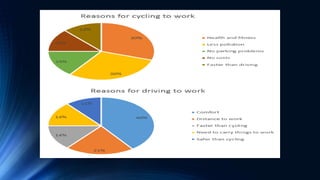
This document contains two pie charts comparing reasons why people in the UK travel to work by bicycle versus car. The highest percentages of cyclists do so because it is healthier than driving and causes less pollution. In contrast, the largest group of drivers prefer the comfort of a car. Overall, most cyclists cite health and environmental benefits, while car commuters value comfort over longer distances.