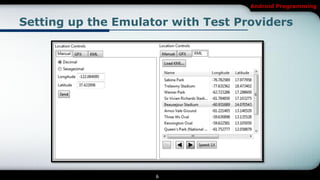
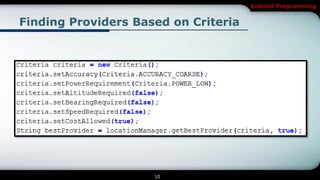
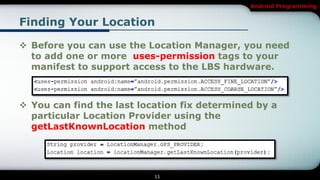
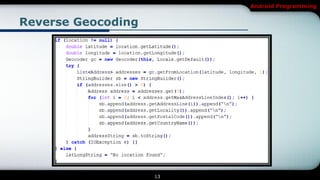
The document covers Android programming focused on maps, geocoding, and location-based services (LBS). It discusses key components like LocationManager, various location providers, and how to implement them in an Android app, including permissions for accessing hardware. It also details geocoding methods and how to create a map-based activity using MapView and MapActivity.