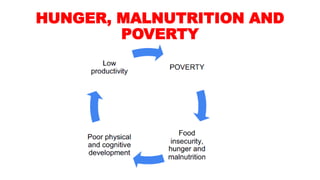
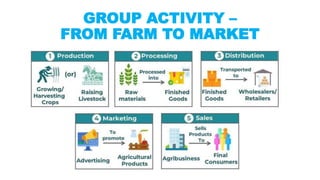
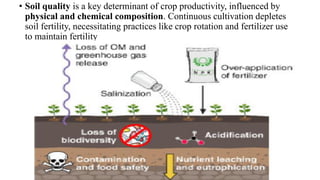
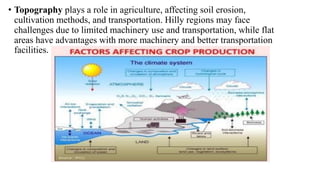
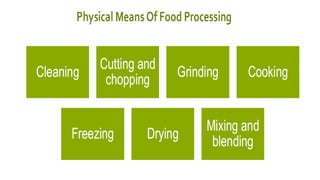
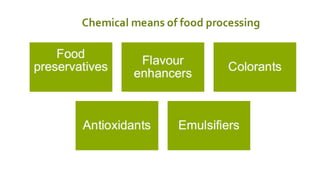
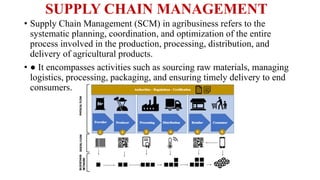
The document discusses the importance of agribusiness management for students in botany, nutrition, and food science, emphasizing its impact on efficient and sustainable agricultural practices. Key components of agribusiness include primary production, processing, distribution, and risk management, all of which contribute to the global economy and food security. Various farming types and practices, such as subsistence and organic farming, are highlighted, along with the significance of supply chain management in optimizing agricultural production and delivery.