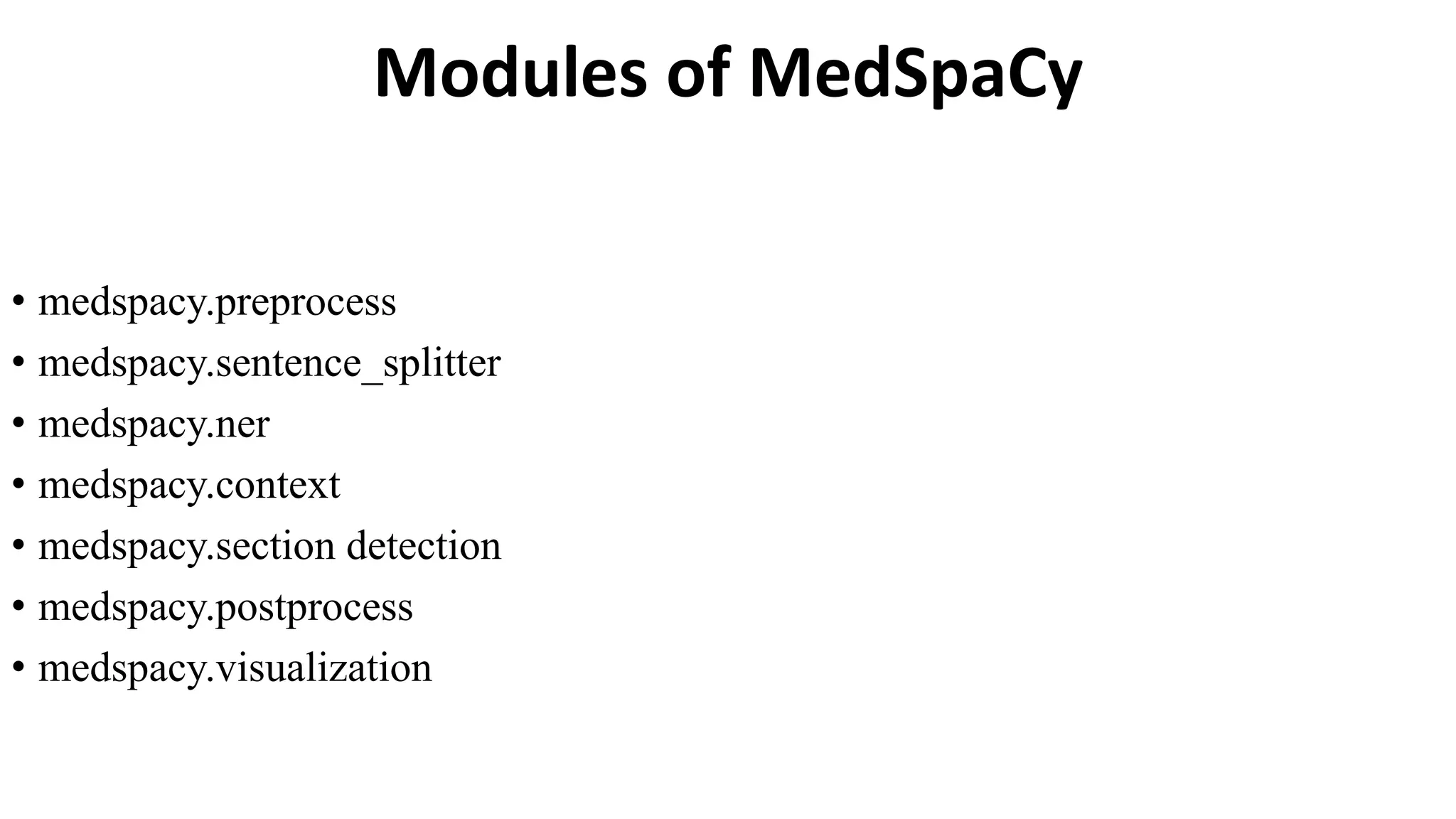
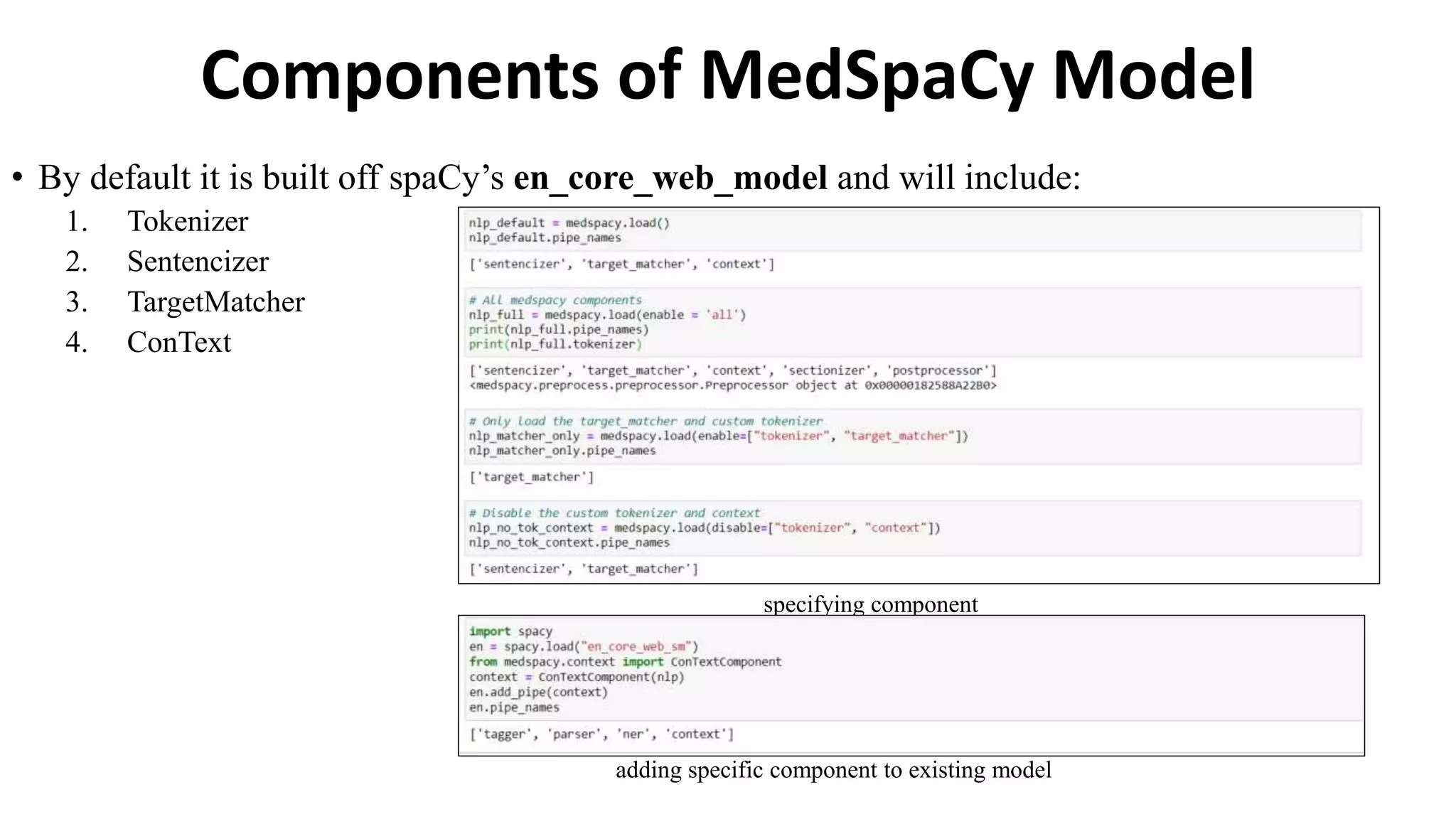
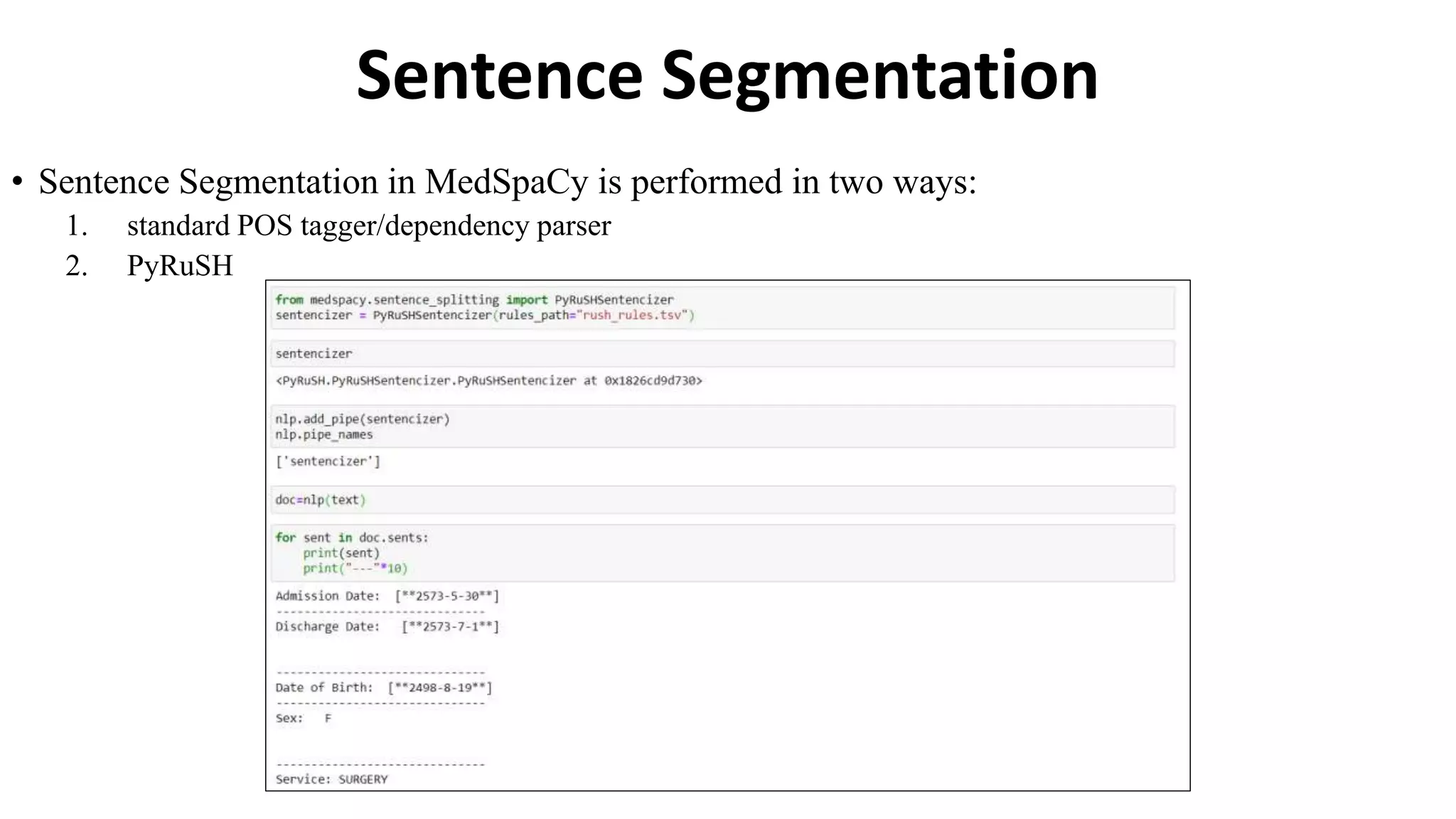
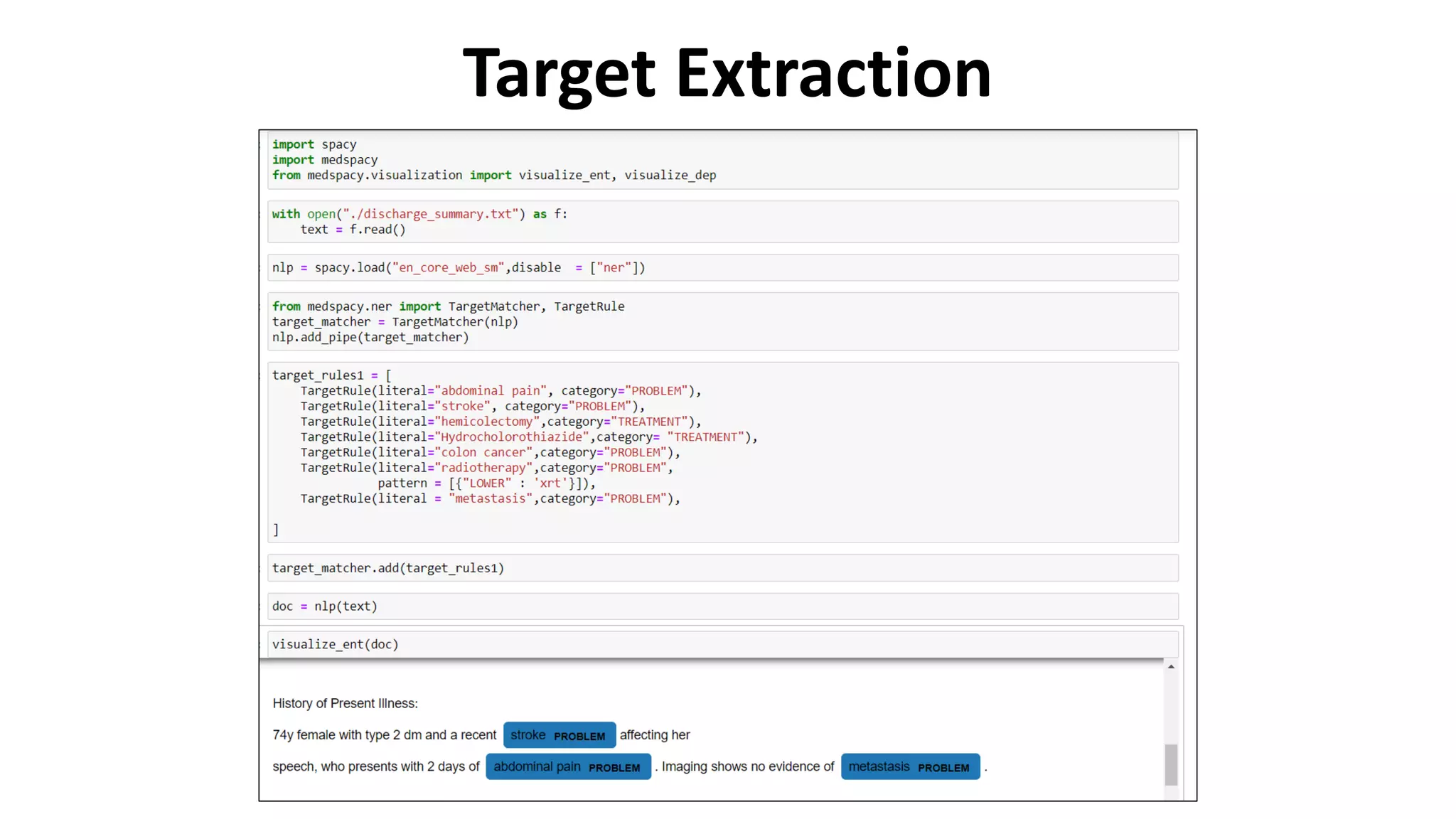
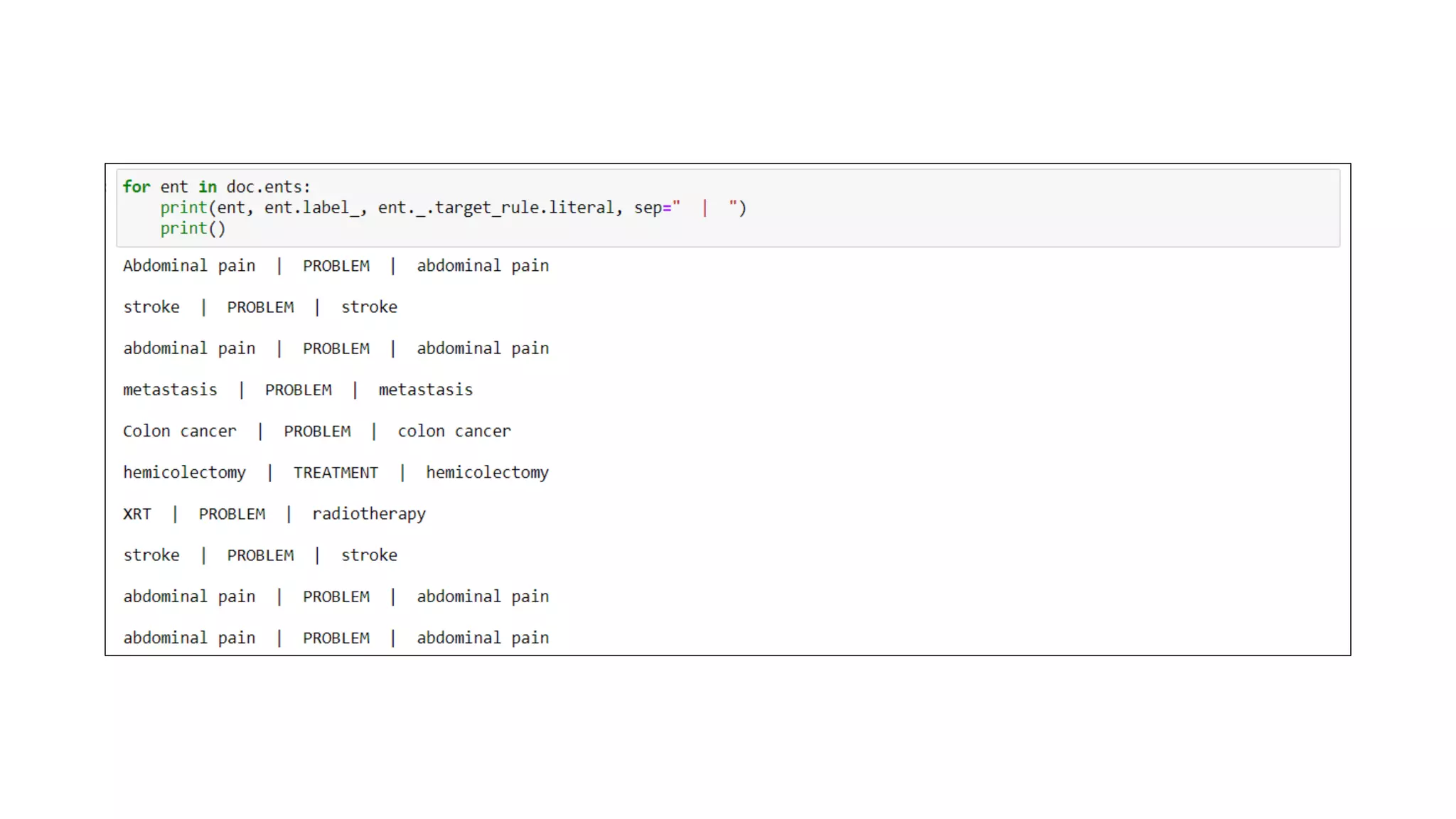
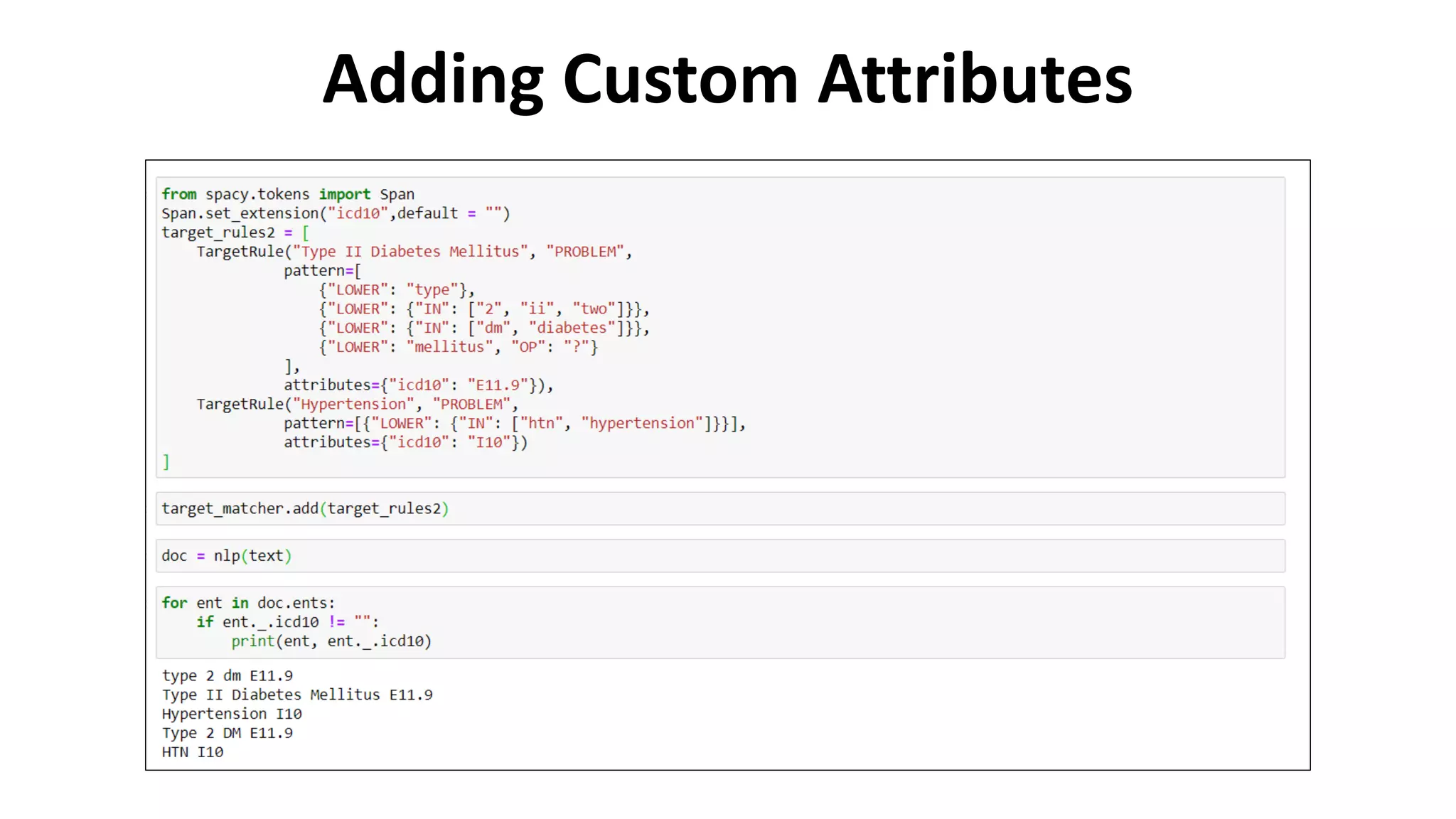
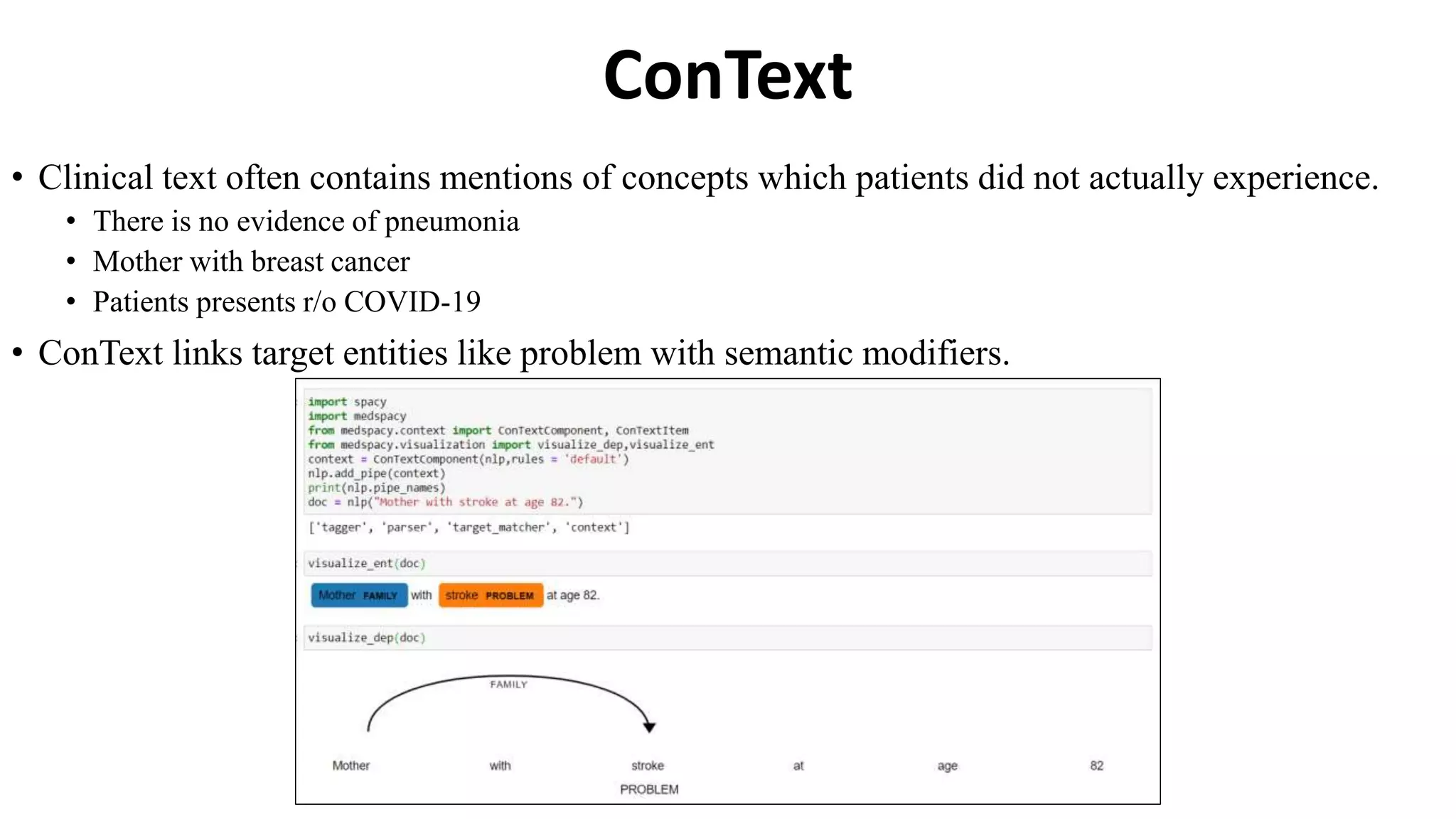
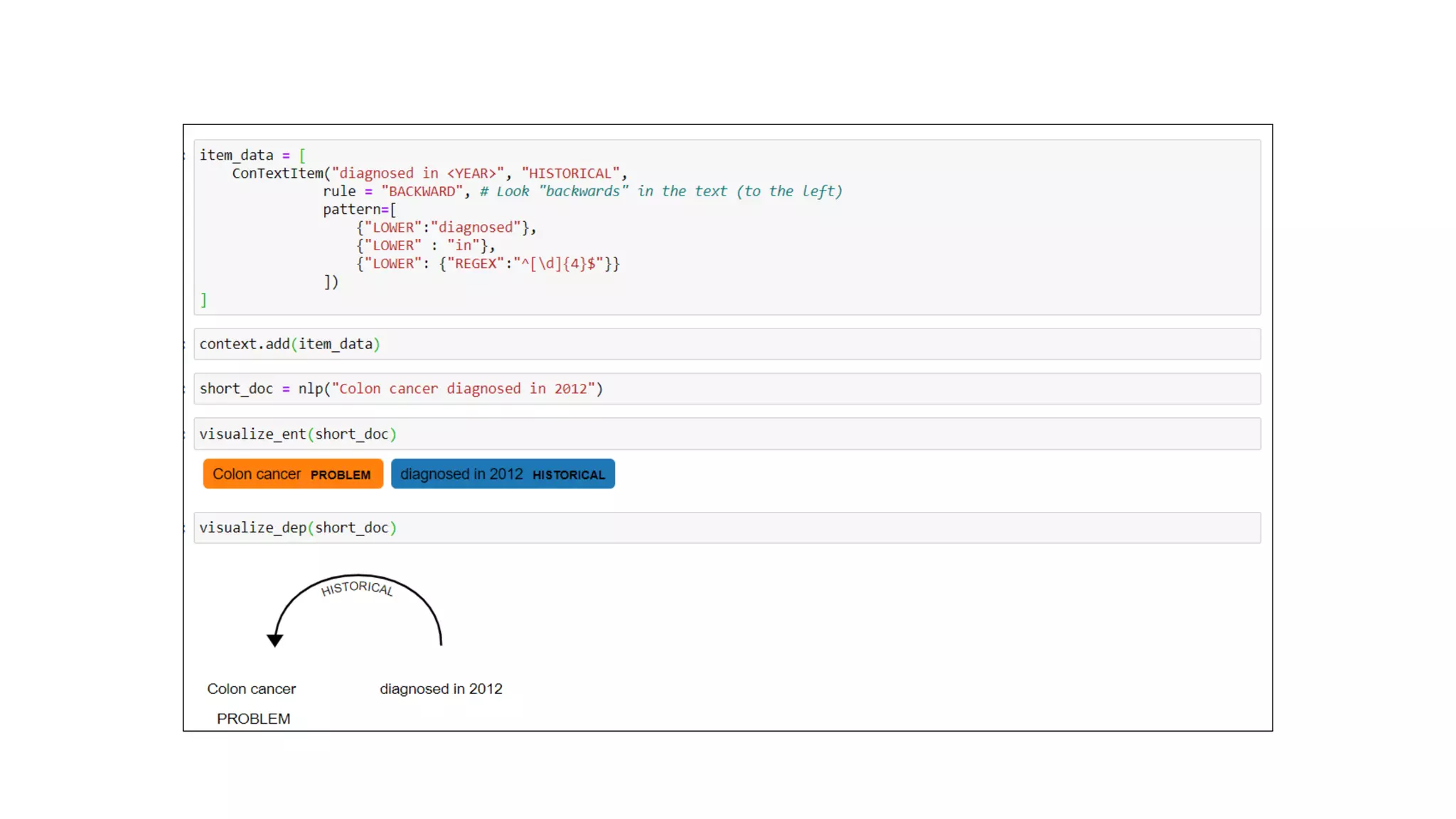
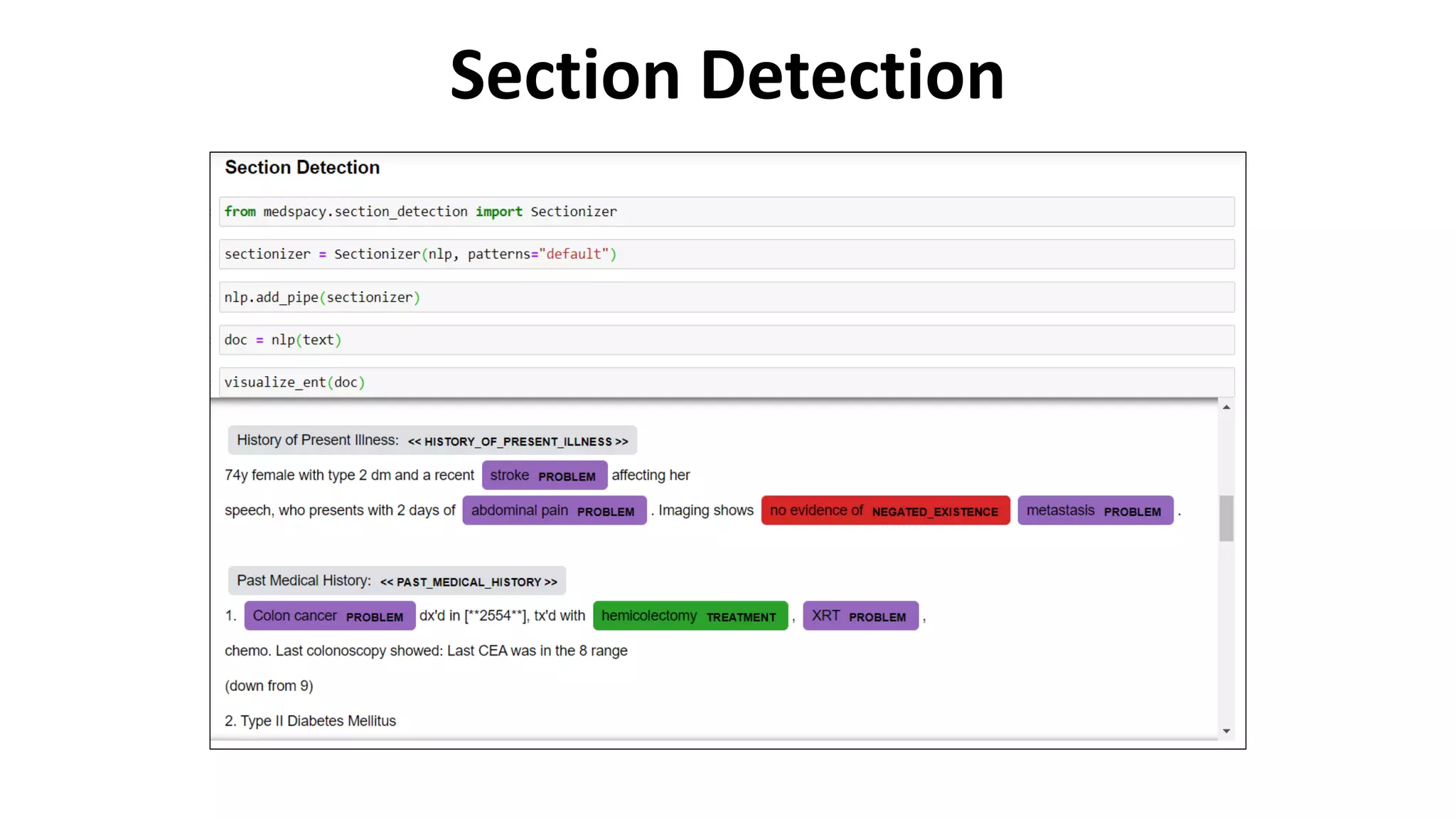
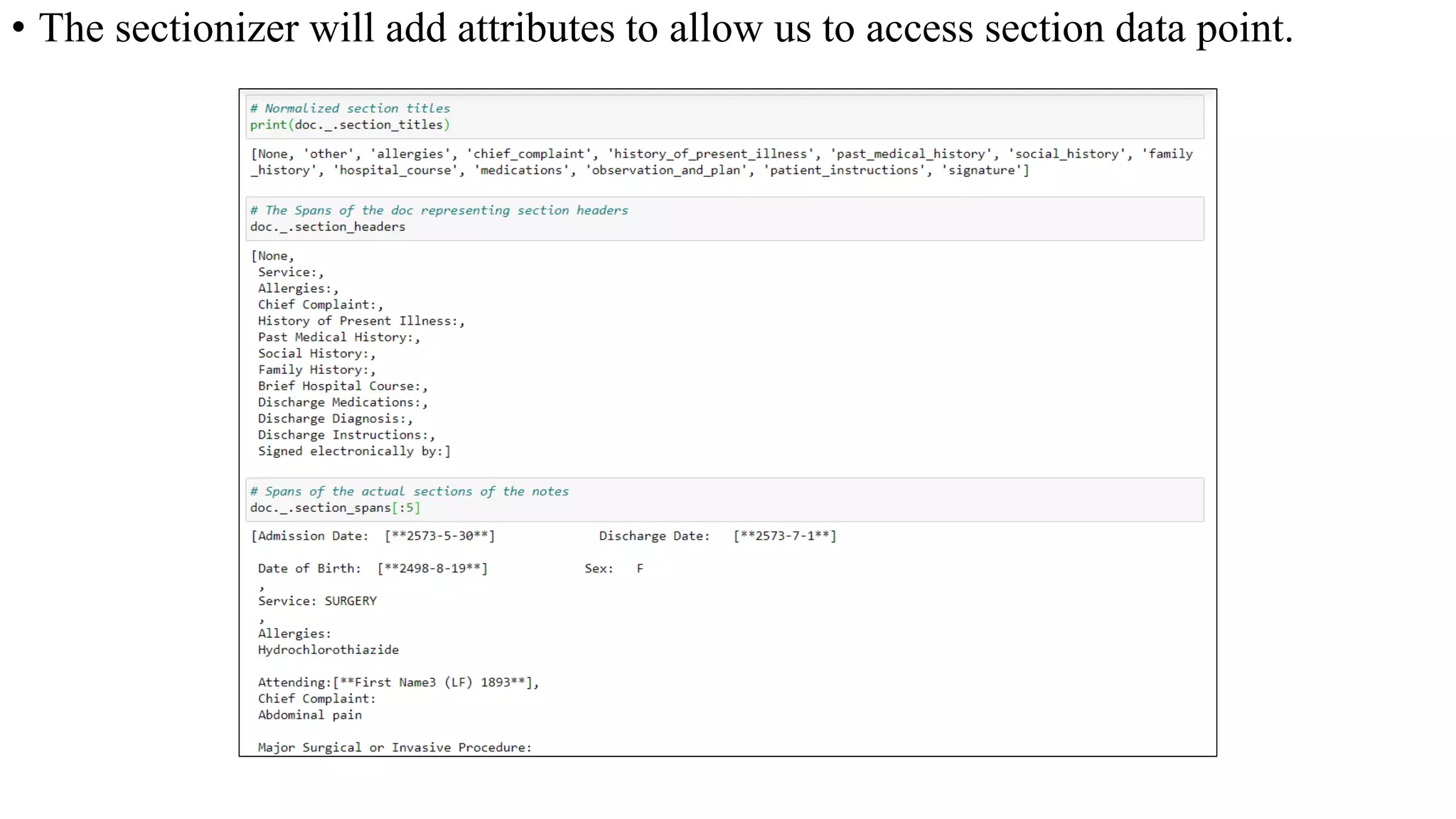
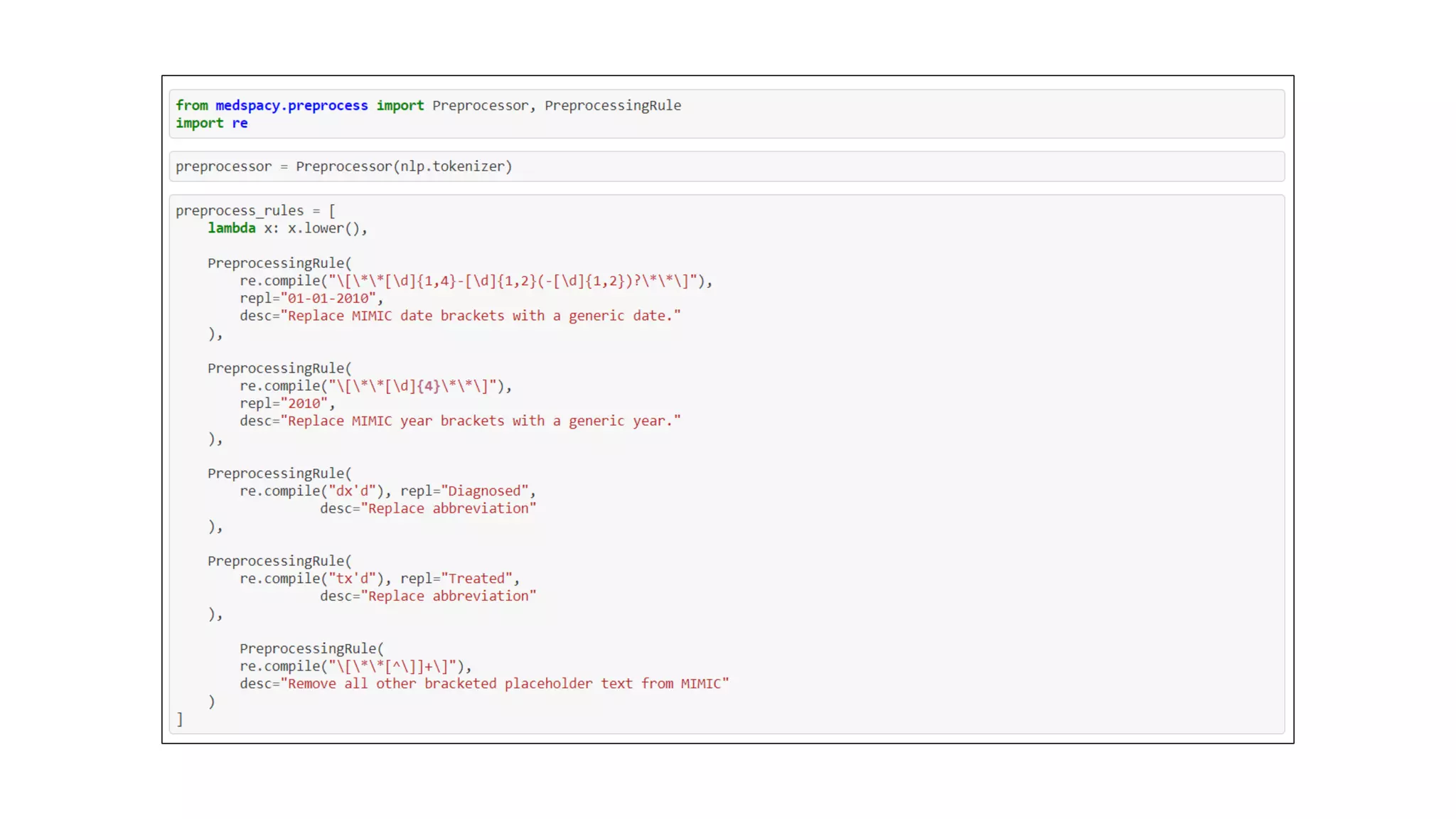
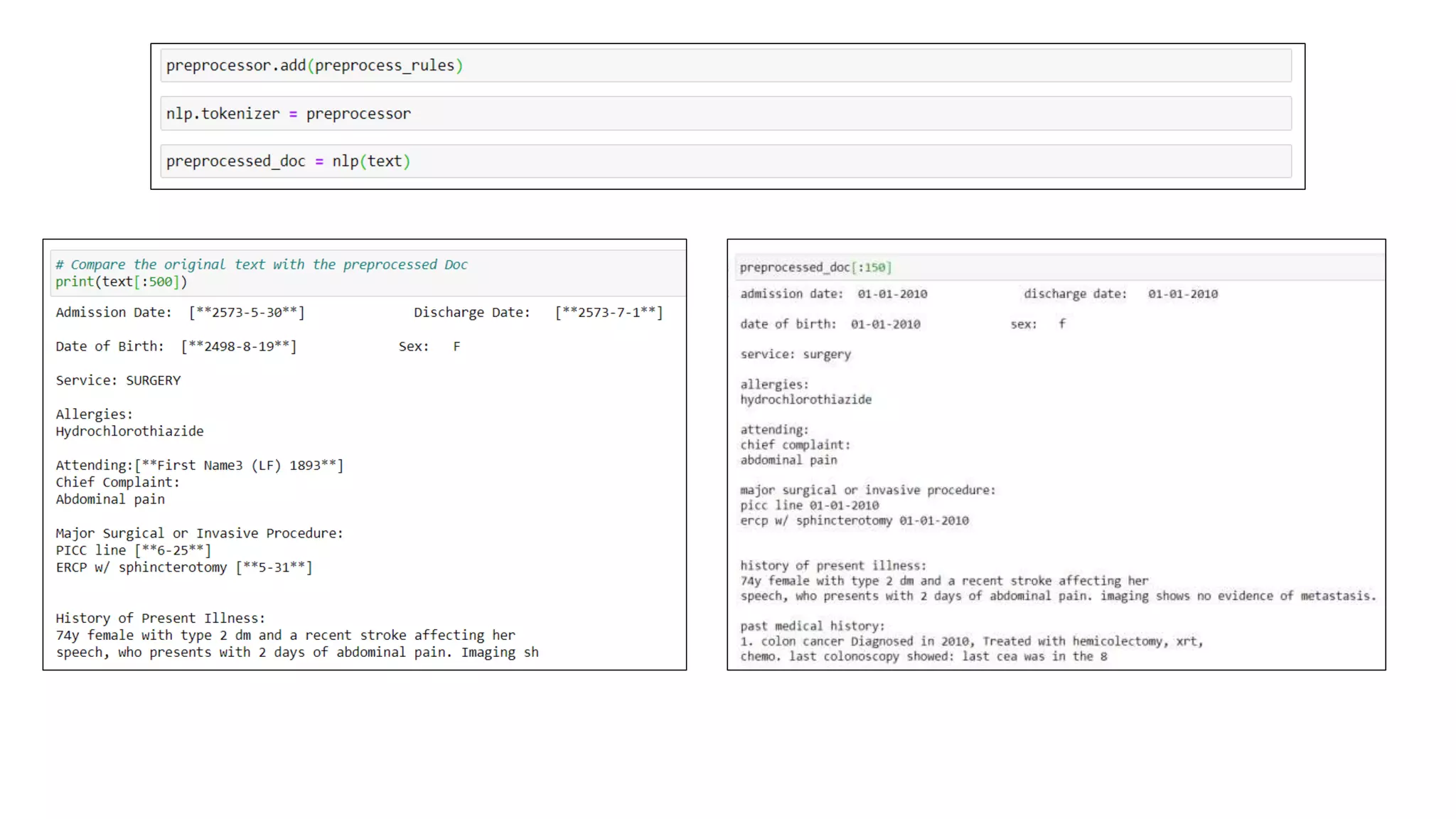
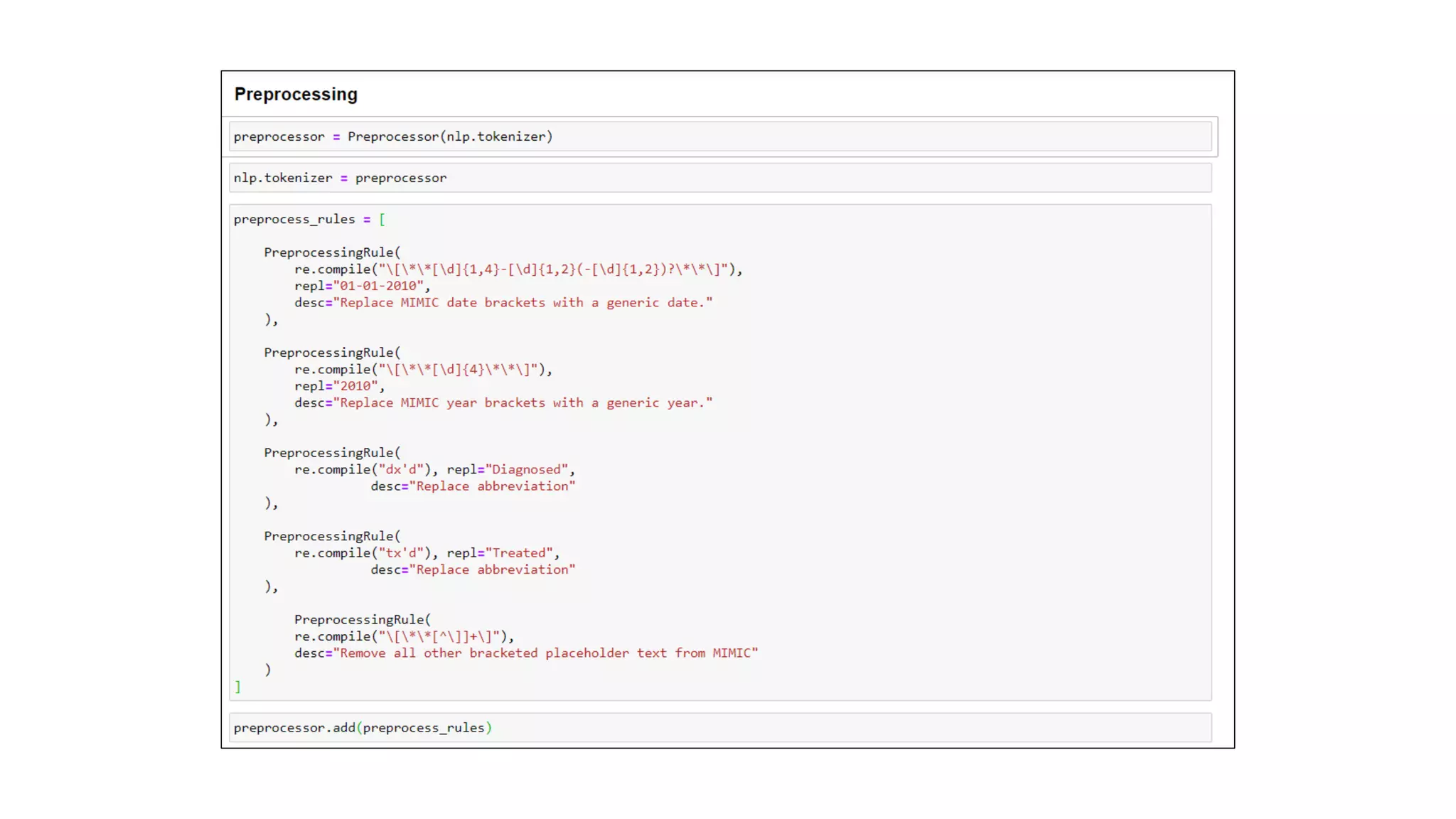
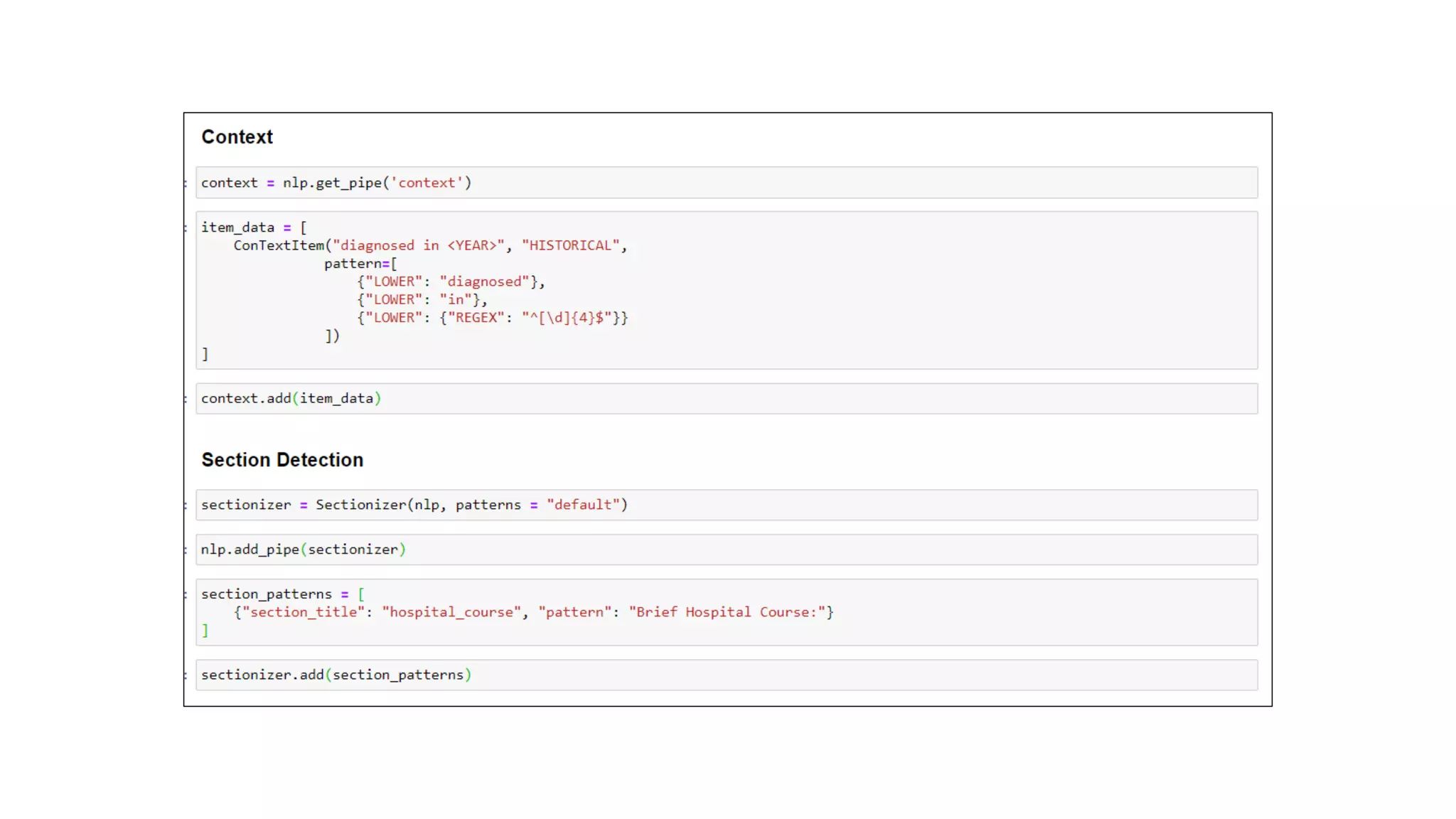
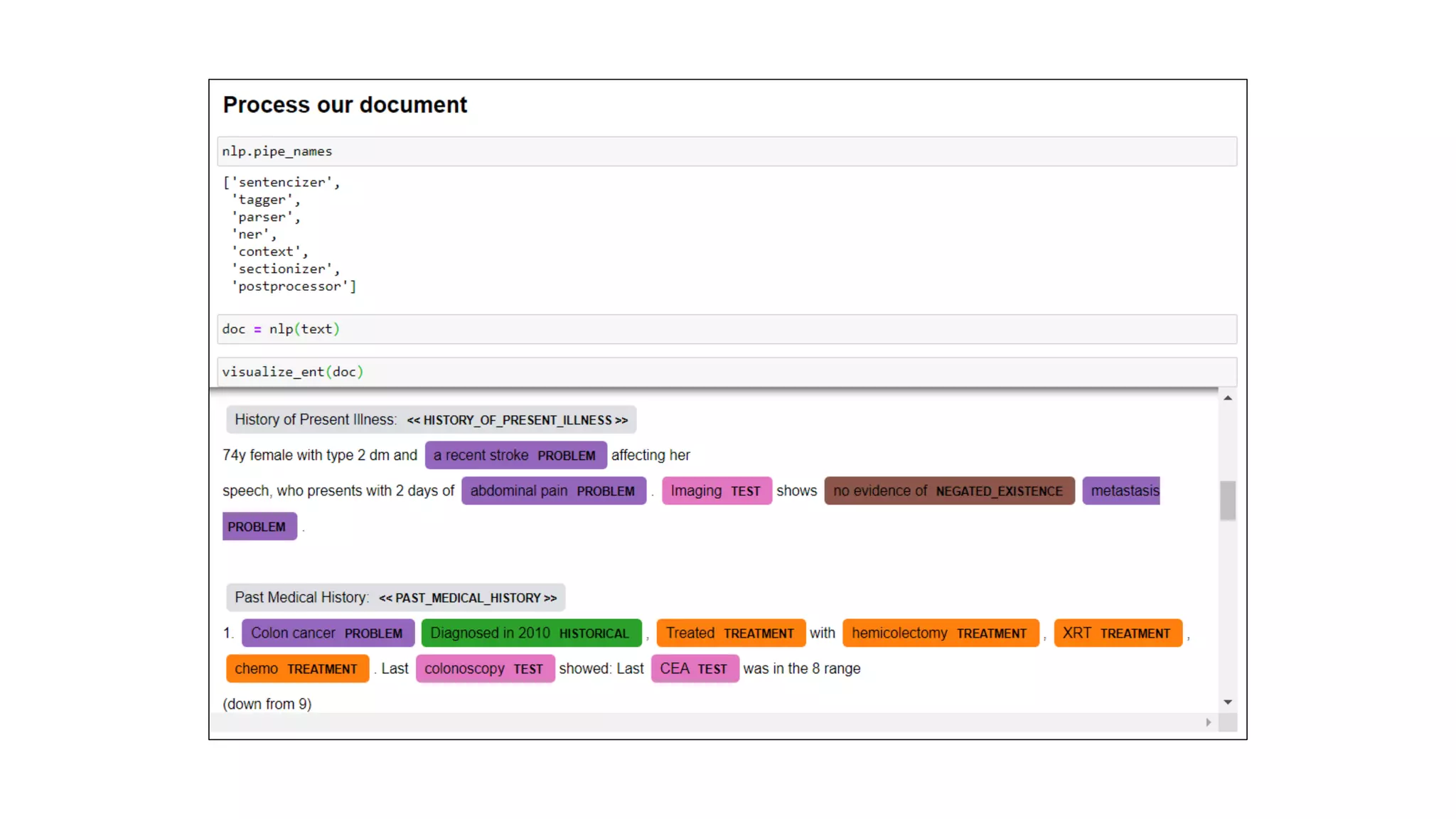
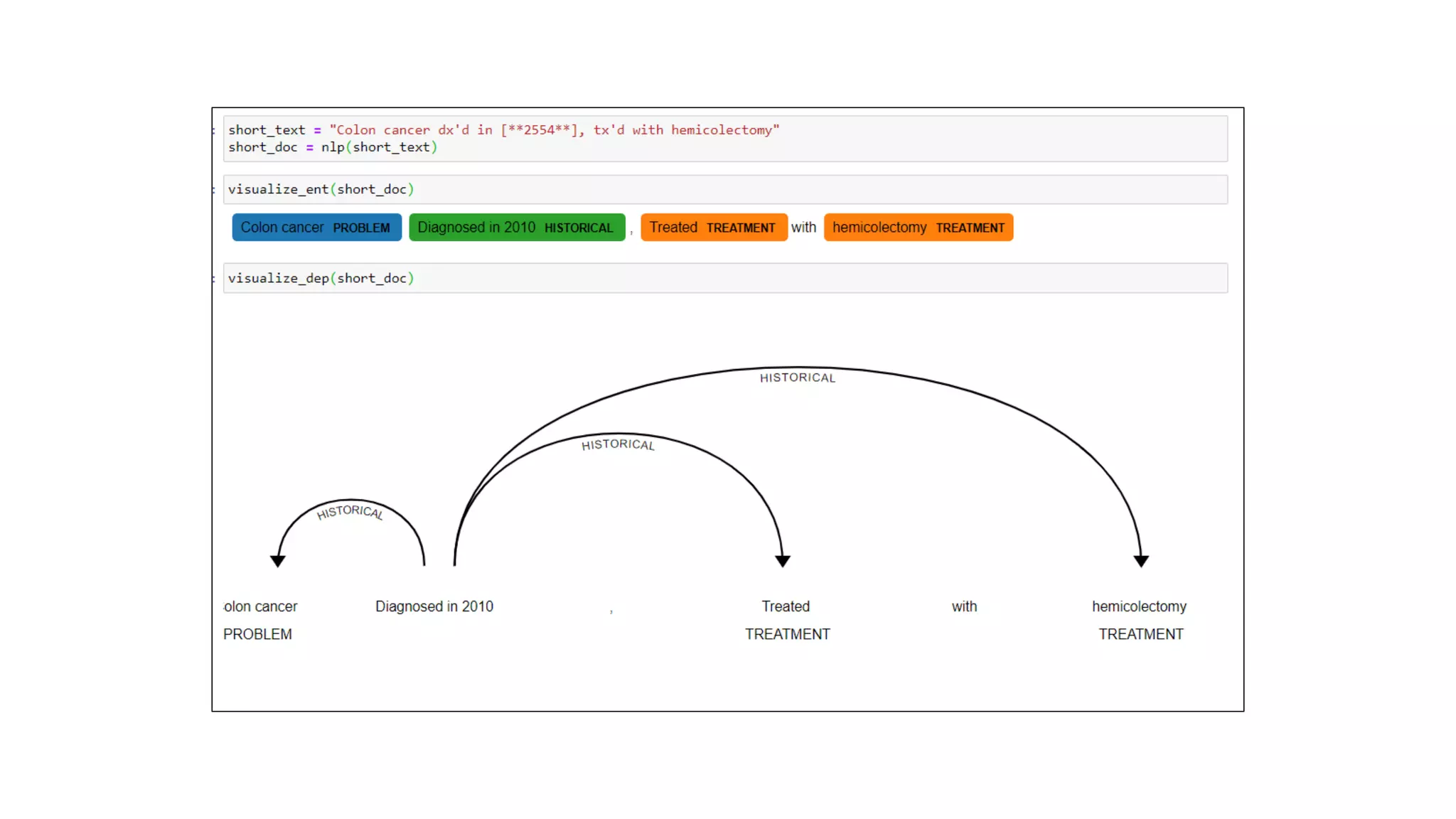
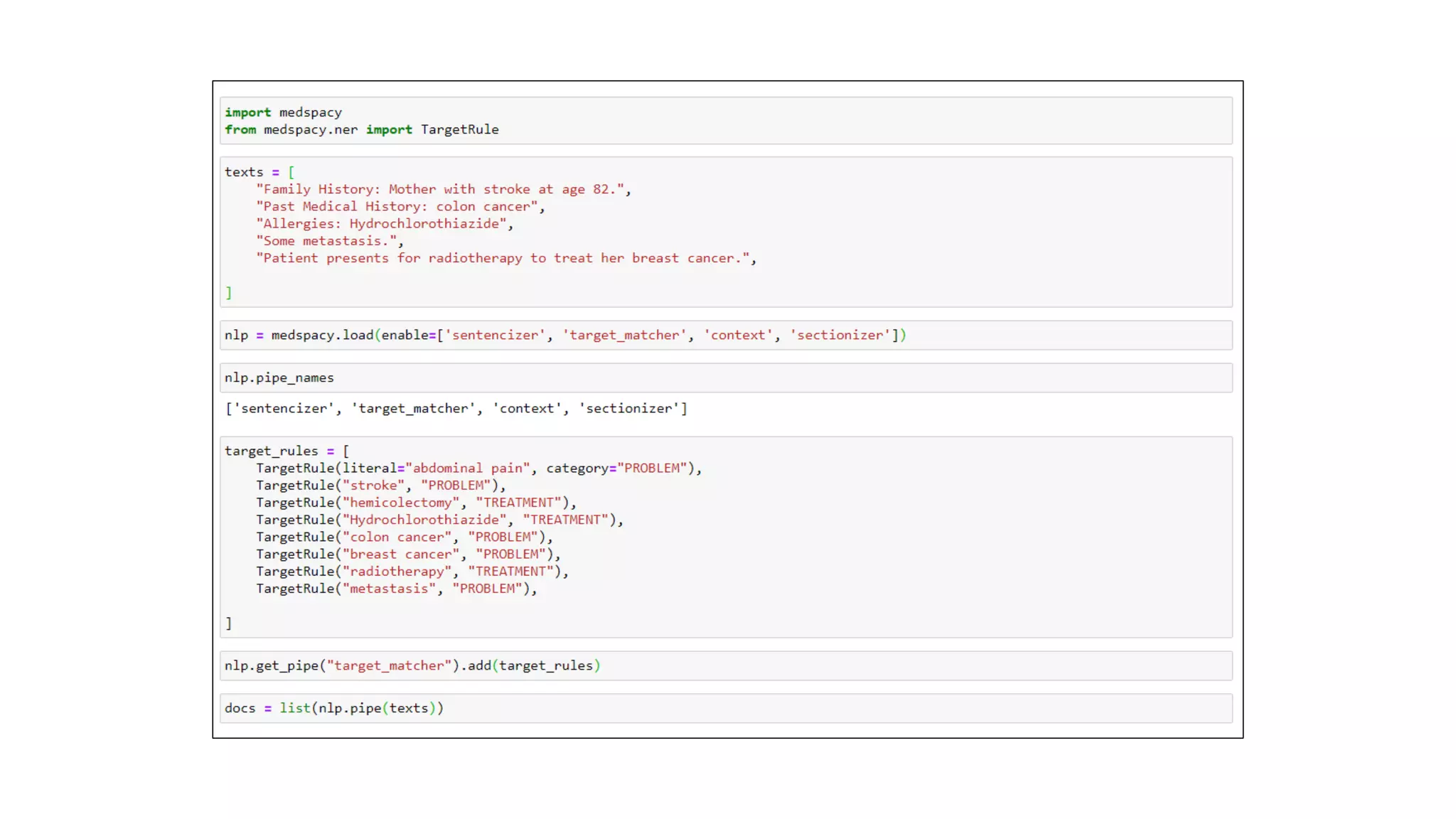
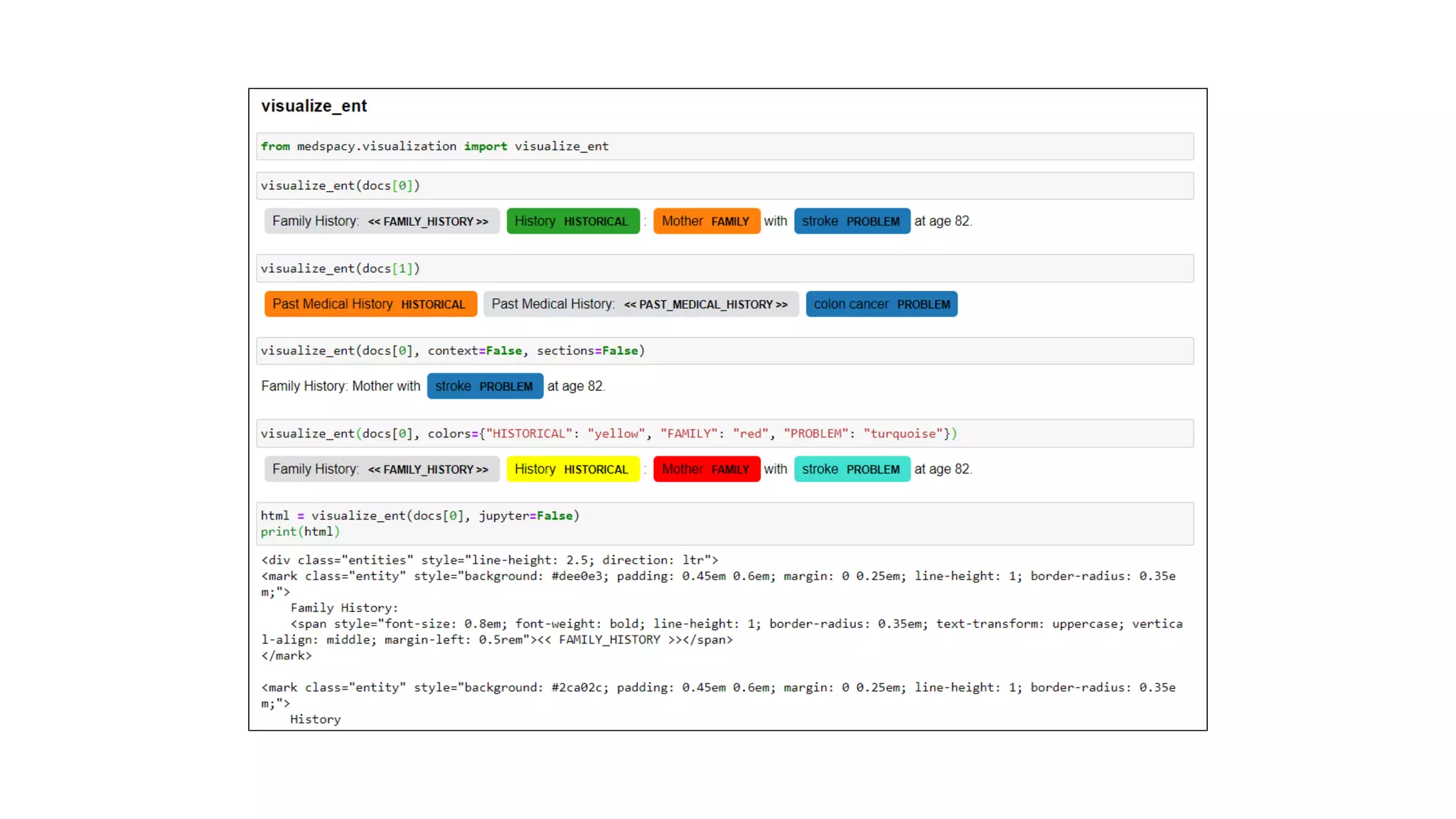
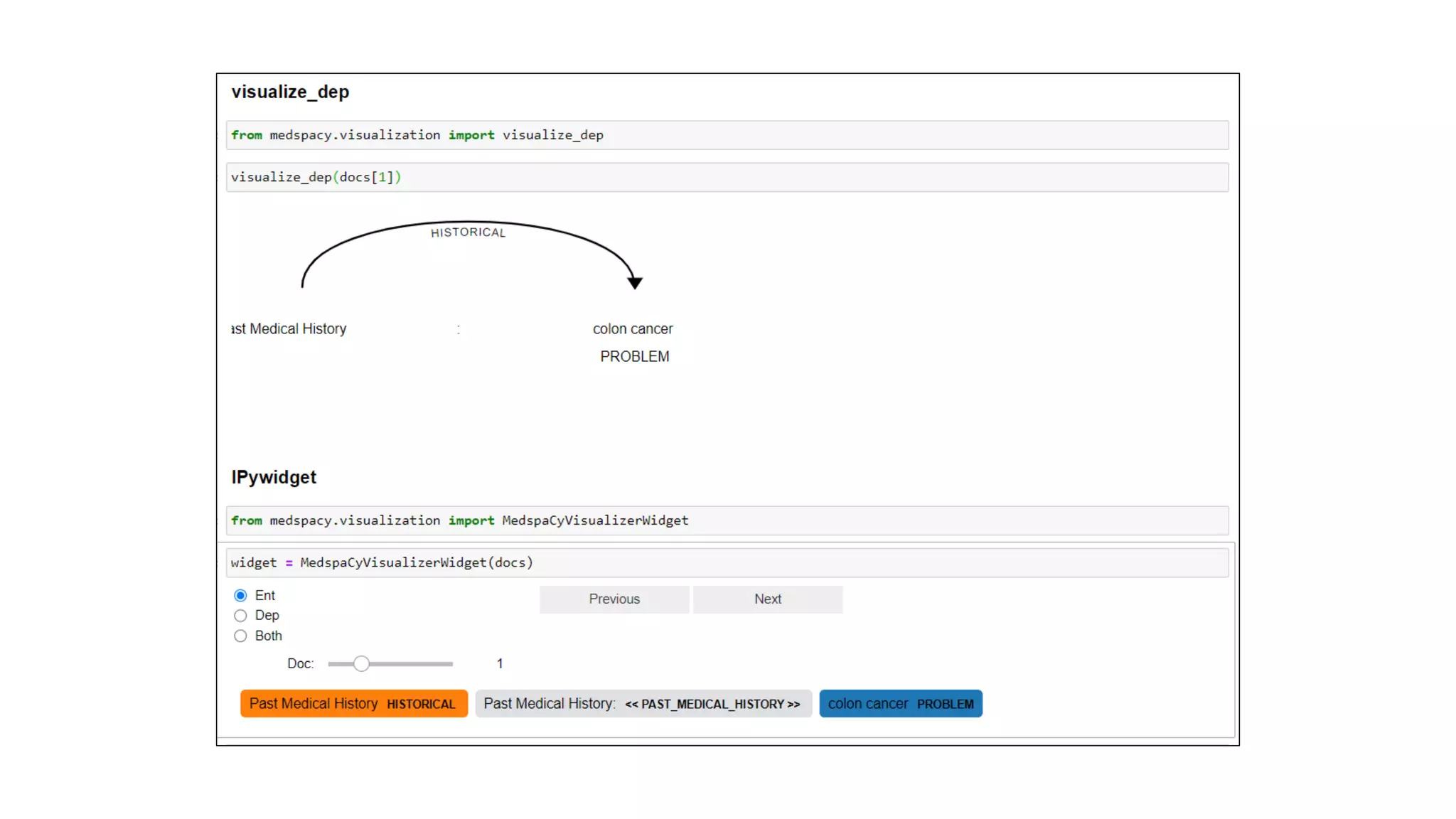
MedSpacy is a library designed for clinical NLP and text processing, integrating various modules for tasks like sentence segmentation and contextual analysis. It features a custom tokenizer and components such as section detection and preprocessing rules to handle the peculiarities of clinical language. The library also includes visualization tools to analyze the outputs of NLP models.