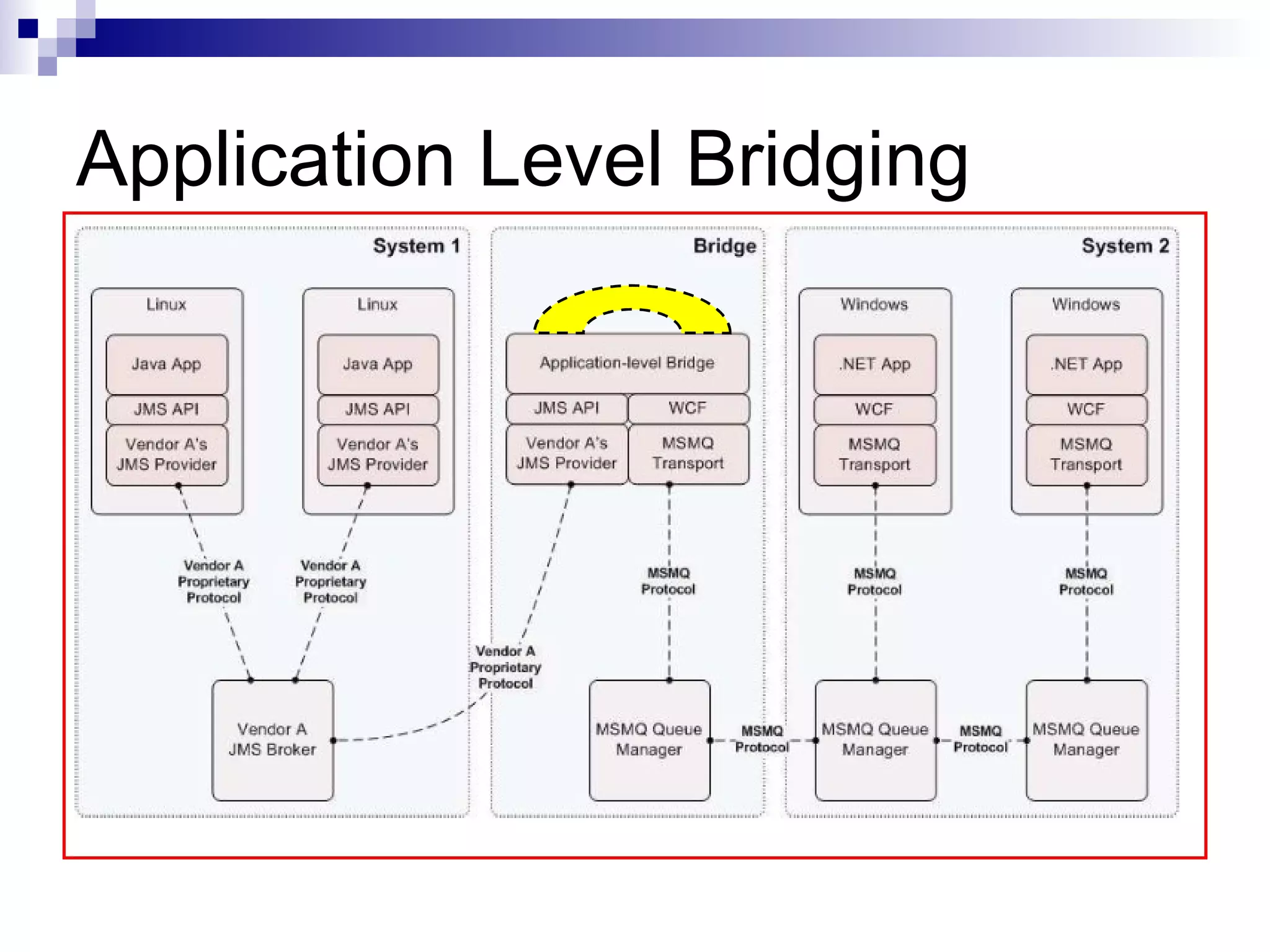
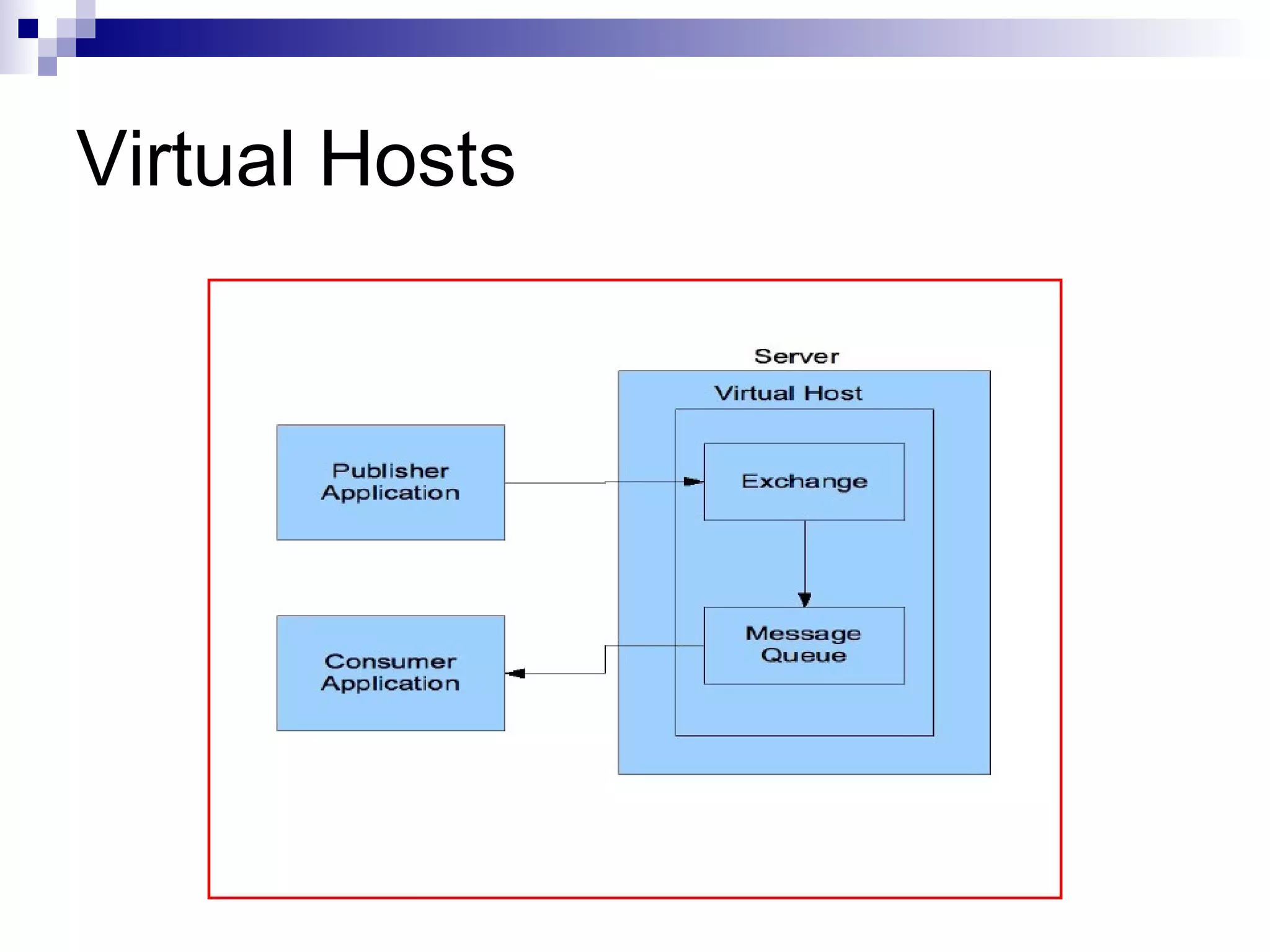
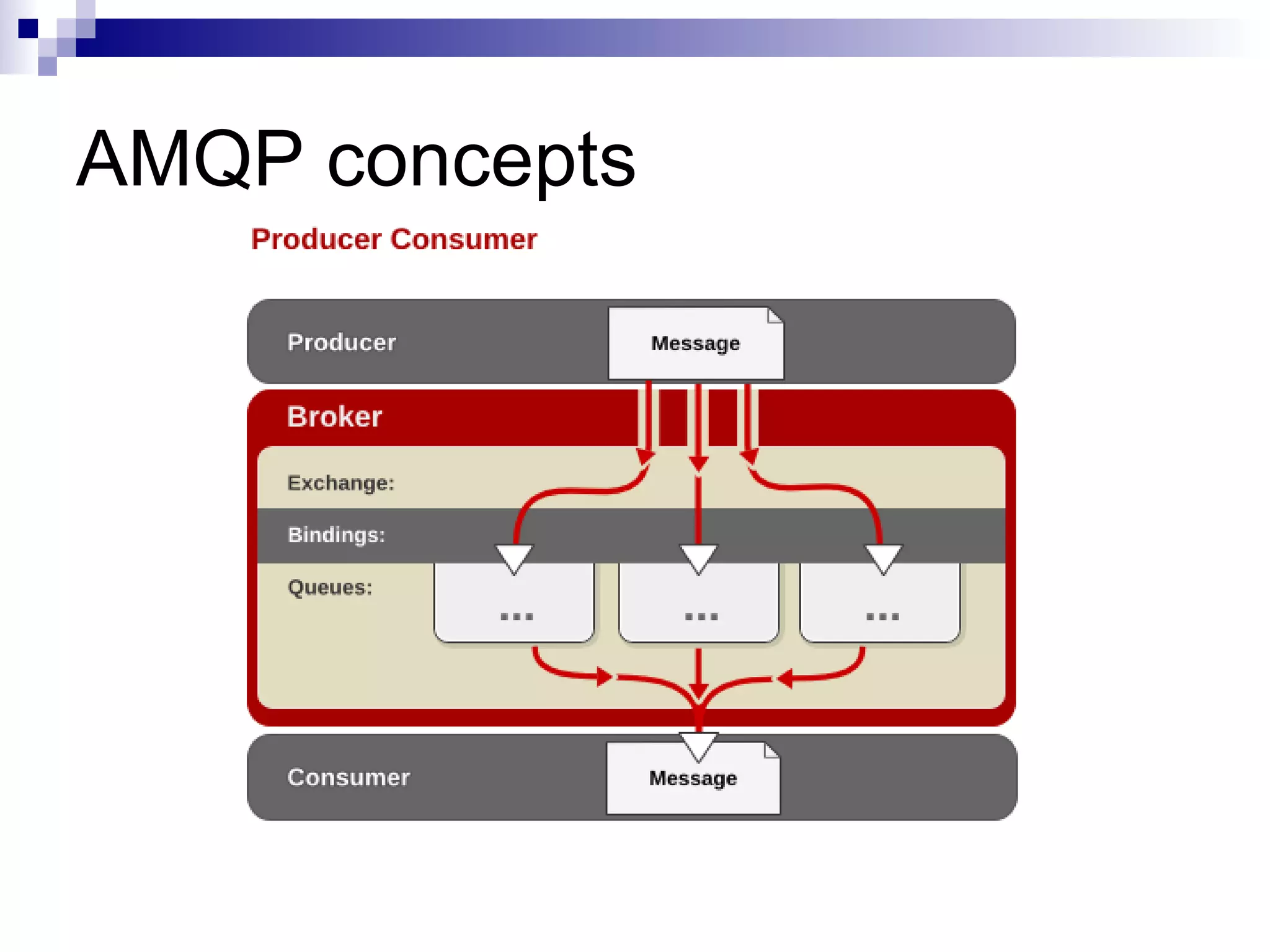
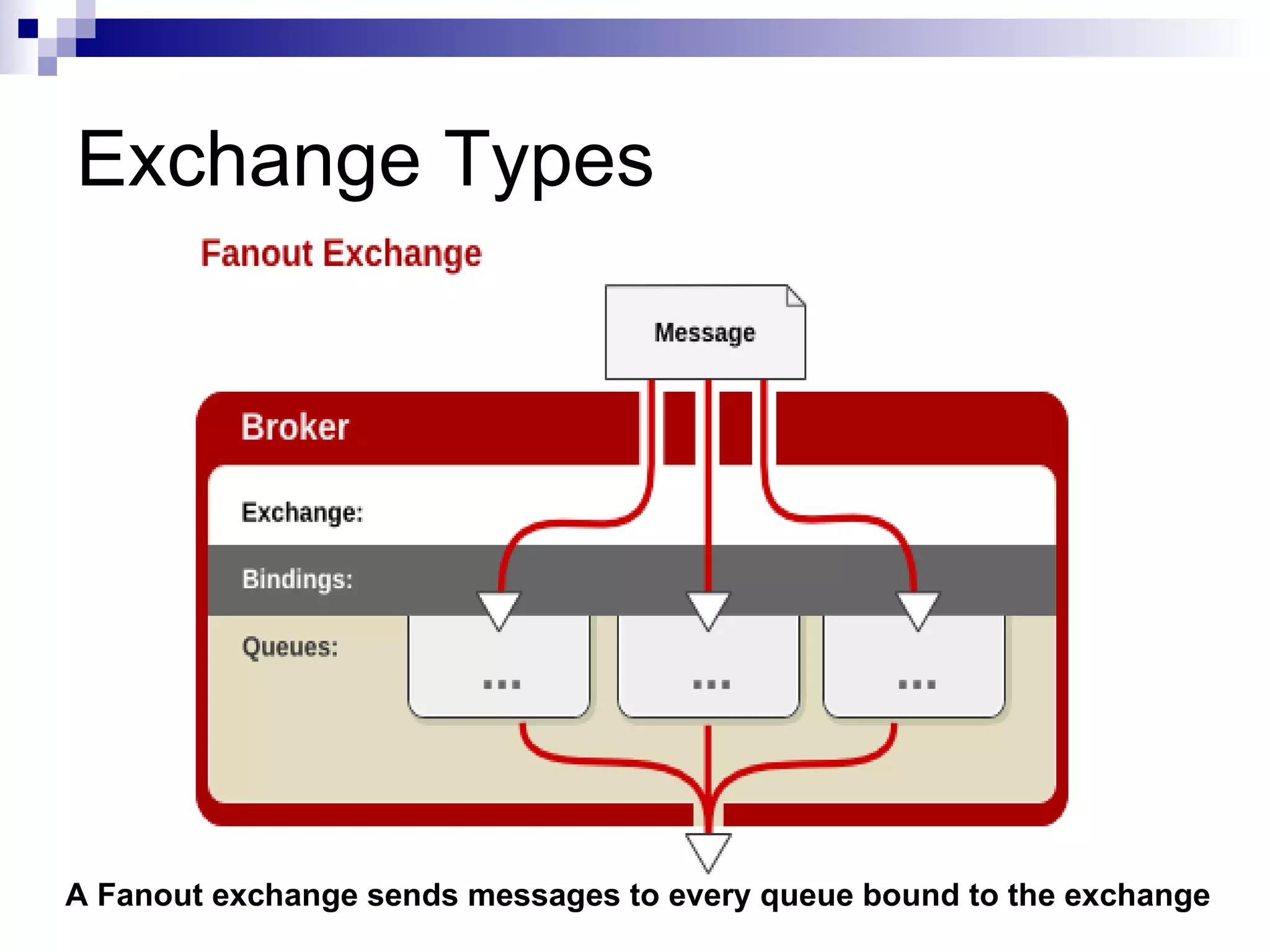
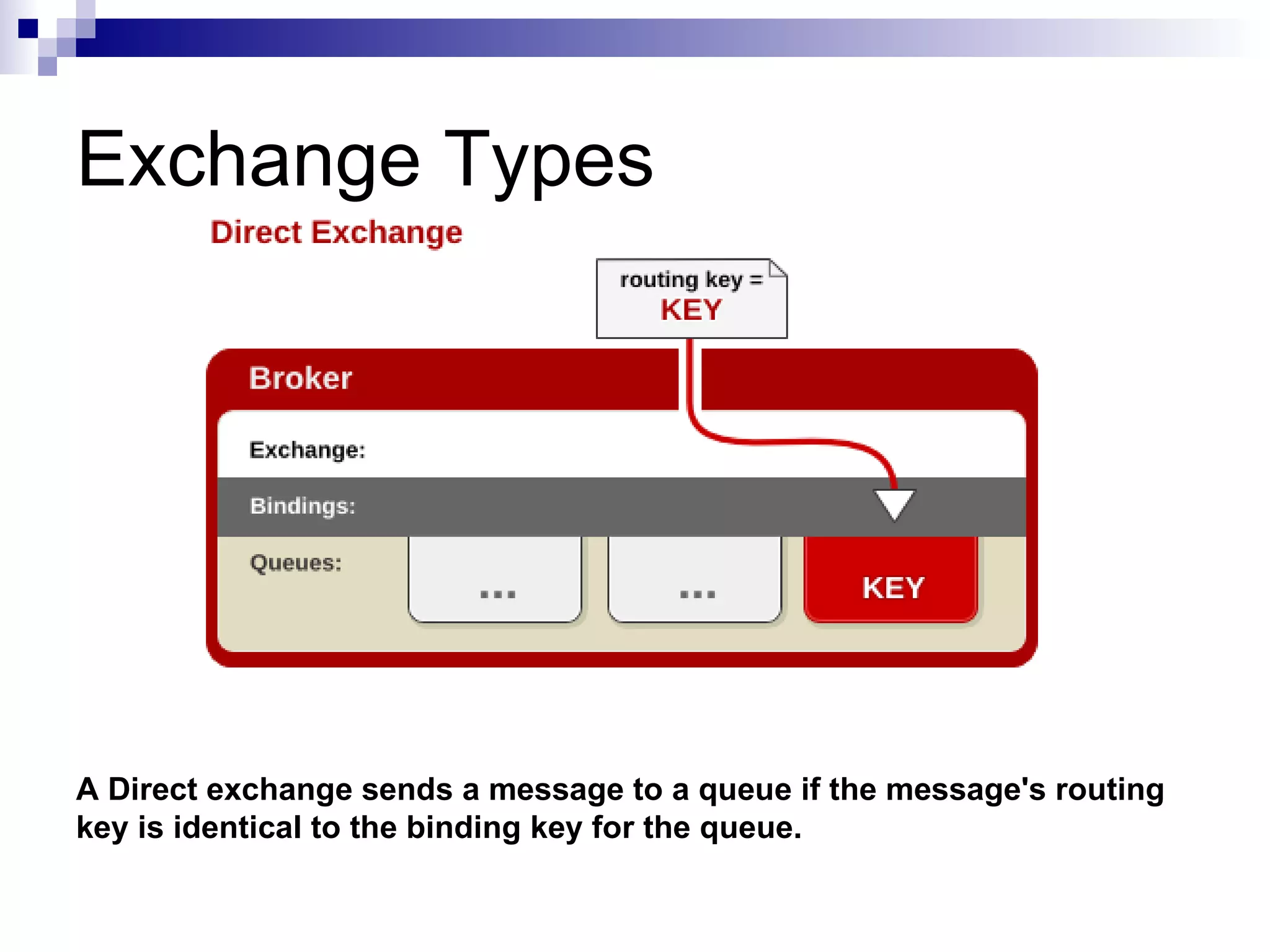
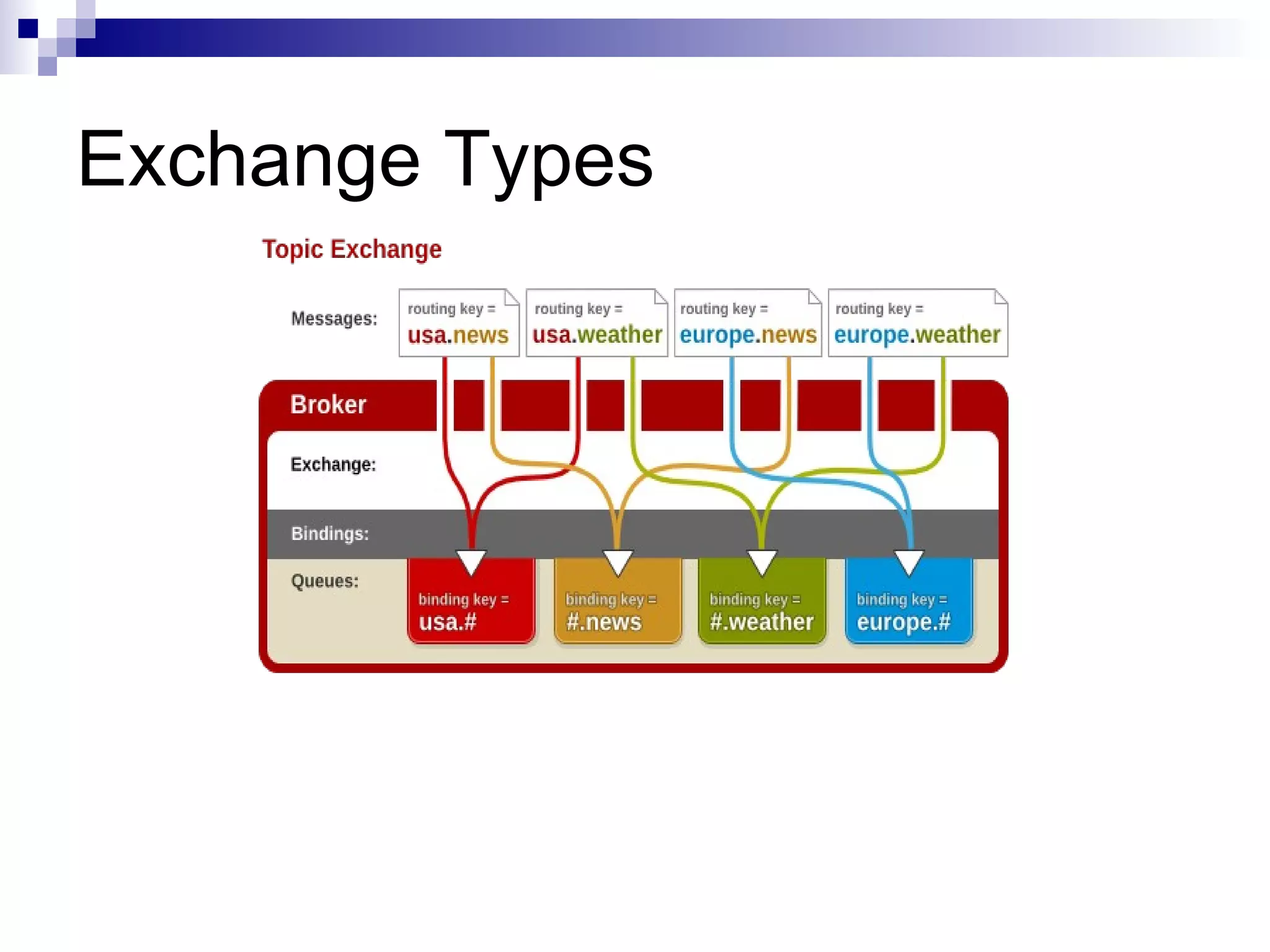
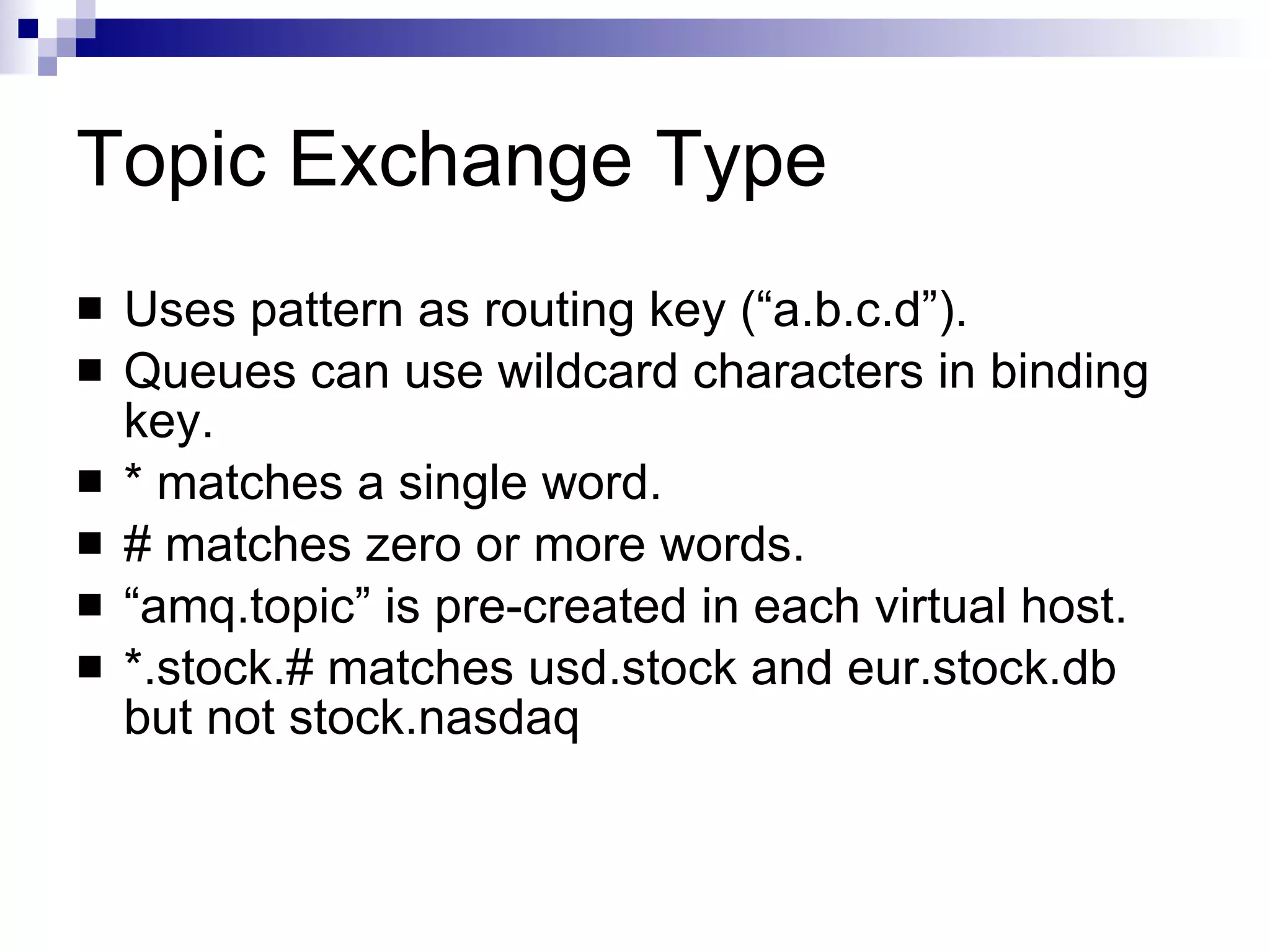
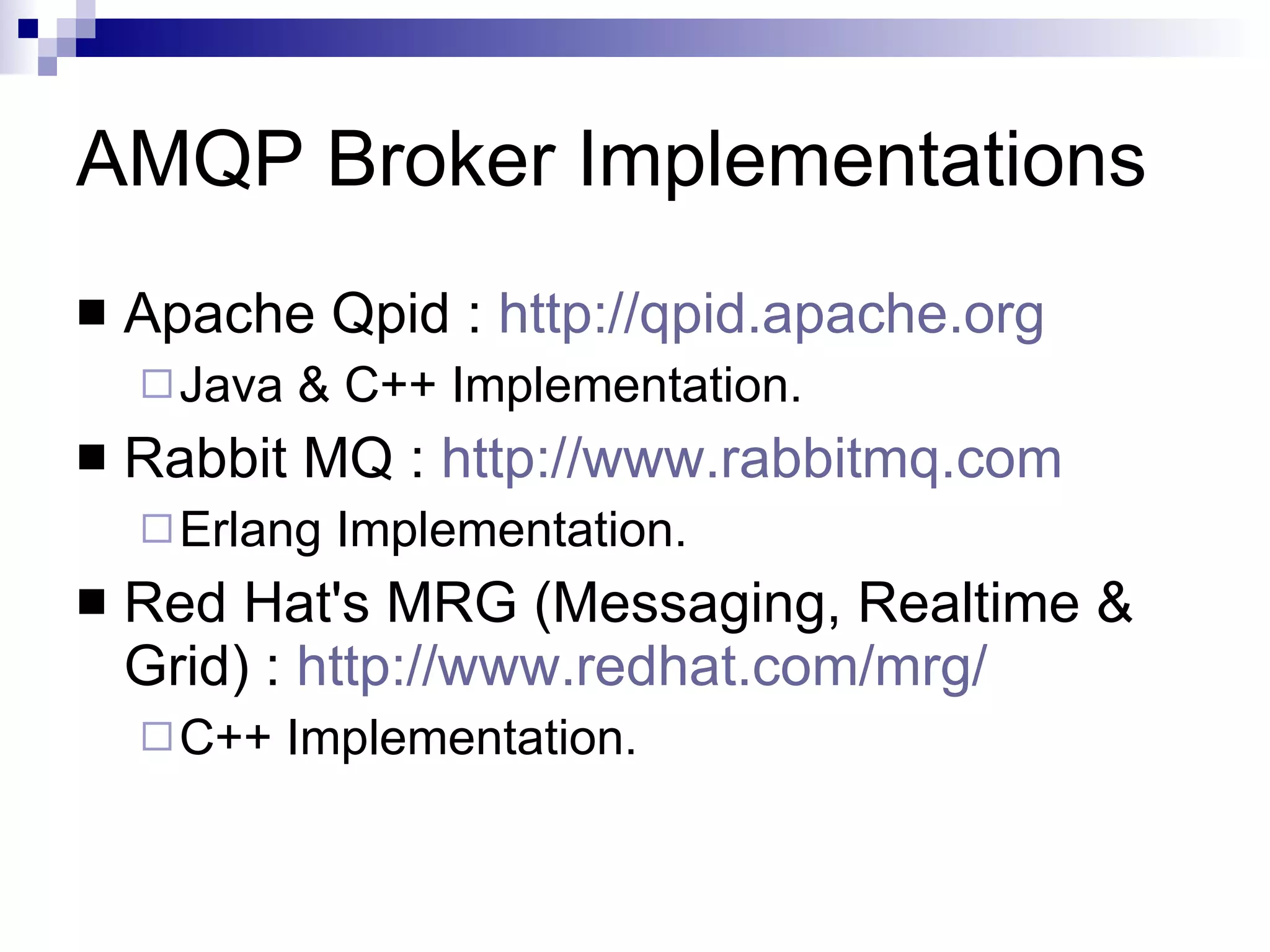
AMQP (Advanced Message Queuing Protocol) is an open standard protocol for message queuing that aims to provide interoperability between platforms and vendors. It defines a wire-level protocol for message passing that can be implemented by different technologies, unlike proprietary middleware which is locked to specific platforms. AMQP includes concepts like exchanges, bindings, queues, and different exchange types (fanout, direct, topic) to route messages from publishers to subscribers in a decoupled manner. Several open source and commercial brokers like RabbitMQ and Qpid implement the AMQP standard.