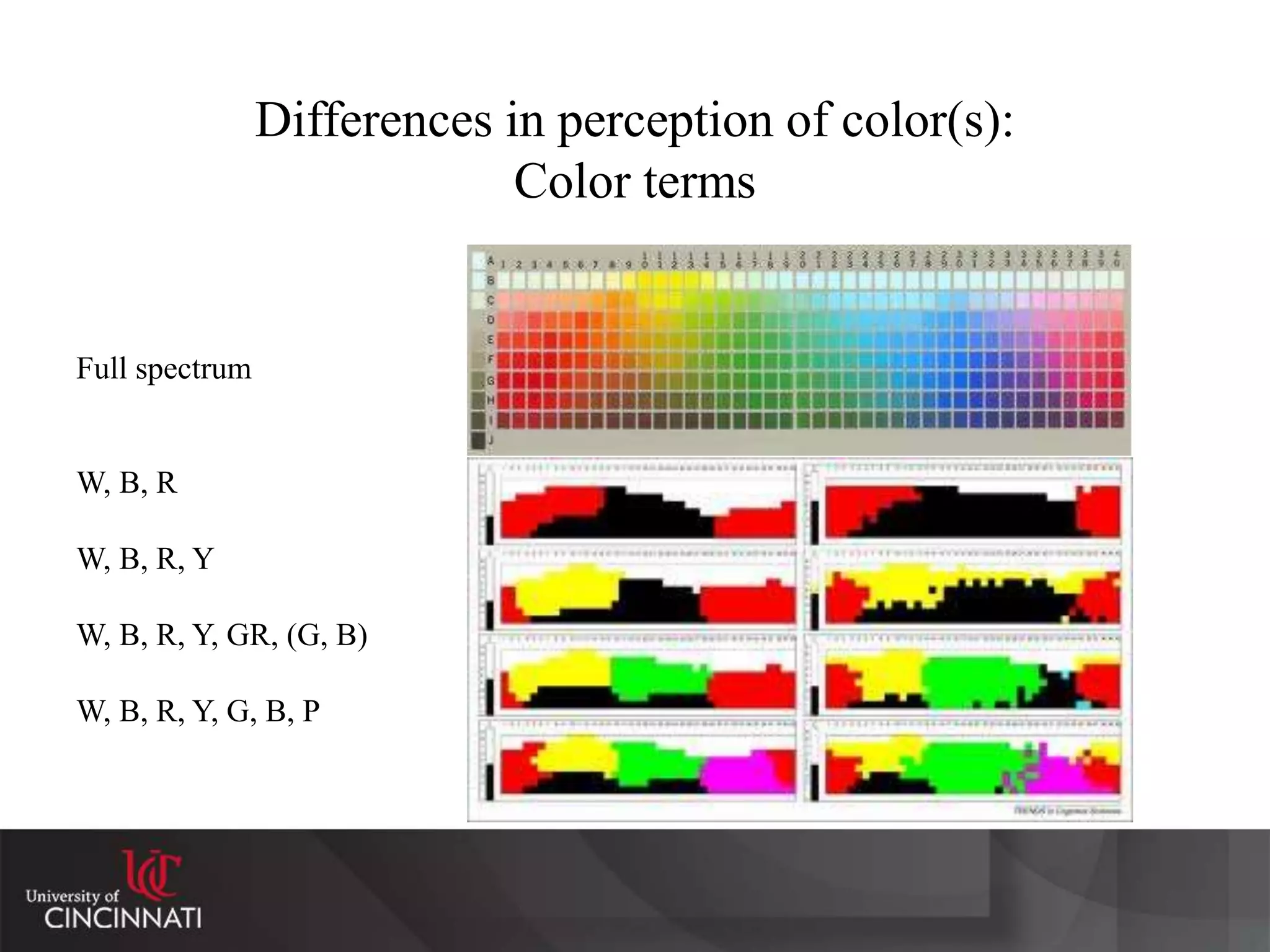
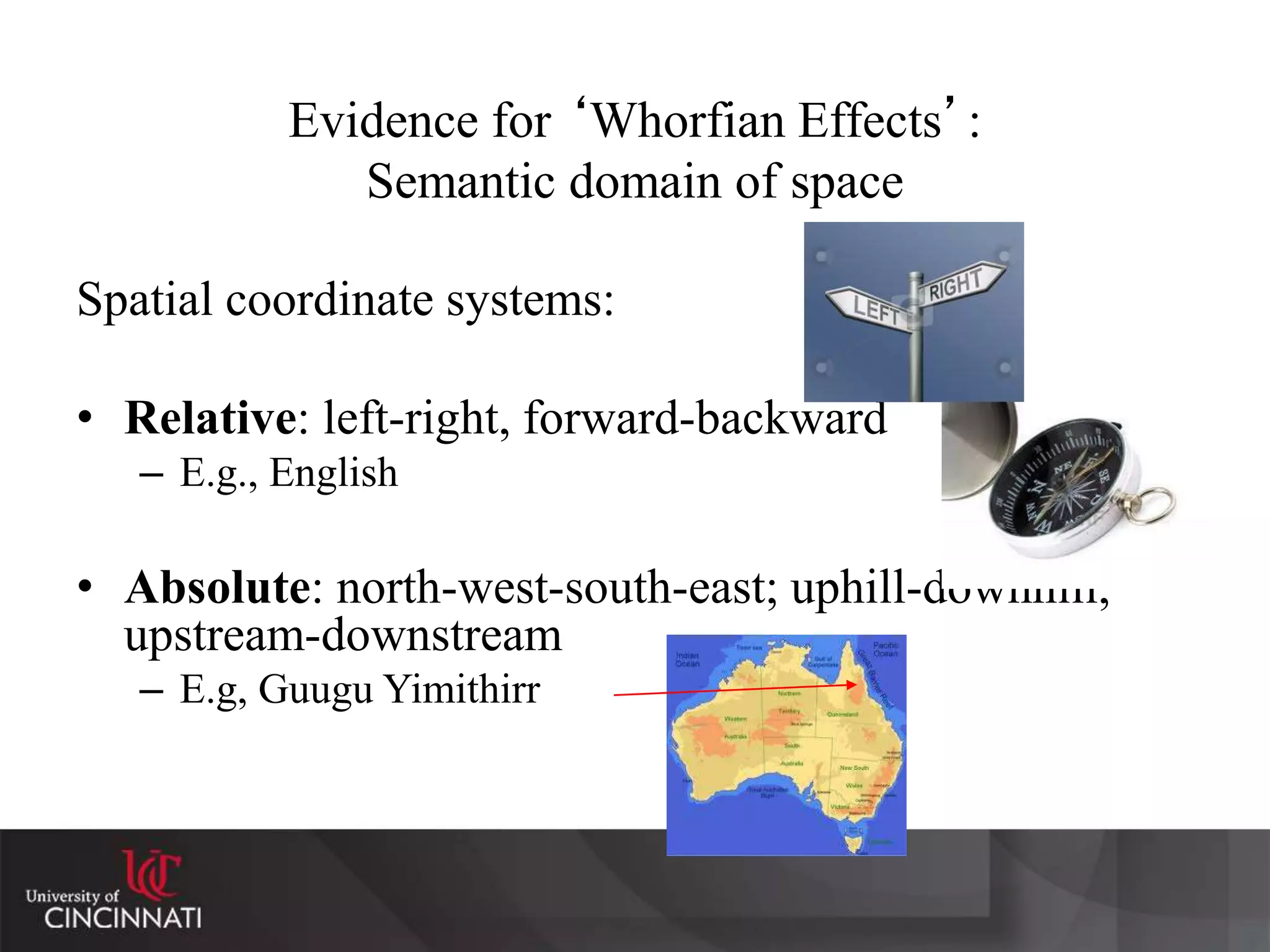
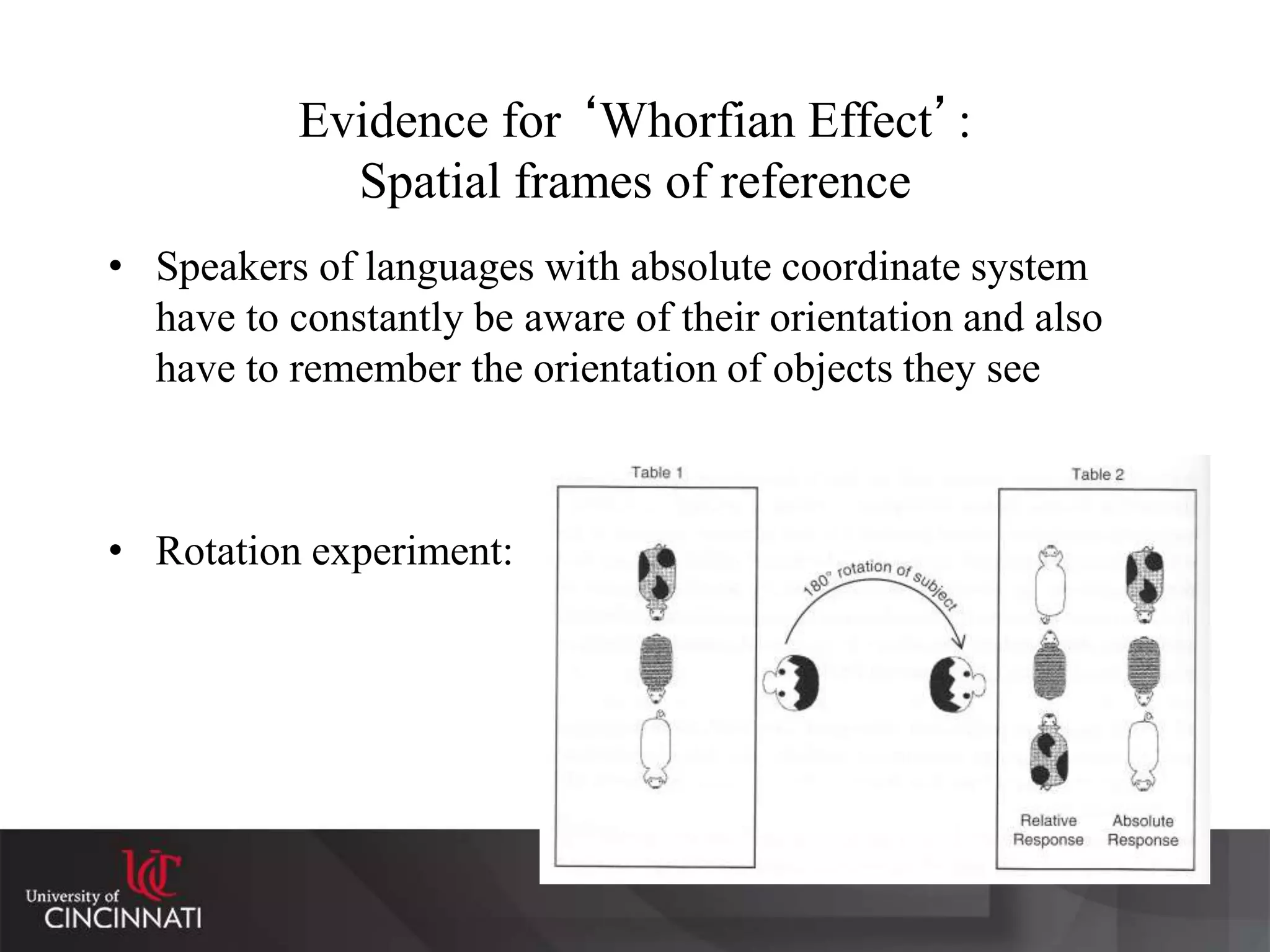
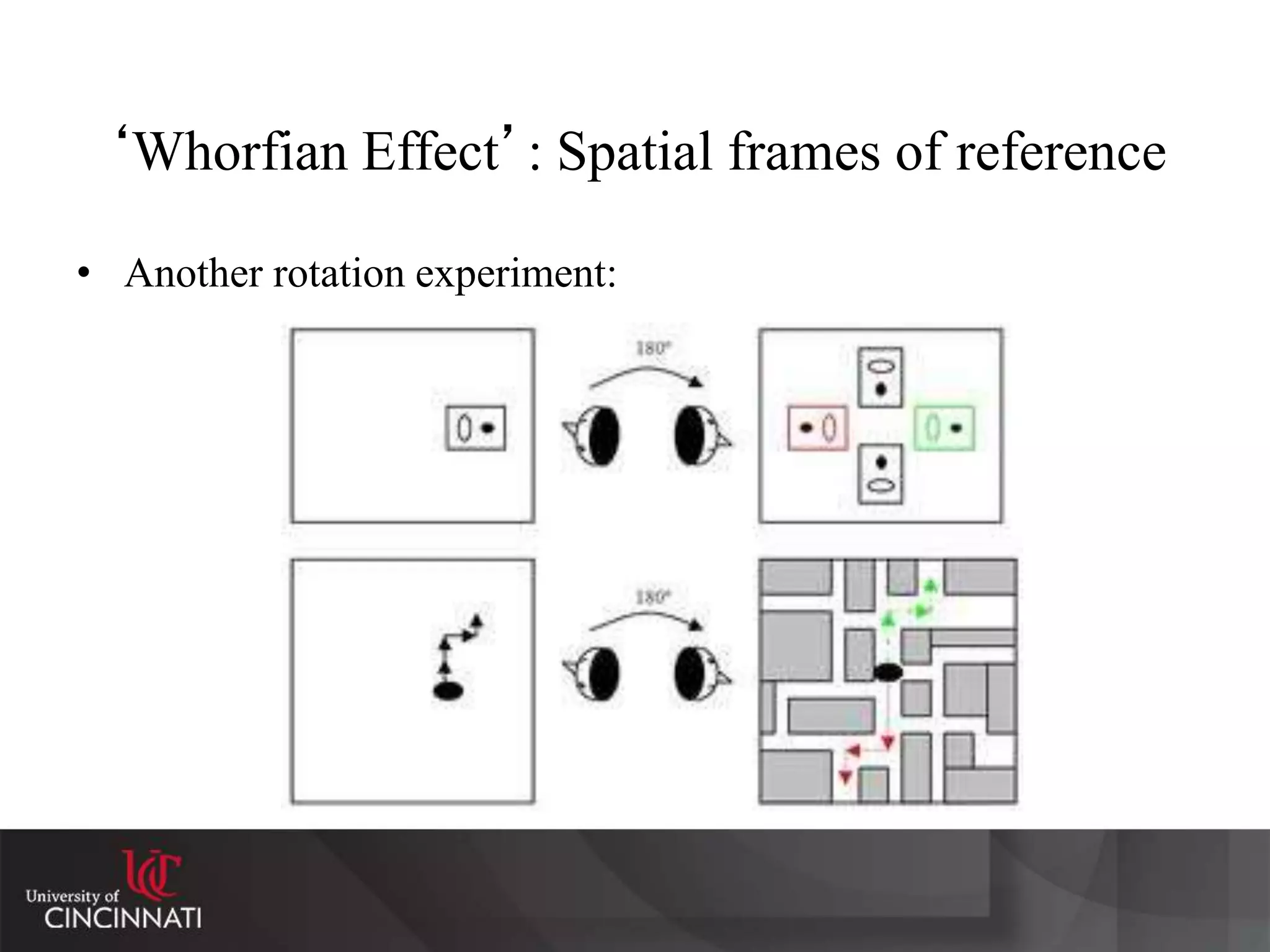
The document discusses the relationship between language, thought, and culture. It explores the Sapir-Whorf hypothesis, which claims that the language we speak shapes how we think. The document examines the work of Sapir and Whorf, who argued that different languages lead to different worldviews. As evidence, it analyzes Whorf's study of the Hopi language and his claim that it conveyed a different concept of time than English. While the strong version of linguistic determinism has been debunked, evidence suggests there may be weaker "Whorfian effects," where language predisposes certain ways of thinking.












![Plurality in SAE and Hopi
SAE:
• Use of cardinal numbers with real and imaginary plurals,
e.g., ‘day’ counted as an object, a ‘length of time:
‘three days’
Hopi:
• Use of ordinal numbers with units of time, e.g., ‘day’
experienced as cyclicity (i.e., the same day recurring over
and over):
‘payistala’ or ‘the third day’
[‘paayo’ (three) ‘s’ (times) ‘taala’ (daylight) ‘three-times-
daylight’]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2188-anth1007languagethought-180923190427/75/ANTH1007-Language-Thought-and-Culture-13-2048.jpg)