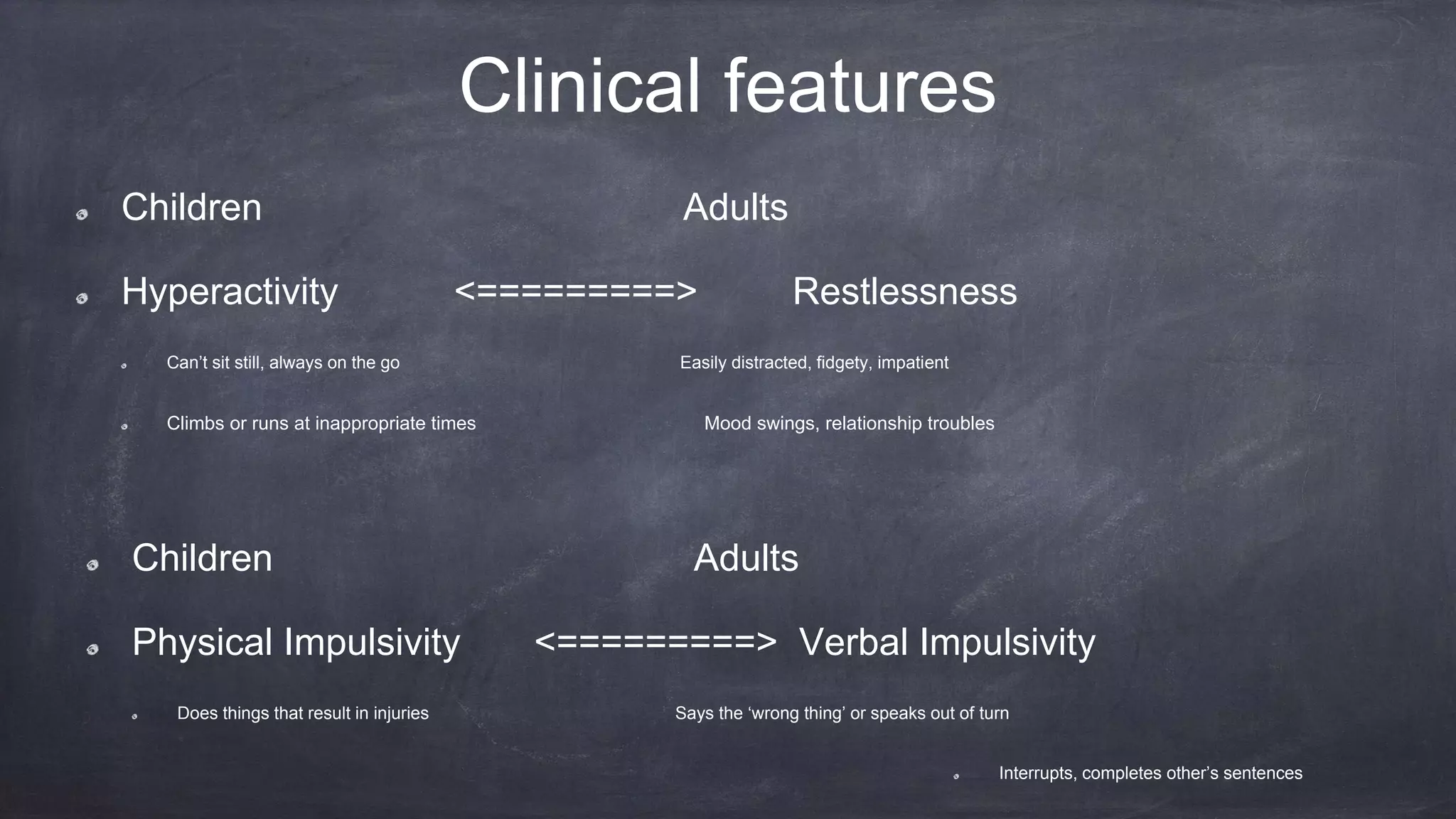
1. ADHD is one of the most common childhood disorders, with 30-60% of cases persisting into adulthood. It is caused by dysfunction in brain circuits involving catecholamines like dopamine and norepinephrine.
2. Adult ADHD presentations do not always neatly match the DSM criteria, which were developed for children. Evaluations require assessing specific symptoms, impairment levels, psychiatric history, and collateral information.
3. Effective treatment involves stimulant medications like methylphenidate and amphetamines, which work by increasing dopamine and norepinephrine levels. Screening tools can aid diagnosis, but labs and cardiac screening are also important aspects of the assessment process.