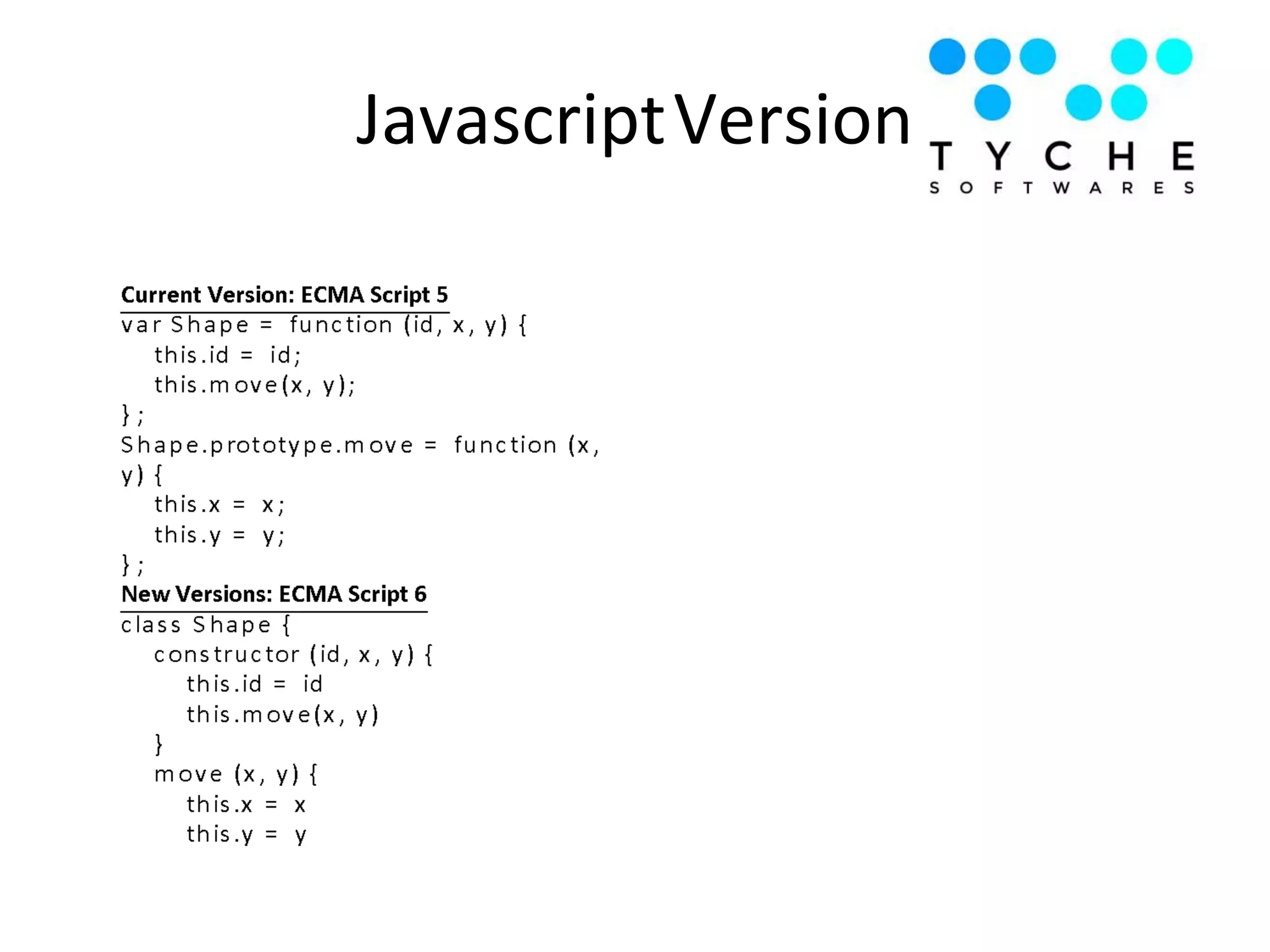
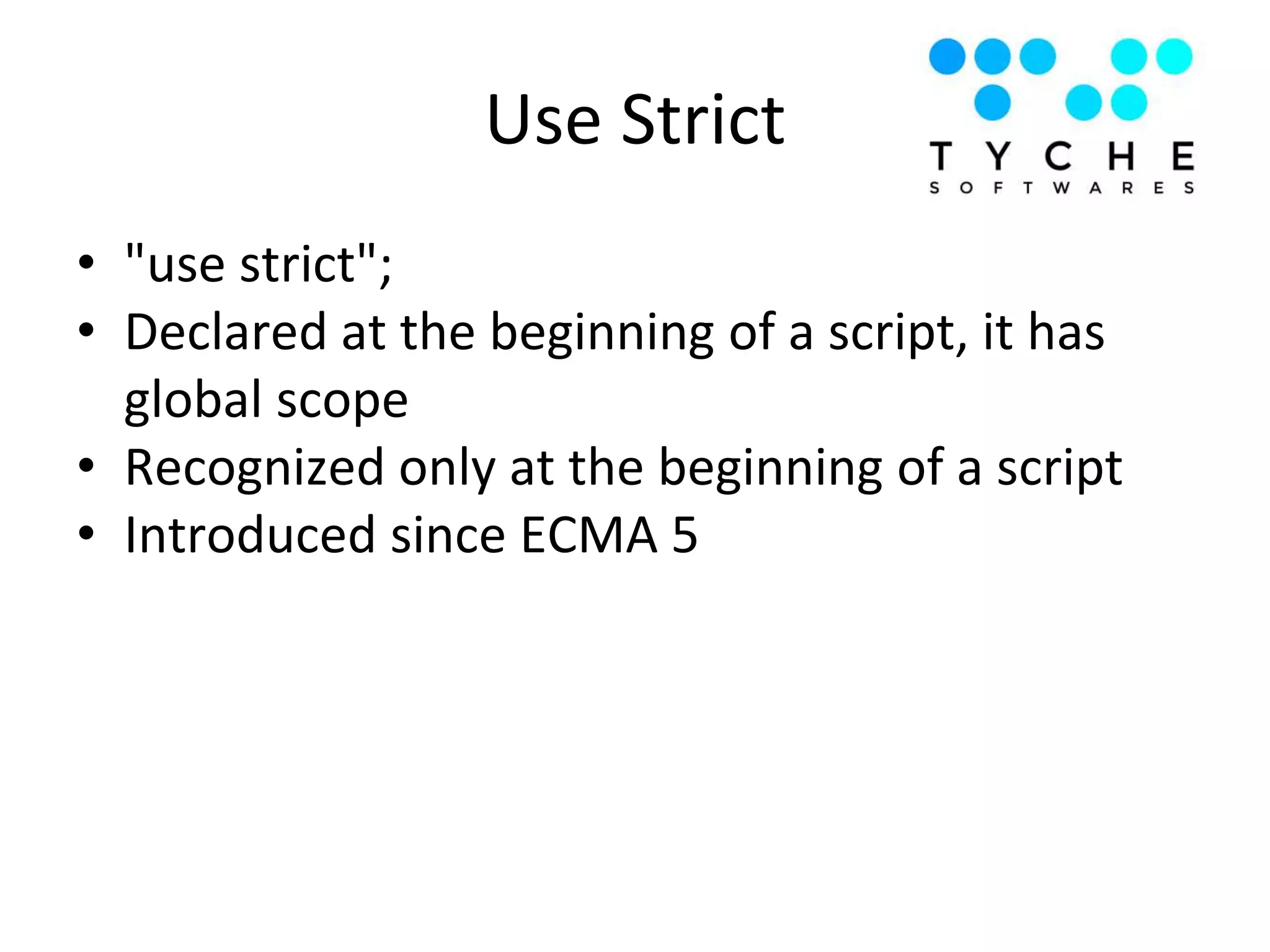
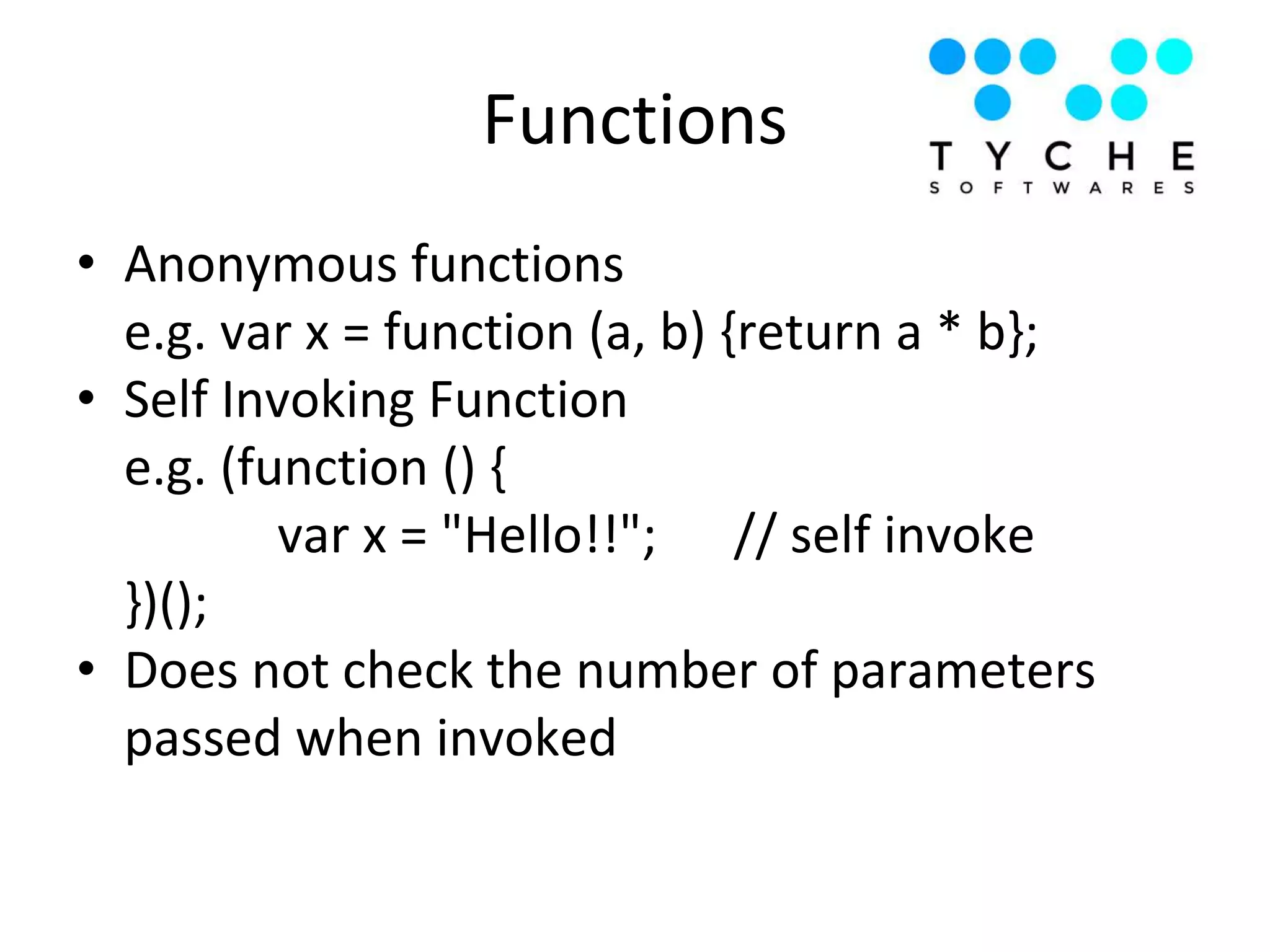
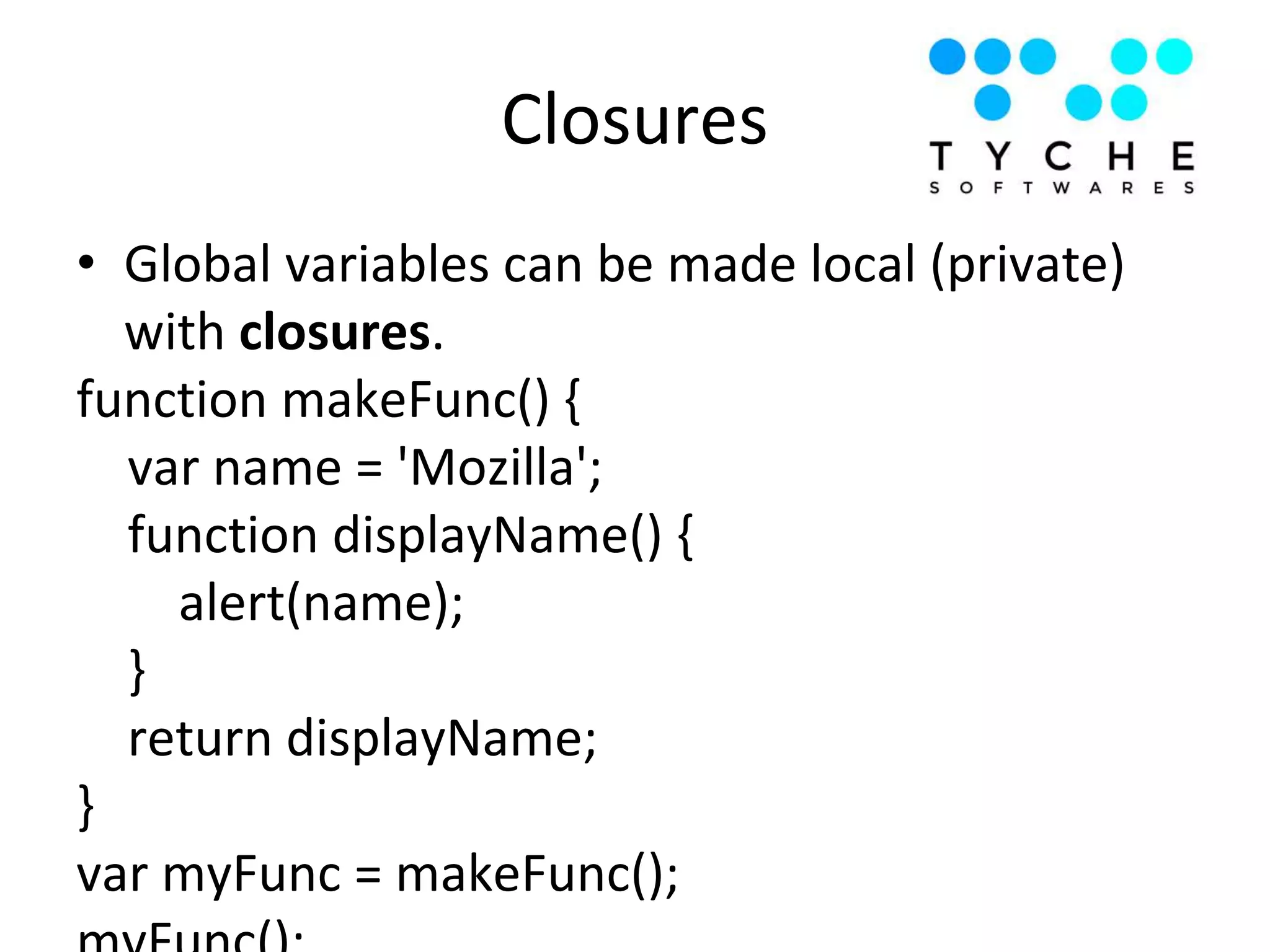
1) The document discusses advanced JavaScript topics like hoisting, strict mode, functions as objects, prototypes, closures, and important JavaScript functions like call, apply, bind.
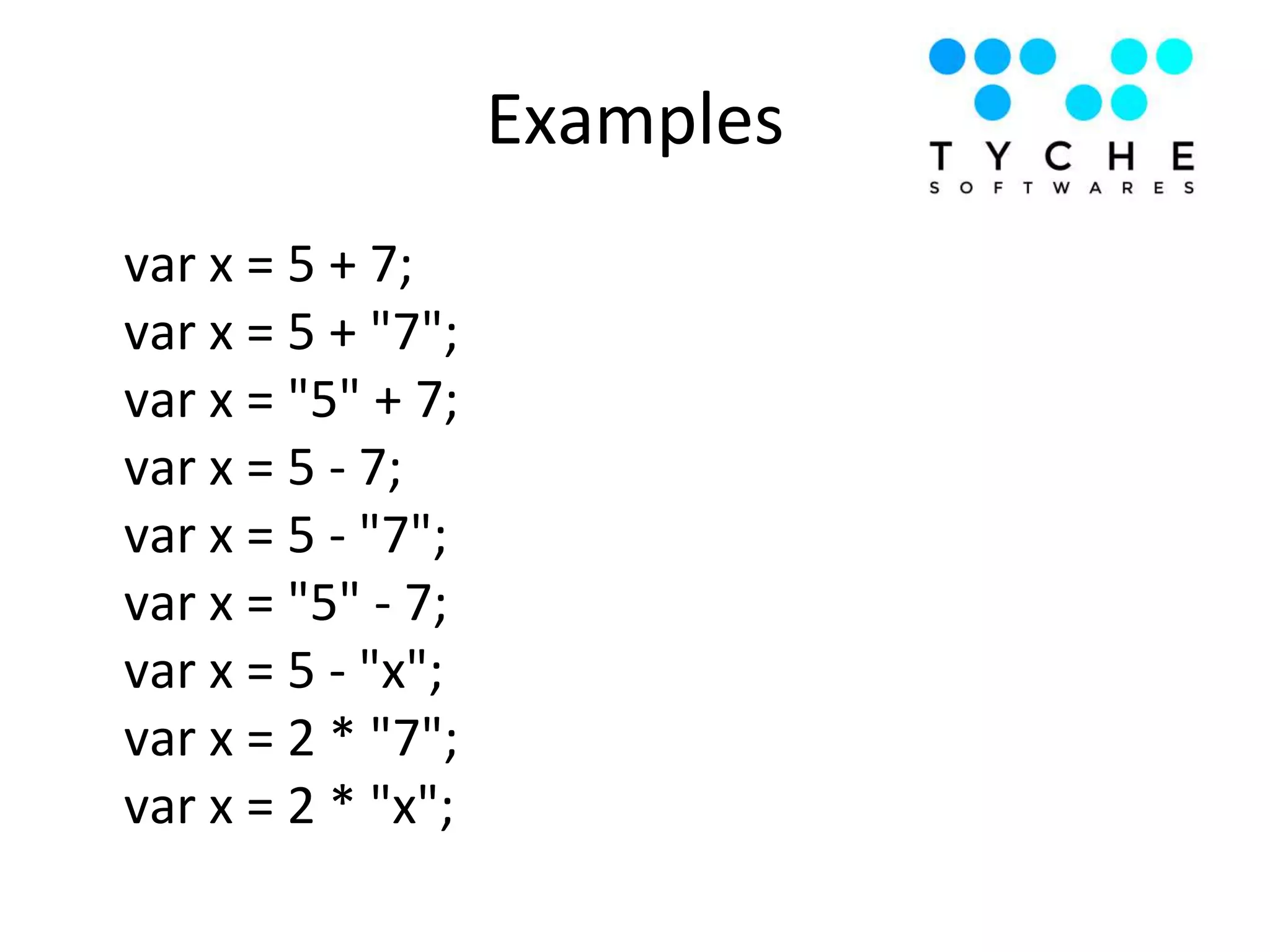
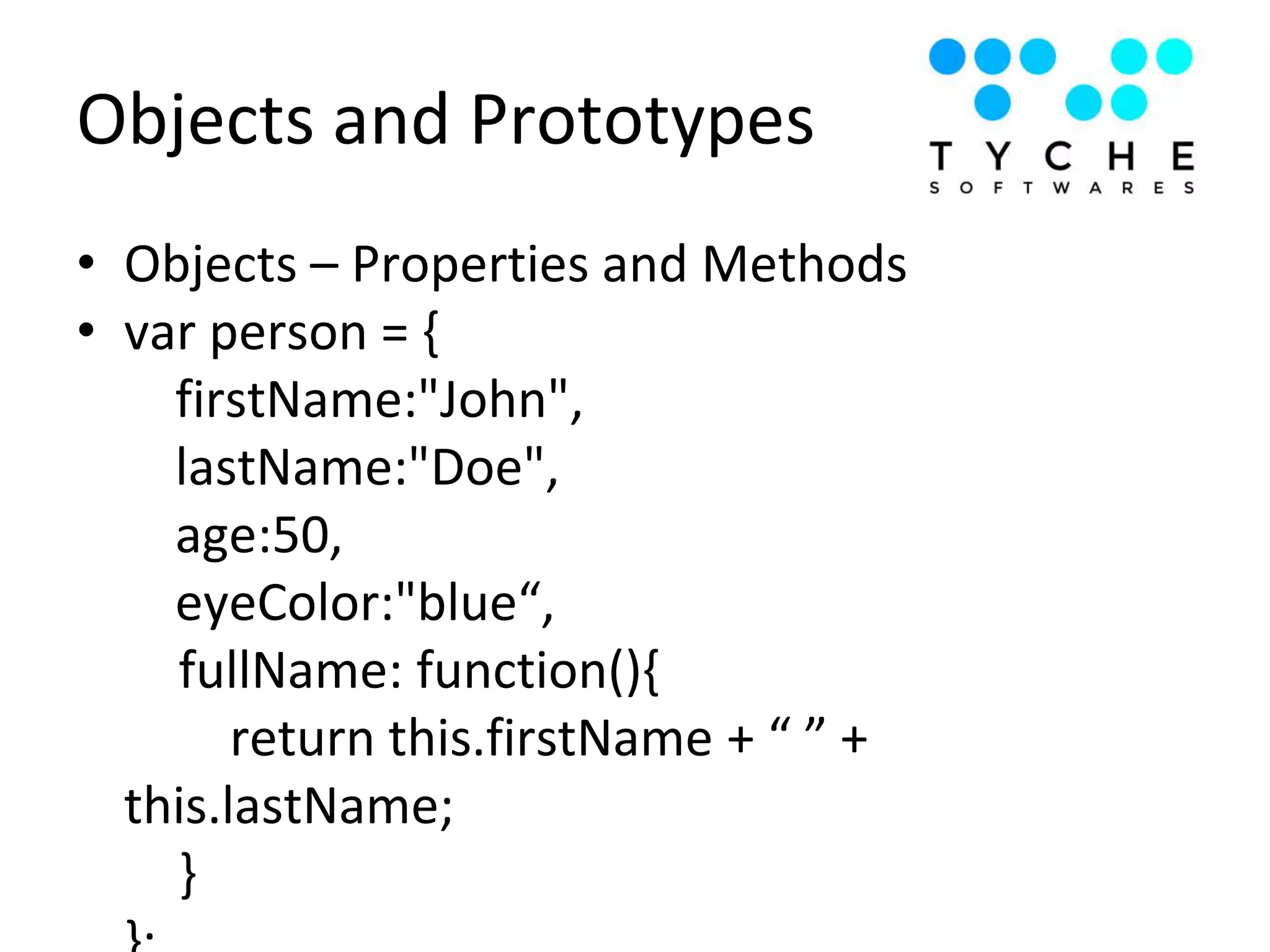
2) It provides examples of hoisting, strict mode, best practices for avoiding globals and type comparisons, and functions, objects, and prototypes.
3) Important JavaScript functions covered include timing functions like setTimeout and setInterval, global objects like window, location, and navigator, and newer JavaScript versions and APIs.




![Call vs Apply vs Bind
Parameter Call Apply Bind
Definition calls a function with
a given this value
and arguments
provided
individually
calls a function with
a given this value,
and arguments pro
vided as an array
(or an array-like
object
Function gets
executed when
event is triggered
or some condition
is satisfied
Syntax function.call(thisArg
, arg1, arg2, ...)
fun.apply(thisArg,
[argsArray])
fun.bind(thisArg[,
arg1[, arg2[, ...]]])](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/advancedjavascript-170802050335/75/Advanced-Javascript-11-2048.jpg)