This document provides an overview of AngularJS concepts covered in Unit II of the course IT2304 – Full Stack Web Development, including modules and dependency injection, scopes, directives, filters, and services. It defines modules, controllers, dependencies, scopes, common directives like ng-repeat and ng-if, filters like currency and date, and services like $http, $timeout, and custom services. Example code is provided to demonstrate key concepts.
![IT2304 – Full Stack Web Development Unit II - AngularJS
Prepared by Dr. R. Arthy 1
Department of Information Technology
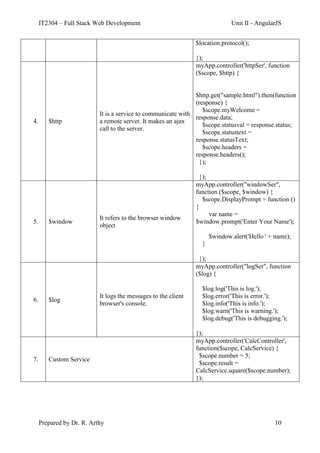
2023 – 2024 (ODD SEMESTER)
Year : III IT Course Code : IT2304
Faculty
Name
: Dr. R. Arthy, AP/IT Course Name : Full Stack Web Development
Course code
(as per
NBA)
: 21ITC304 Regulation : R2021
UNIT II – ANGULARJS
CHEAT SHEAT
Topic 1: Modules and Dependency Injection
Modules
An AngularJS module defines an application.
The module is a container for the different parts of an application.
The module is a container for the application controllers.
Controllers always belong to a module.
Create a module named myModule1.
var appName = angular.module(“myModule1”,[])
Defining a Controller and using it:
var appName = angular.module(“myModule1”,[]);
appName.controller(“SampleController”,
function($scope,){
//Members to be used in view for binding
$scope.city=”Hyderabad”;
});
In the view:
<div ng-controller=”SampleController”>
<!-- Template of the view with binding expressions using members of $scope -->
<div>{{city}}</div>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/angularjs-231202084435-f3cd86d1/85/ANGULARJS-pdf-1-320.jpg)
![IT2304 – Full Stack Web Development Unit II - AngularJS
Prepared by Dr. R. Arthy 2
</div>
Dependency Injection:
AngularJS has a built-in dependency injector that keeps track of all components
(services, values, etc.) and returns instances of needed components using dependency
injection. Angular‟s dependency injector works based on names of the components.
AngularJS provides following core components which can be injected into each other
as dependencies.
o Value
o Factory
o Service
o Provider
o Constant
A simple case of dependency injection:
myModule.controller(“MyController”, function($scope,
$window, myService){
});
Here, $scope, $window and myService are passed into the controller through
dependency injection.
Defining a Service:
var appName = angular.module(“myModule1”,[]);
appName.service(“sampleService”, function(){
var svc = this;
var cities=[“New Delhi”, “Mumbai”, “Kolkata”, “Chennai”];
svc.addCity = function(city){
cities.push(city);
};
svc.getCities = function(){
return cities;
}
});
Factory:
A factory is a function that returns an object](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/angularjs-231202084435-f3cd86d1/85/ANGULARJS-pdf-2-320.jpg)
![IT2304 – Full Stack Web Development Unit II - AngularJS
Prepared by Dr. R. Arthy 3
var appName = angular.module(“myModule1”,[]);
appName.factory(“sampleFactory”, function(){
var cities = [“New Delhi”, “Mumbai”, “Kolkata”, “Chennai”];
function addCity(city){
cities.push(city);
}
function getCities(){
return cities;
}
return{
getCities: getCities,
addCity:addCity
};
});
Value:
angular.module(“myModule”).value(“sampleValue”, {
cities : [“New Delhi”, “Mumbai”, “Kolkata”, “Chennai”],
addCity: function(city){
cities.push(city);
},
getCities: function(){
return cities;
}
});
A value is a simple JavaScript object.
It is created just once, so value is also a singleton.
All members of a value are public.
Constant:
angular.module(“myModule”).
constant(“sampleConstant”,{pi: Math.PI});
A constant is also like a value.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/angularjs-231202084435-f3cd86d1/85/ANGULARJS-pdf-3-320.jpg)
![IT2304 – Full Stack Web Development Unit II - AngularJS
Prepared by Dr. R. Arthy 4
Topic 2: Scope as a Data Model
The scope is the binding part between the HTML (view) and the JavaScript
(controller).
The scope is an object with the available properties and methods.
The scope is available for both the view and the controller.
<script>
var app = angular.module('myApp', []);
app.controller('myCtrl', function($scope) {
$scope.carname = "Volvo";
});
Root Scope
All applications have a $rootScope which is the scope created on the HTML element
that contains the ng-app directive.
The rootScope is available in the entire application.
If a variable has the same name in both the current scope and in the rootScope, the
application uses the one in the current scope.
Script
var app = angular.module("m1", []);
app.controller("c1", function($scope, $rootScope){
$scope.name = "Arthy";
$rootScope.msg1 = "Hello ";
});
app.controller("c2", function($scope, $rootScope){
$scope.name1 = "R.Arthy";
});
View
<body ng-app = "m1">
<div ng-controller = "c1">
<h3> Message {{msg1}} is a root scope </h3>
Name in C1 = {{name}}
{{msg1}} {{name}}
<br/>
</div><hr>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/angularjs-231202084435-f3cd86d1/85/ANGULARJS-pdf-4-320.jpg)
![IT2304 – Full Stack Web Development Unit II - AngularJS
Prepared by Dr. R. Arthy 5
<div ng-controller = "c2">
<h3> Name in c1 is a scope of c1 </h3>
Name in C2 = {{name1}}
{{msg1}} {{name}}
<br/>
</div>
</body>
Output:
Hello is displayed in root scope and scope
Topic 3: Directives
S. No. Directives Description Example
1. ng-app To bootstrap the application
<body ng-app = "myDirectives">
</body>
2. ng-controller To set a controller on a view
<div ng-controller = "c1">
</div>
3. ng-model
Enables two-way data binding on any
input controls and sends validity of
data in the input control to the
enclosing form
<input type = 'text' ng-model =
'order'/>
4. ng-init
Used to evaluate an expression in the
current scope
<body ng-app = "myDirectives"
ng-init = "foods = ['Idly',
'Dosa', 'Chappathi', 'Poori',
'Parota']”>
</body>
5. ng-bind
It binds the content of an html
element to application data.
<input type = 'text' ng-model =
'order' ng-change = "colour =
'red'">
<span style = "color: {{colour}}"](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/angularjs-231202084435-f3cd86d1/85/ANGULARJS-pdf-5-320.jpg)