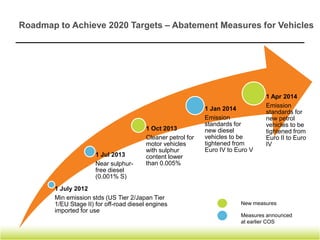
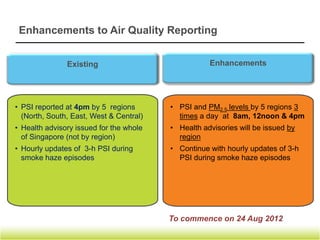
The document discusses trends in Singapore's air quality from 1993 to 2011, noting that air quality has improved significantly over that period. It also compares Singapore's air quality to other Asian and European/US cities. Additionally, it outlines Singapore's targets for reducing various air pollutants by 2020 and long term, and provides roadmaps for achieving the targets through measures related to vehicles and industries. Finally, it mentions enhancements to air quality reporting such as continuing to report the Pollutant Standards Index while also reporting daily PM2.5 levels.