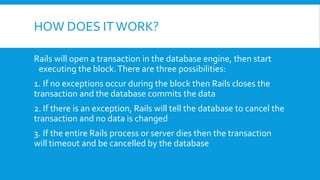
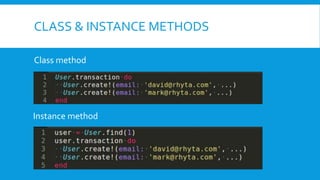
Rails transactions ensure that a series of database operations are executed successfully as a group or rolled back to maintain data integrity. If an operation affecting multiple records fails, the entire transaction is canceled, preventing any partial updates. Key features include automatic handling of transactions during saves, callbacks for success or failure, and the ability to explicitly invalidate transactions.