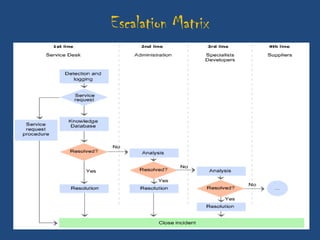
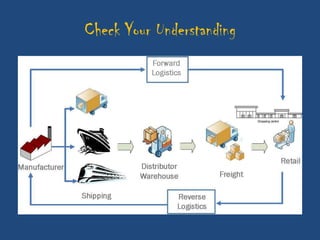
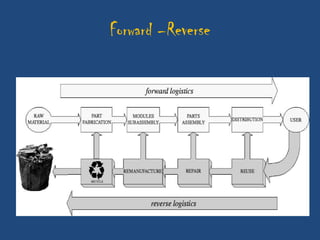
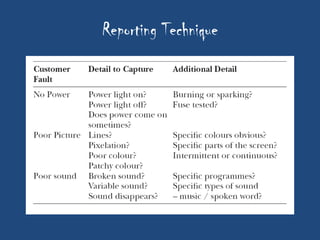
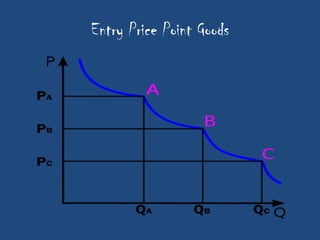
This document discusses the importance of after-sales service for companies. It notes that 77% of Indian consumers will not make a repeat purchase or continue with a company's services after a bad customer experience. Additionally, 76% of Indian consumers are willing to pay 11% more for excellent customer service. The document also outlines some key principles for after-sales service processes, including problem resolution timelines, supplier management, reporting techniques, and escalation processes. Overall, it emphasizes that quality after-sales service leads to customer satisfaction, repeat purchases, and positive word-of-mouth advertising.