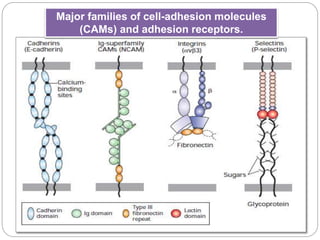
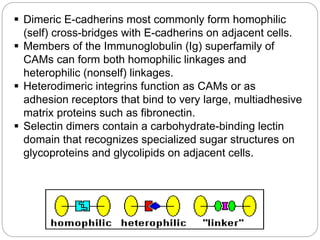
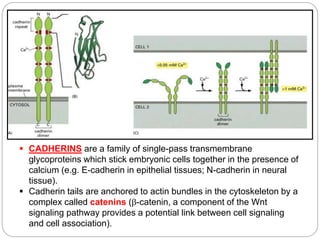
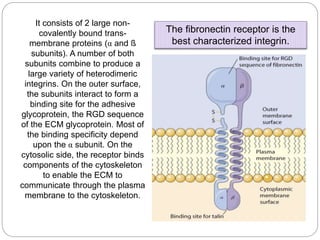
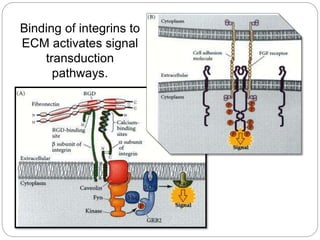
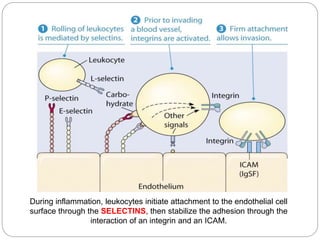
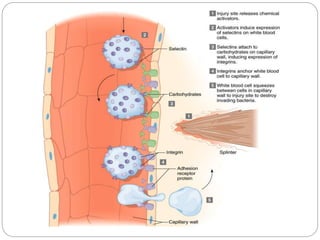
This document discusses different types of cell adhesion molecules (CAMs) and adhesion receptors. It describes several major families of CAMs, including cadherins, integrins, selectins, and neural cell adhesion molecules (N-CAMs). Cadherins are calcium dependent and help bind embryonic cells together. Integrins are receptors that bind the extracellular matrix and require calcium or magnesium. Selectins contain carbohydrate-binding domains and recognize sugar structures on adjacent cells. N-CAMs mediate cell-cell recognition and adhesion during neural tissue formation. The cytoplasmic domains of these adhesion molecules link them to the cytoskeleton or signaling pathways.