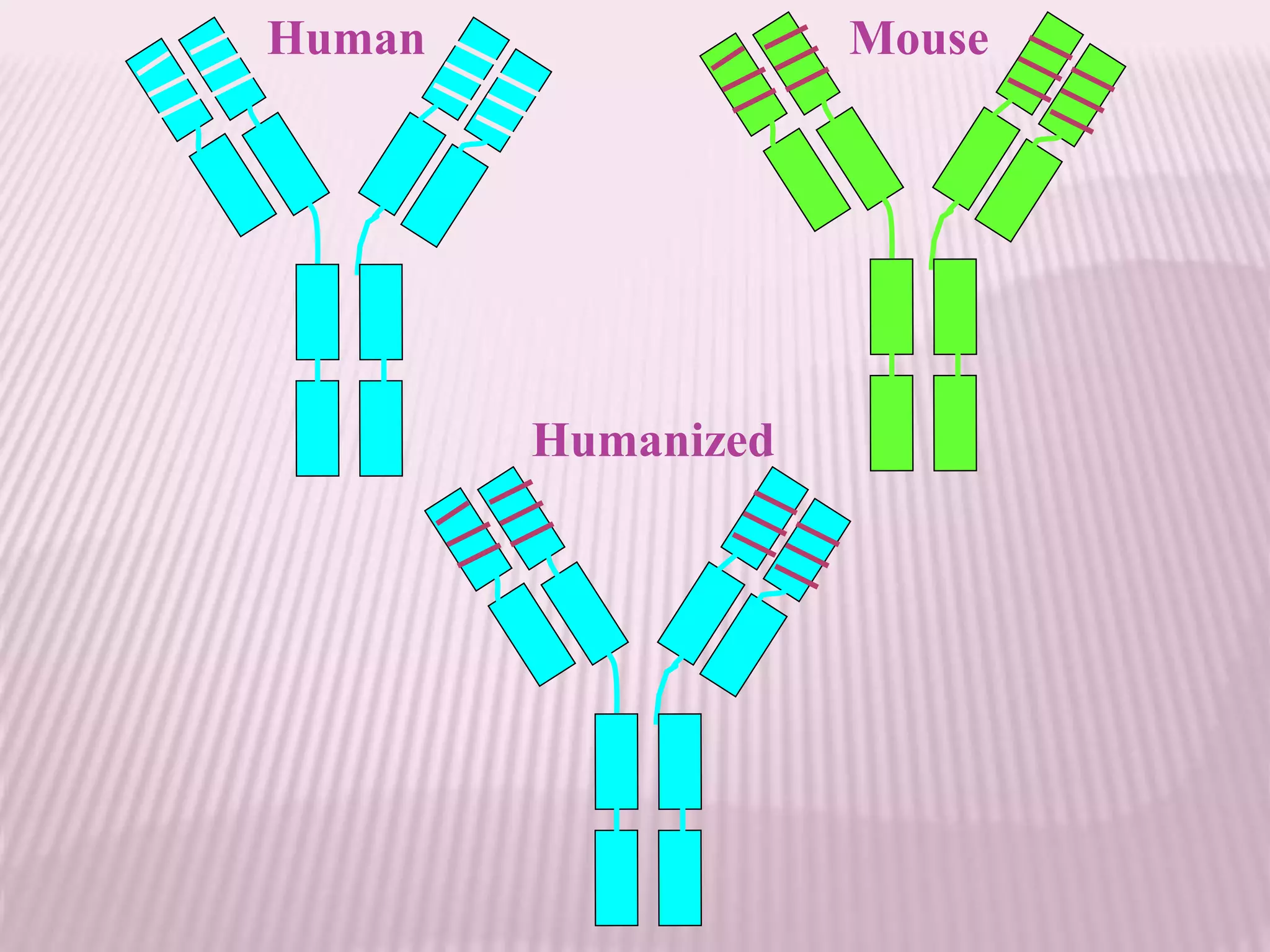
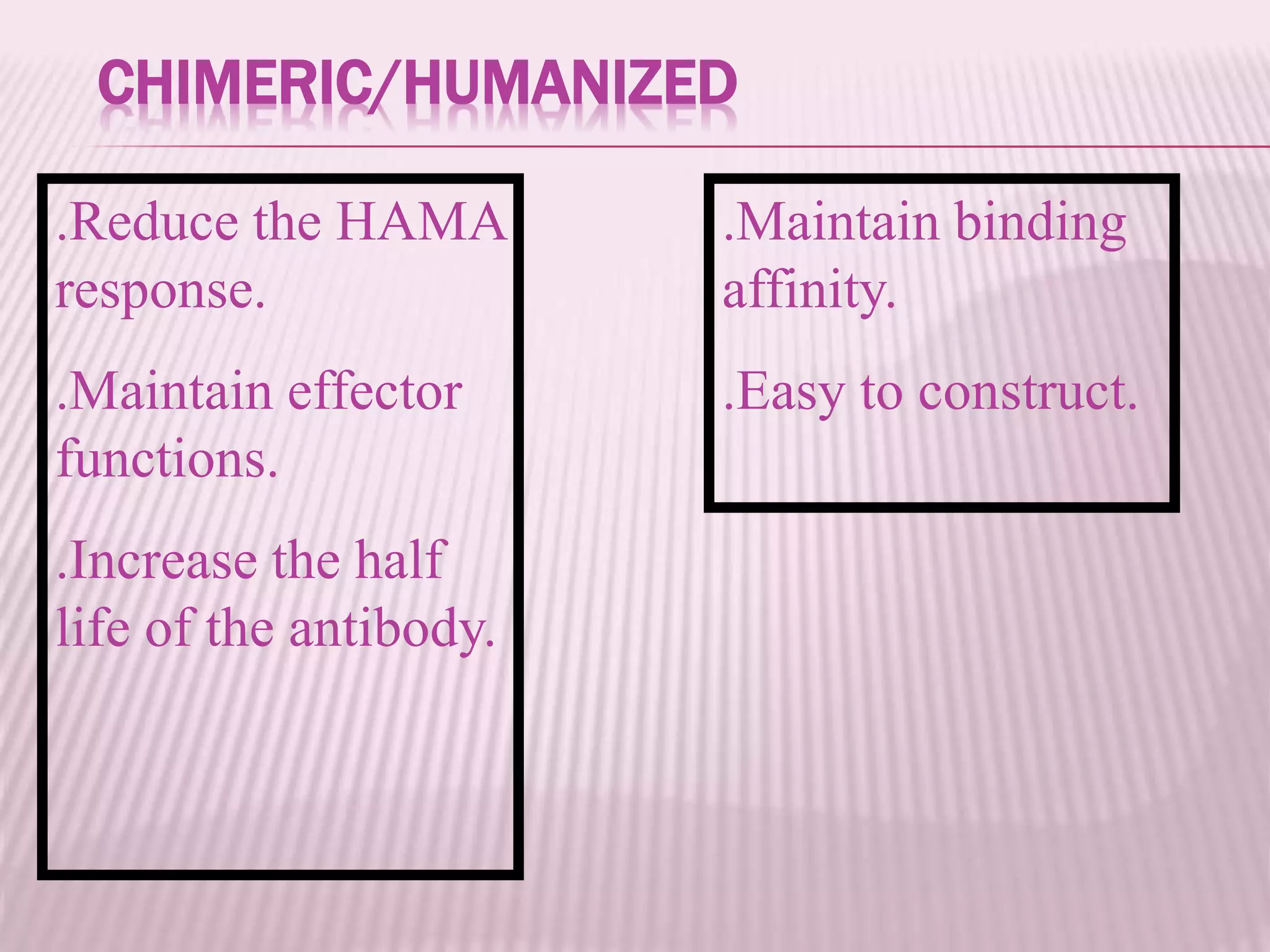
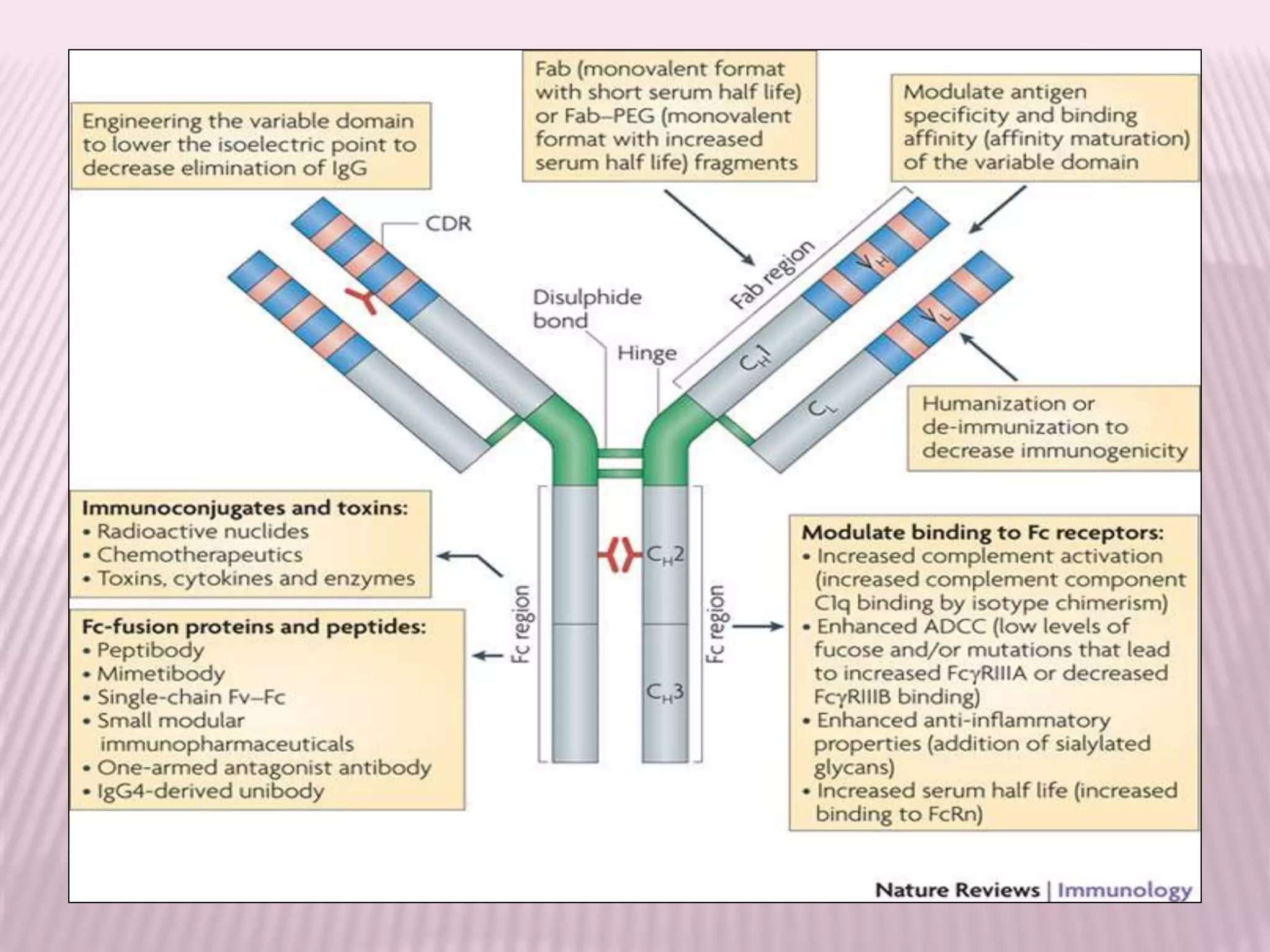
Antibodies can be engineered using genetic techniques to alter their properties for therapeutic applications. Key characteristics that can be modified include immunogenicity, effector function, size and affinity. Techniques like generating chimeric or humanized antibodies can reduce immunogenicity. The effector function can be enhanced or reduced depending on the intended use of the antibody. Size can be decreased by removing nonessential components. Affinity can be increased by altering amino acids in the binding site. Antibody engineering also includes techniques like phage display which can be used to isolate antibodies with desired properties.