1. The document discusses advanced machining processes and provides an overview of conventional and non-conventional machining.
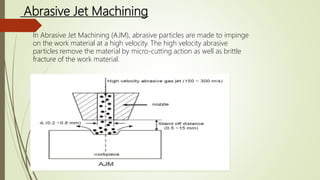
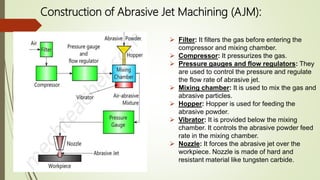
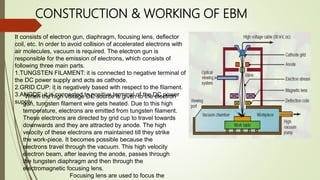
2. Non-conventional machining uses techniques other than traditional cutting tools, such as thermal, electrical, chemical energies. Examples covered include abrasive jet machining, electrochemical machining, and electron beam machining.
3. Key characteristics of non-conventional machining are that material can be removed without chip formation, there may not be a physical tool, and the tool need not be harder than the workpiece.