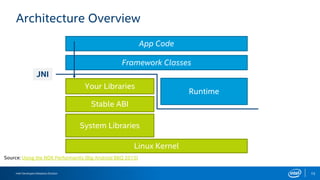
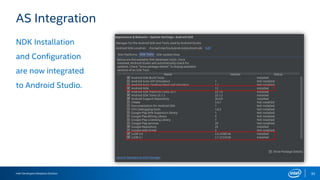
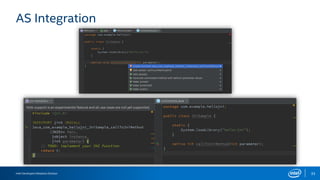
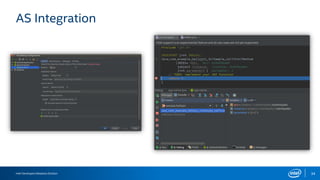
The document discusses the Android Native Development Kit (NDK) and its benefits for integrating native code in applications, especially for performance-intensive tasks like game engines and computer vision. It outlines the usability, common barriers for adoption, and best practices for utilizing the NDK, including the integration with Android Studio and Gradle. The document also highlights some limitations and the necessary precautions when using NDK in development.




























![Intel Developers Relations Division 39
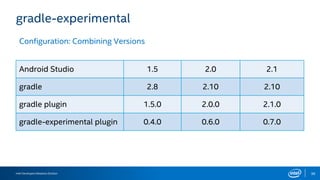
gradle-experimental
Configuration: multiple apks.
apply plugin: 'com.android.model.application'
model {
}
def actualVersionCode = 13;
// … gradle stuff
// … other gradle stuff
def baseVersionCode = 1000000;
def versionCodeABIPrefixes = [
'armeabi':1, 'armeabi-v7a':2, 'arm64-v8a':3,
'mips': 5,'mips64': 6,
'x86': 8, 'x86_64': 9];
def calculateVersionCodeFor = { String abi ->
return versionCodeABIPrefixes.get(abi, 0) *
baseVersionCode + actualVersionCode
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/entrando-no-mundo-nativo-com-android-ndkenus-160509124316/85/Android-ndk-Entering-the-native-world-37-320.jpg)








