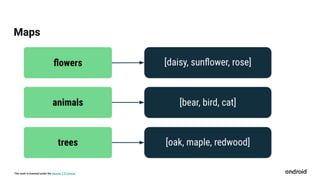
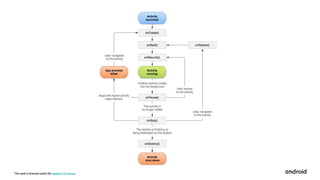
This document outlines the curriculum for an Android development course using Android Studio, covering topics like Kotlin programming, app design, user input, navigation, and data handling. Participants will learn to create apps including a birthday card, dice roller, and tip calculator, while understanding collections and activity lifecycles. The course includes badges for achievements and requires basic computer skills and access to a computer with internet and optionally an Android device.