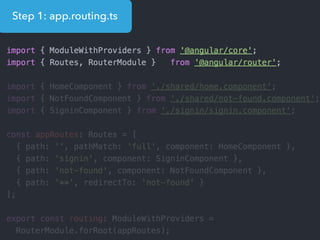
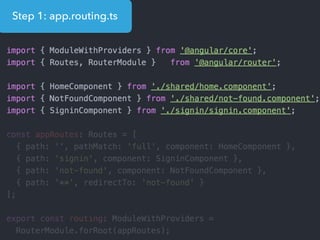
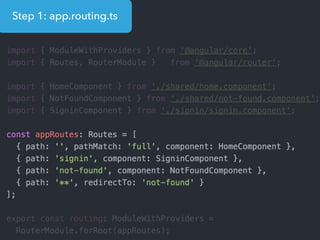
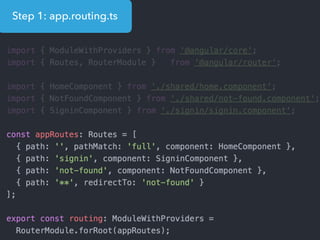
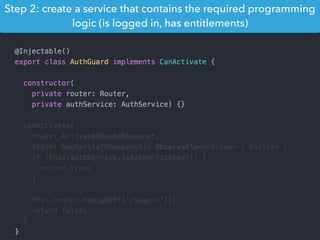
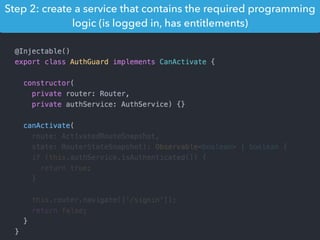
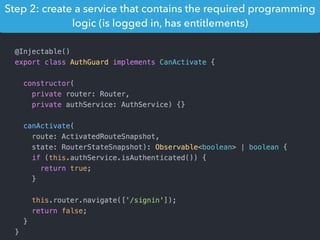
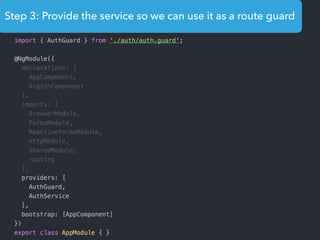
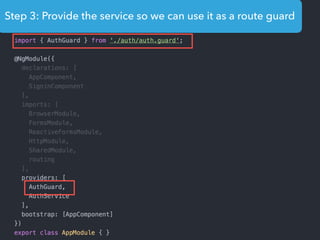
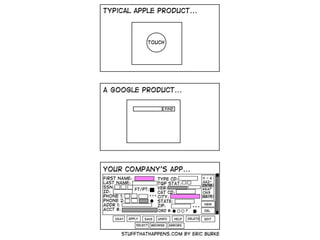
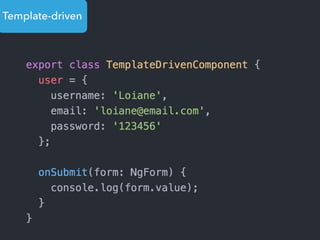
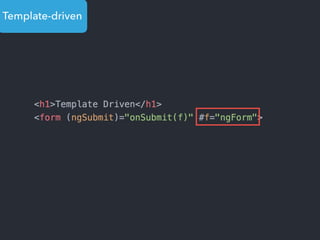
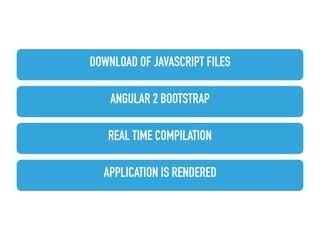
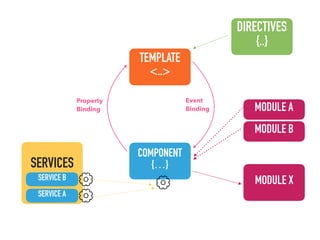
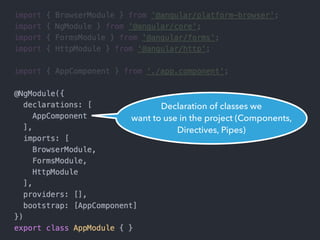
This document provides an overview of Angular 2 including:
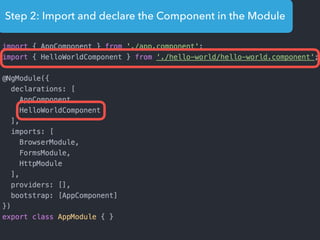
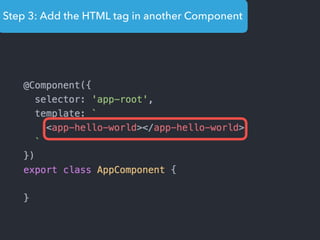
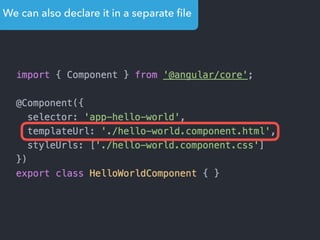
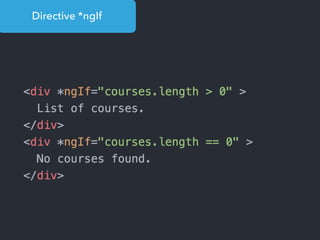
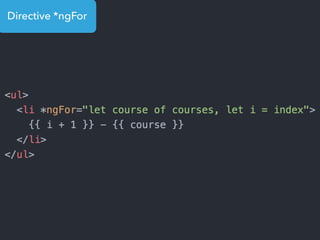
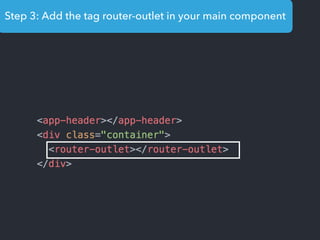
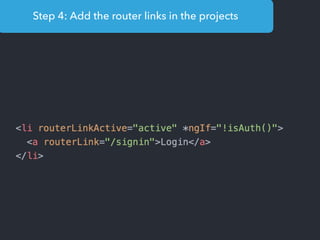
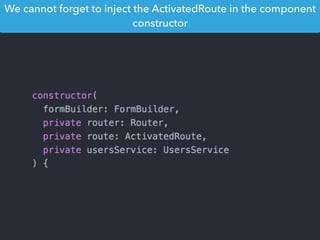
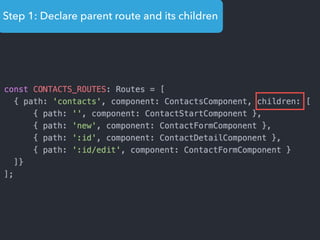
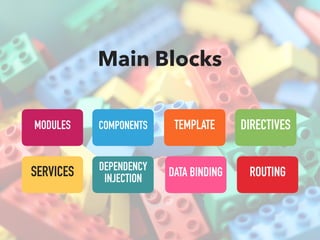
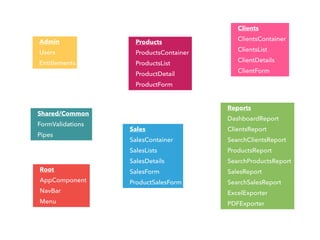
- Main blocks like components, directives, services, routing etc.
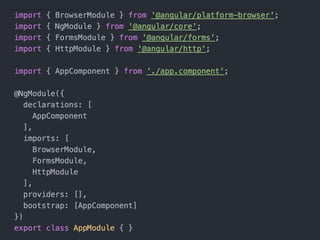
- How to set up a development environment with Node.js and TypeScript
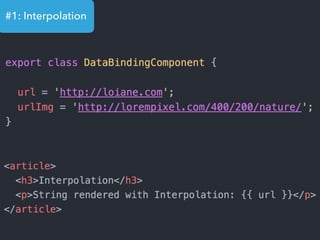
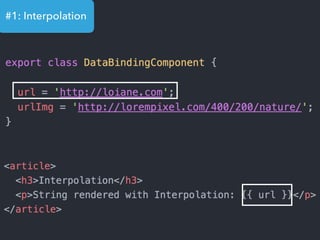
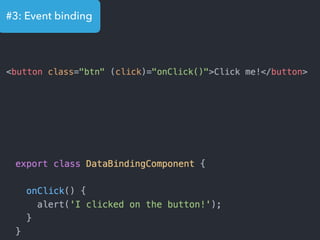
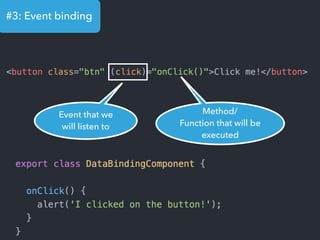
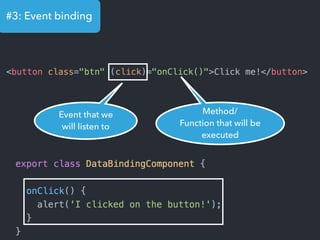
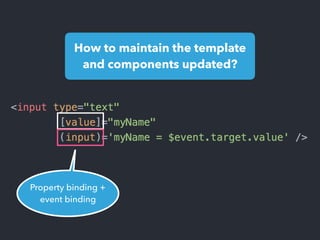
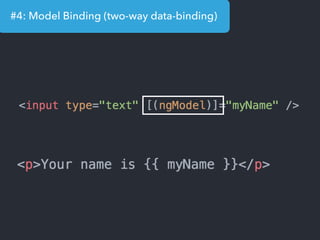
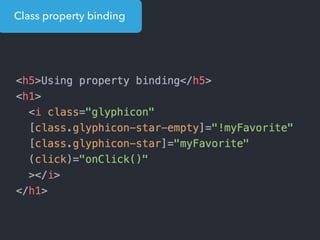
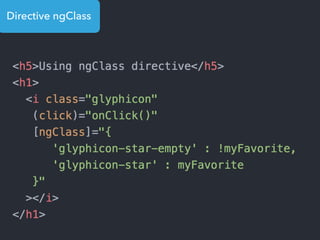
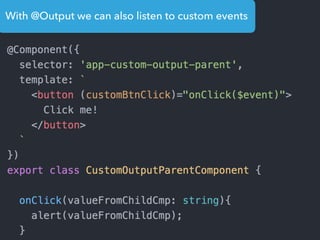
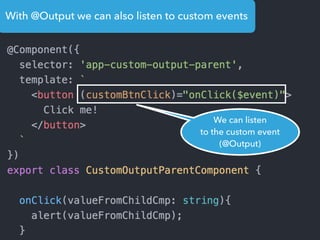
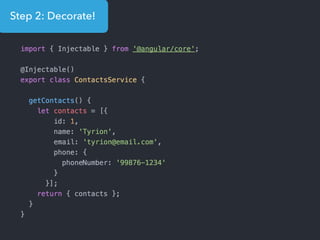
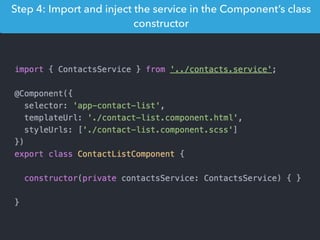
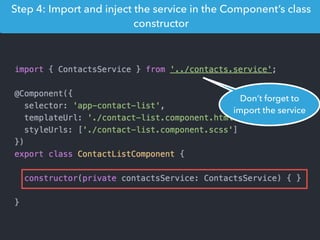
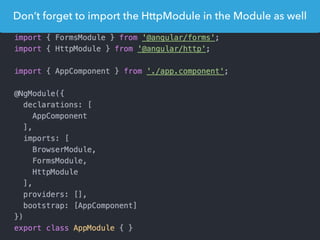
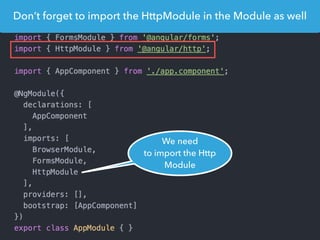
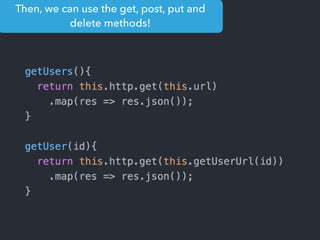
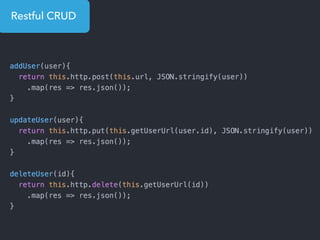
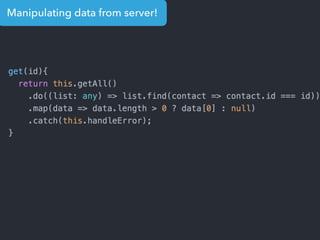
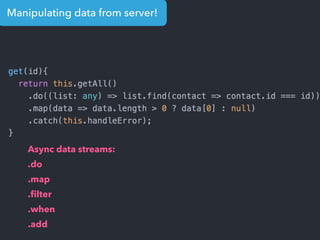
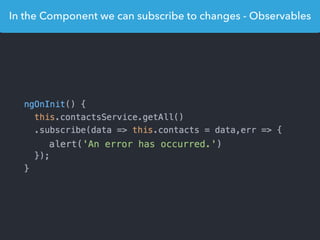
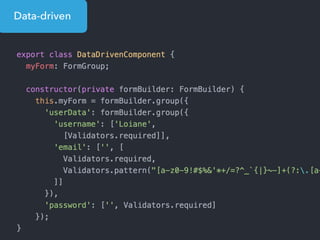
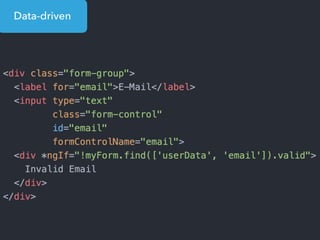
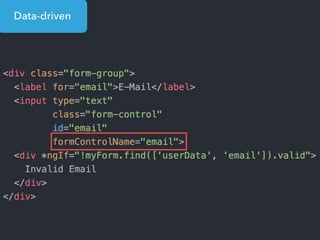
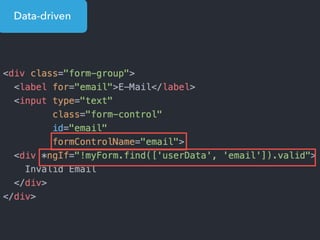
- Examples of core features like data binding, communication between components, dependency injection, and HTTP requests
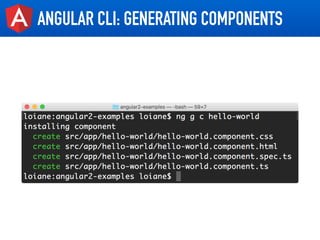
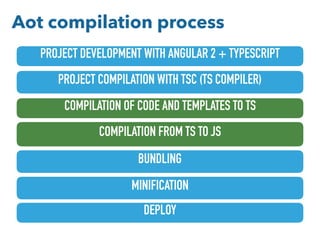
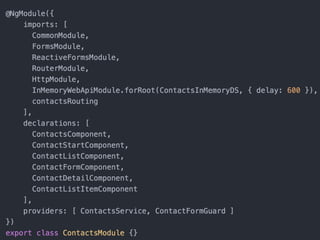
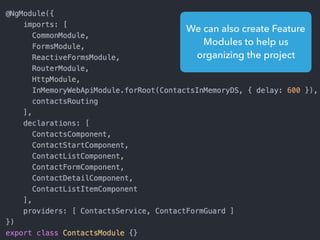
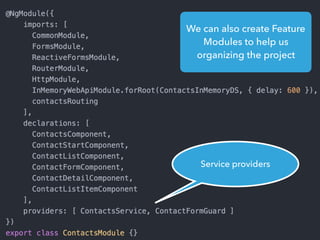
- Tips for organizing projects, lazy loading modules, ahead of time compilation, and using the Angular CLI











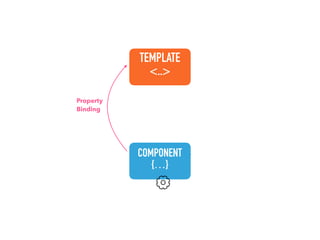
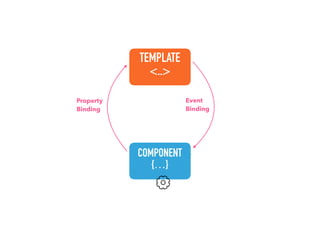
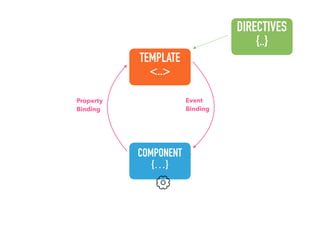
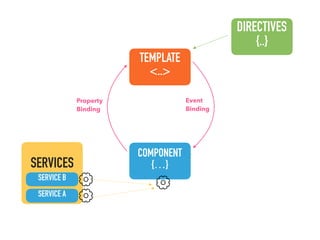




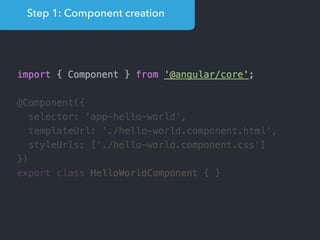
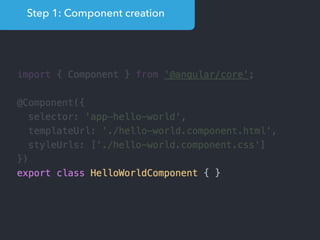

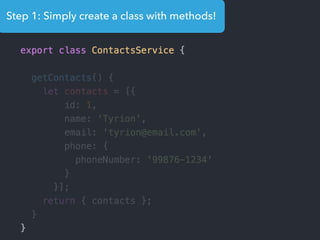
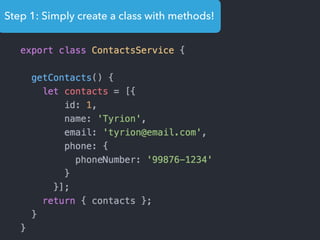
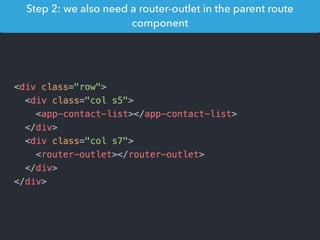
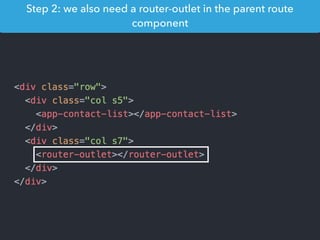
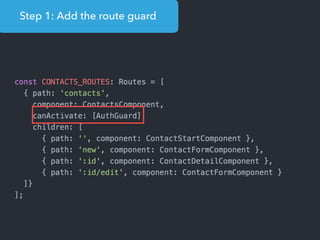
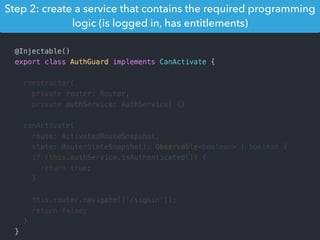
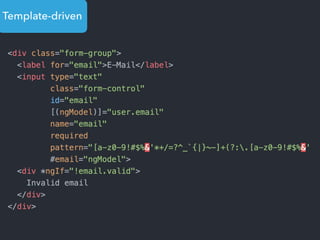
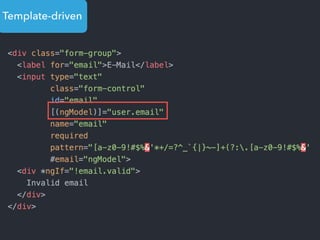
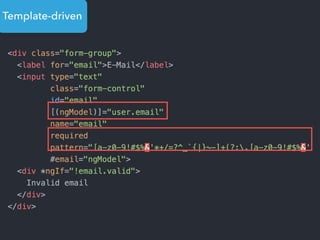
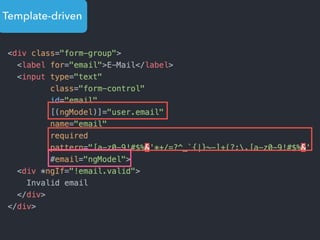
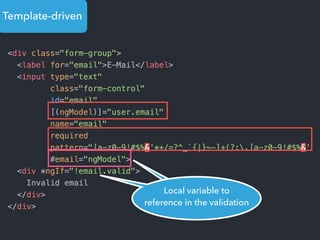
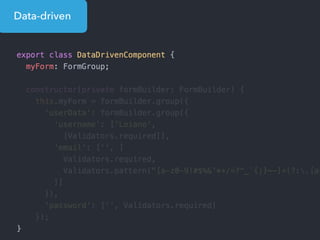
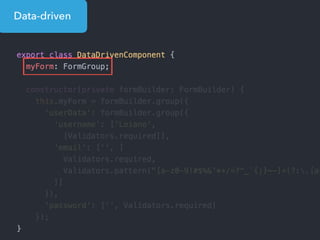
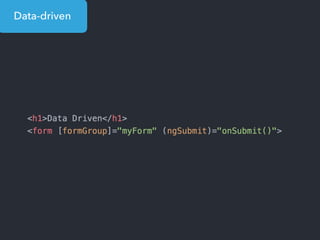
![Step 1: Component creation
[Web Components]
Name of the HTML tag for
this Component](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/angular2-60minutes-en-161214234046/85/Angular-2-overview-in-60-minutes-35-320.jpg)