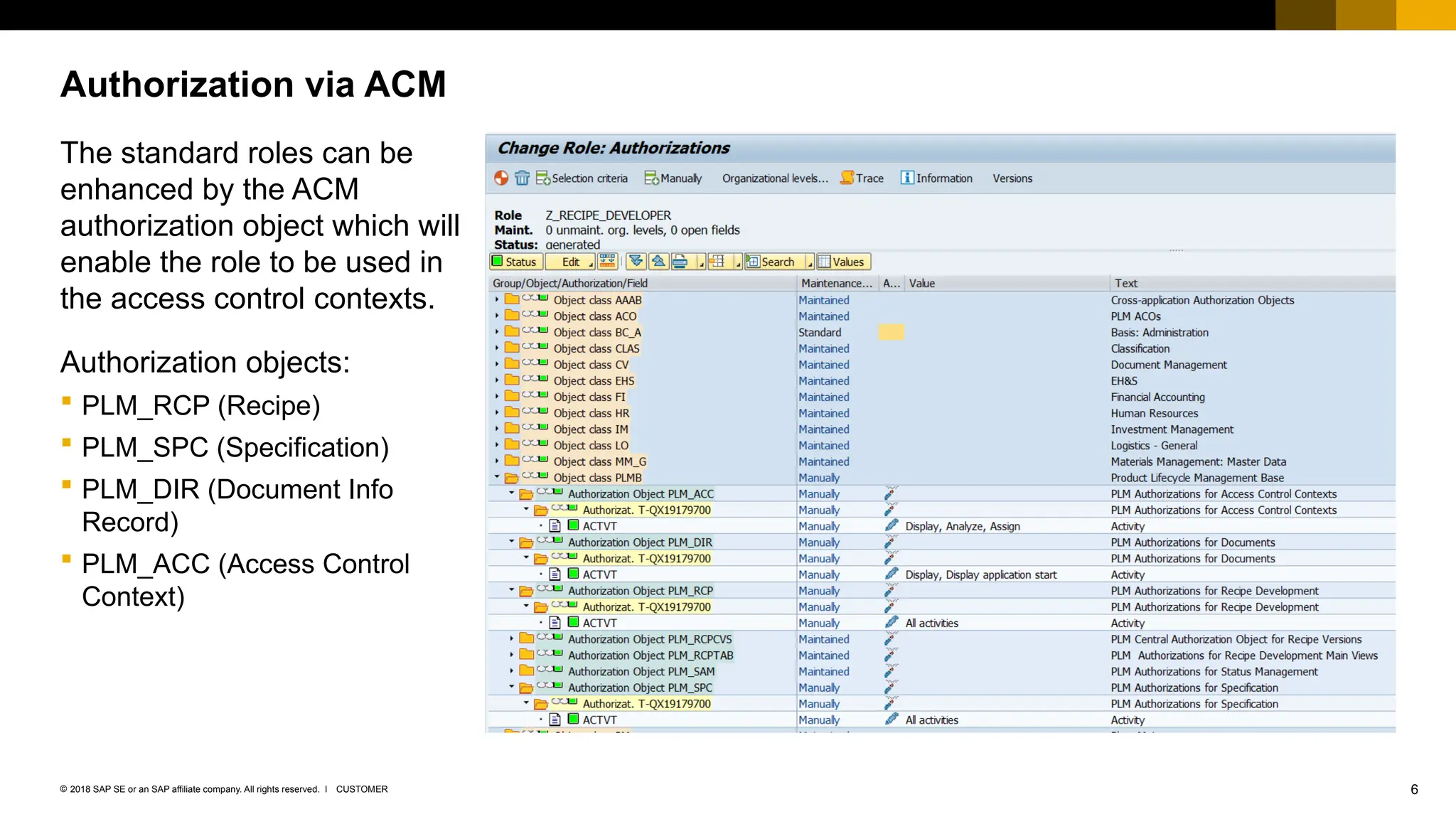
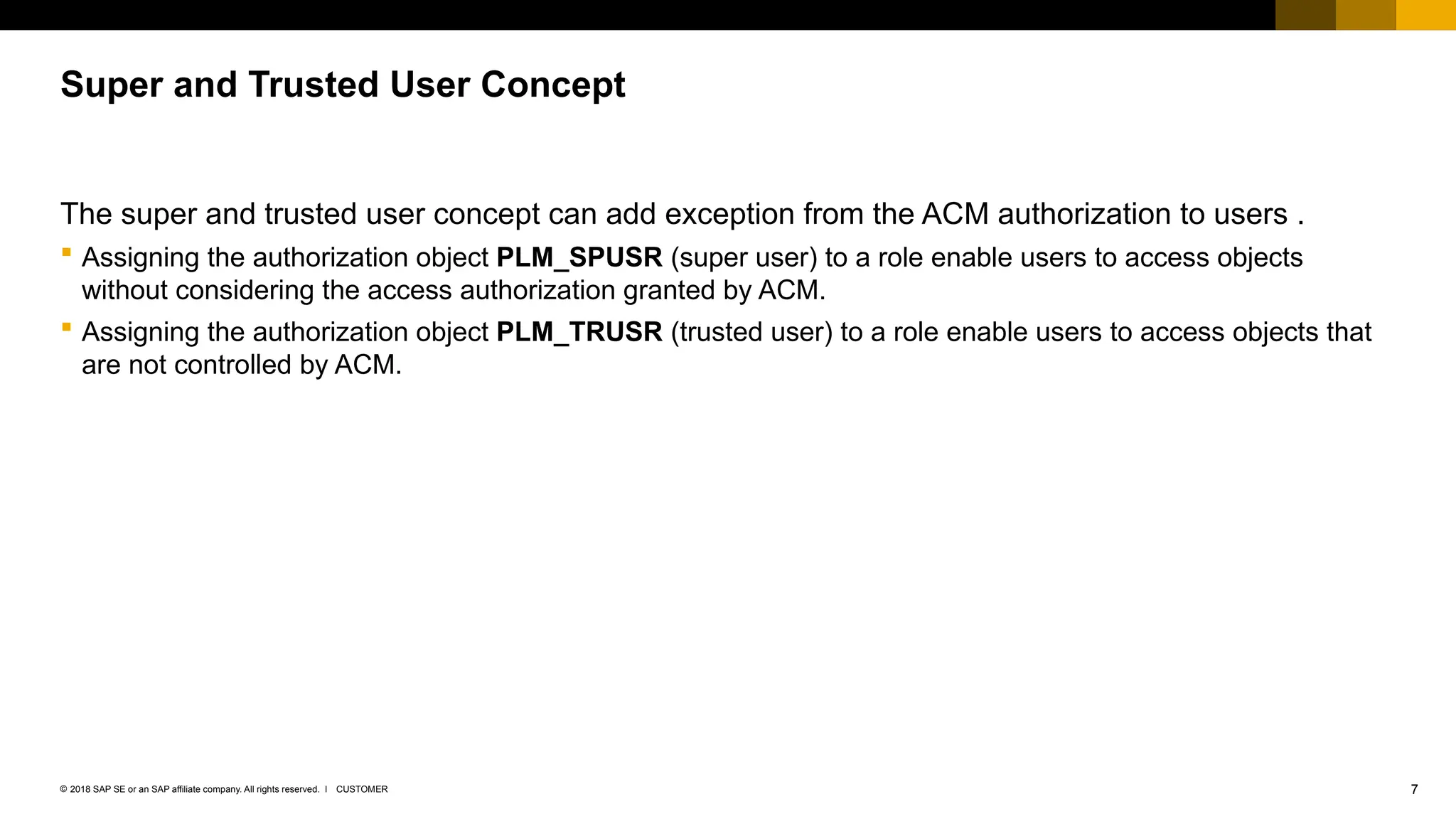
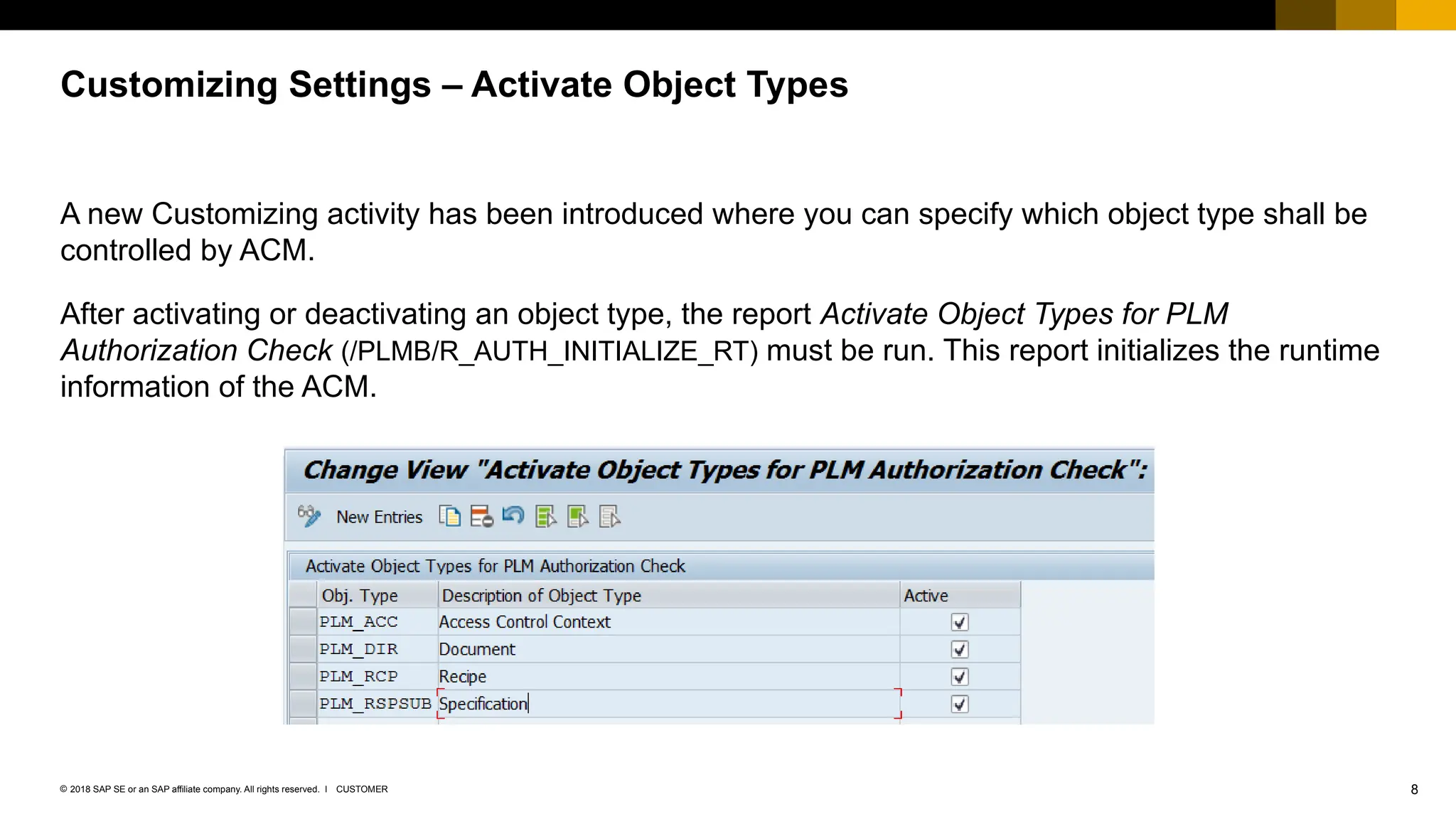
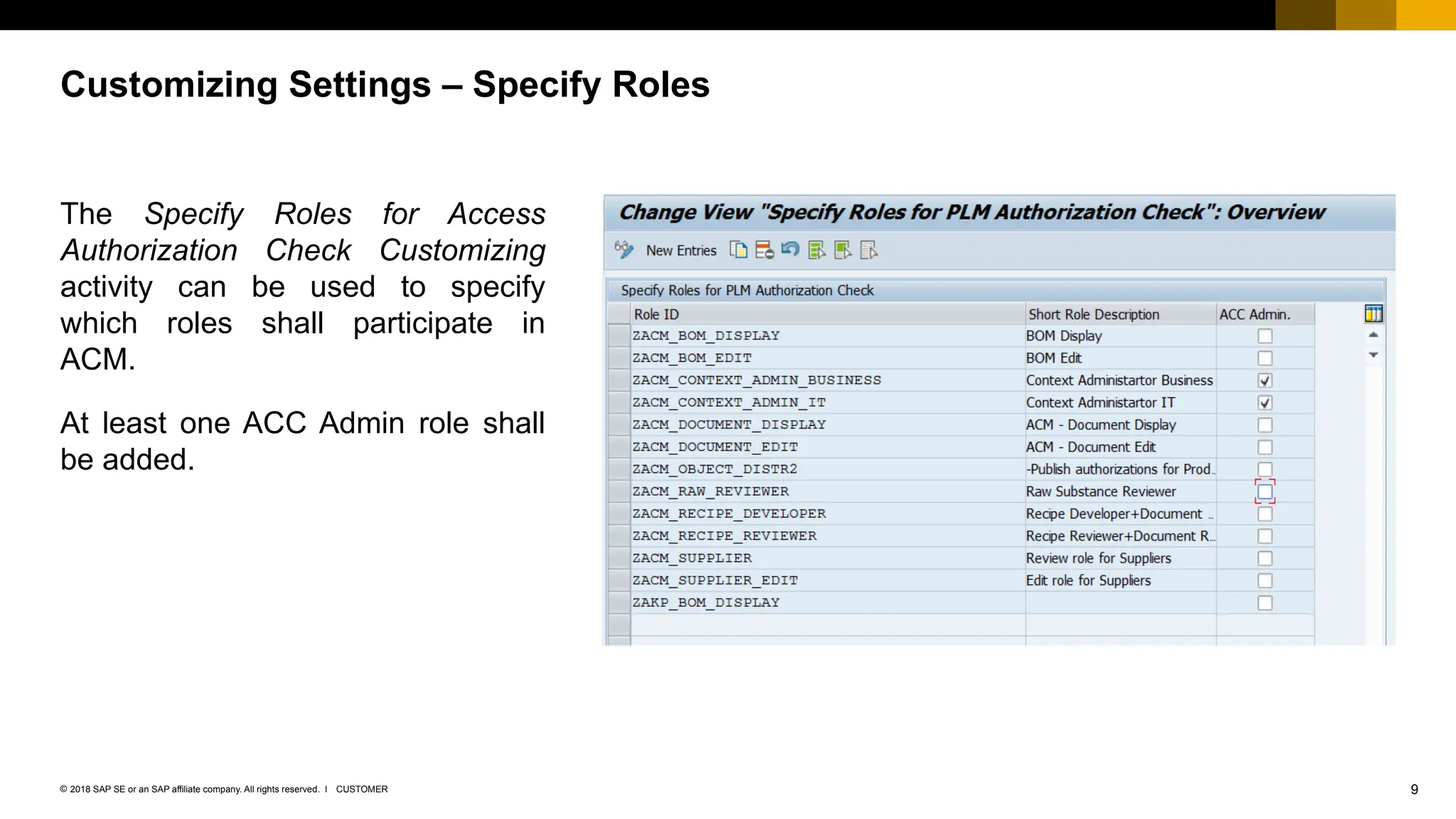
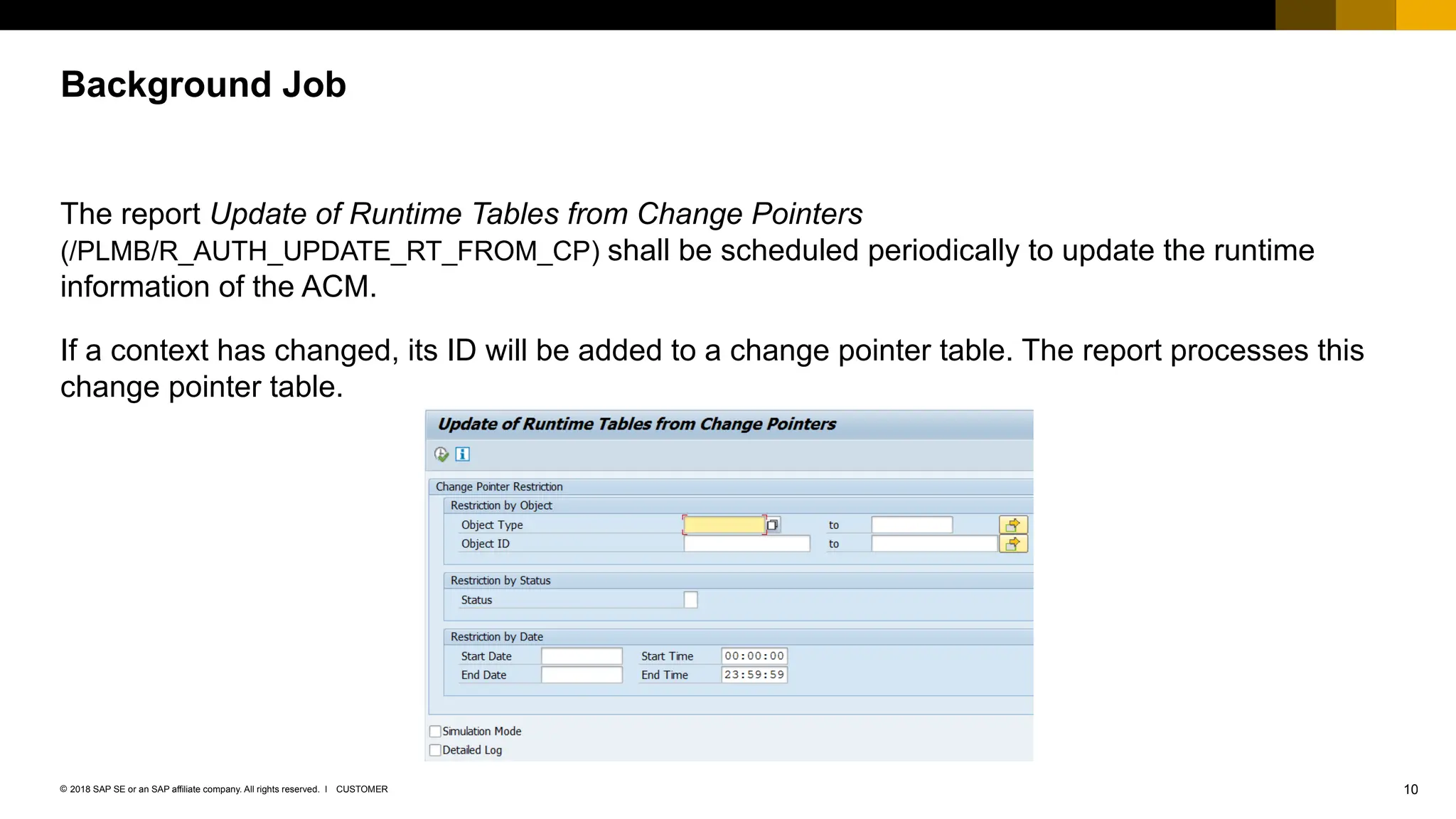
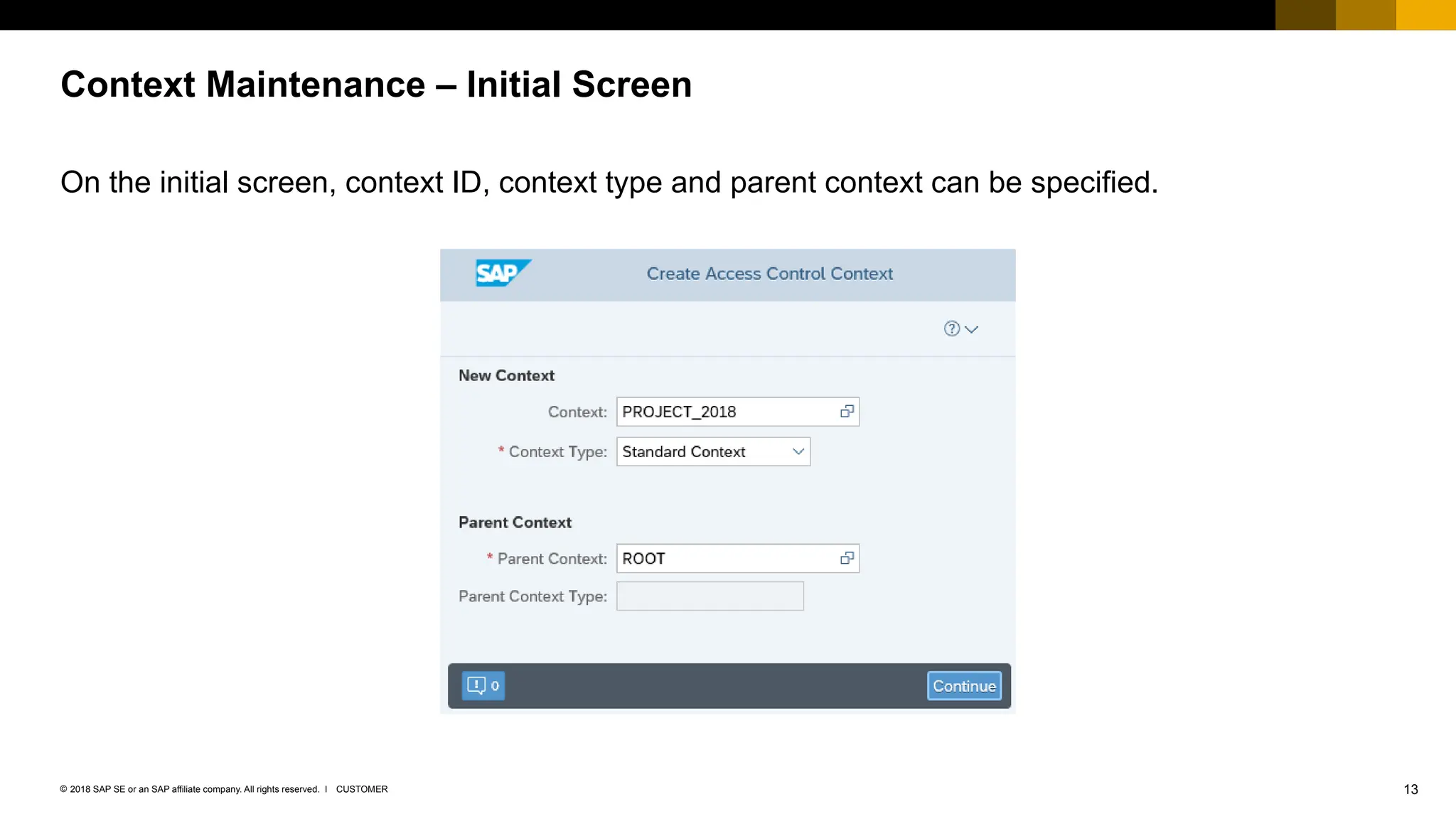
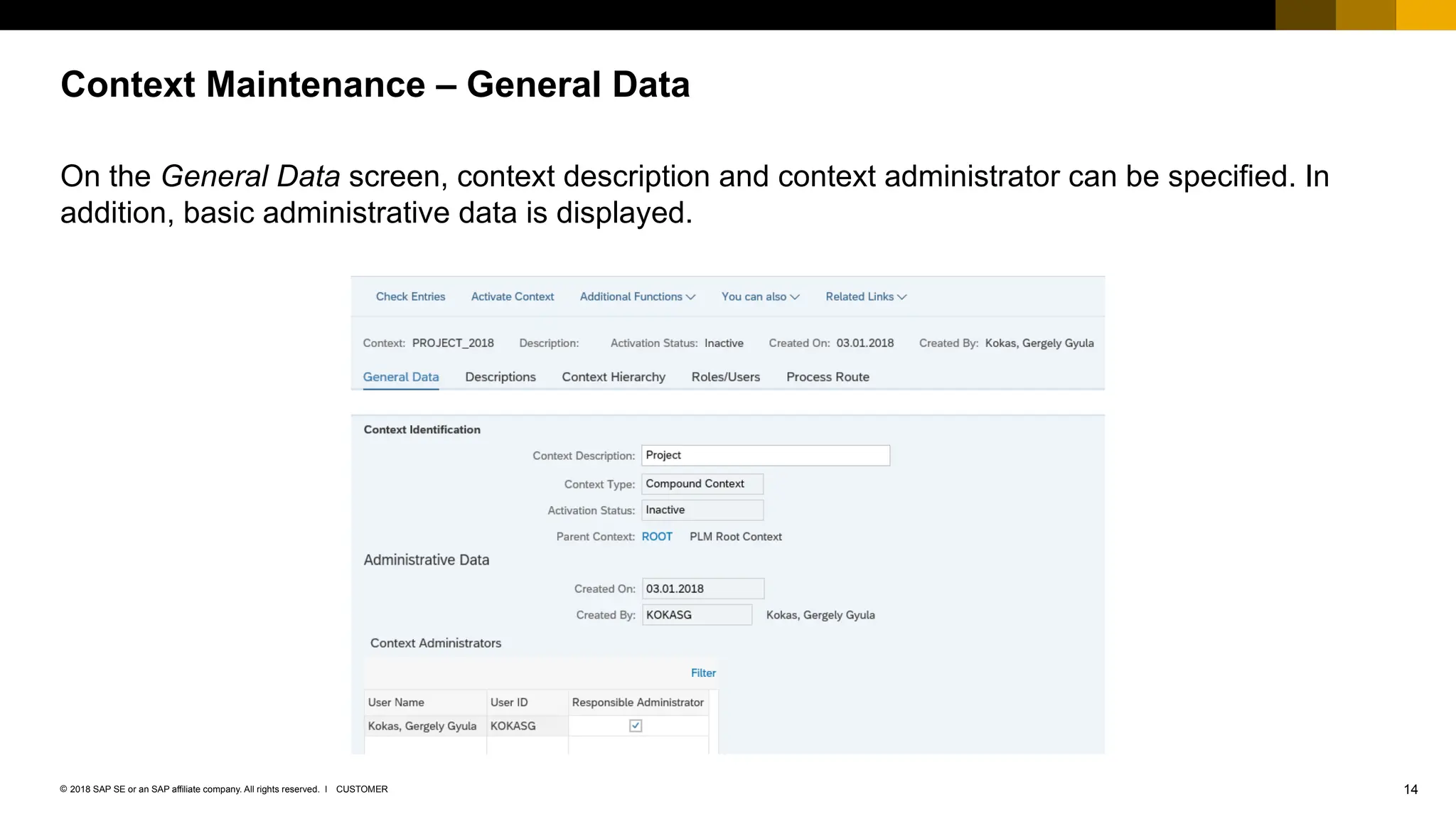
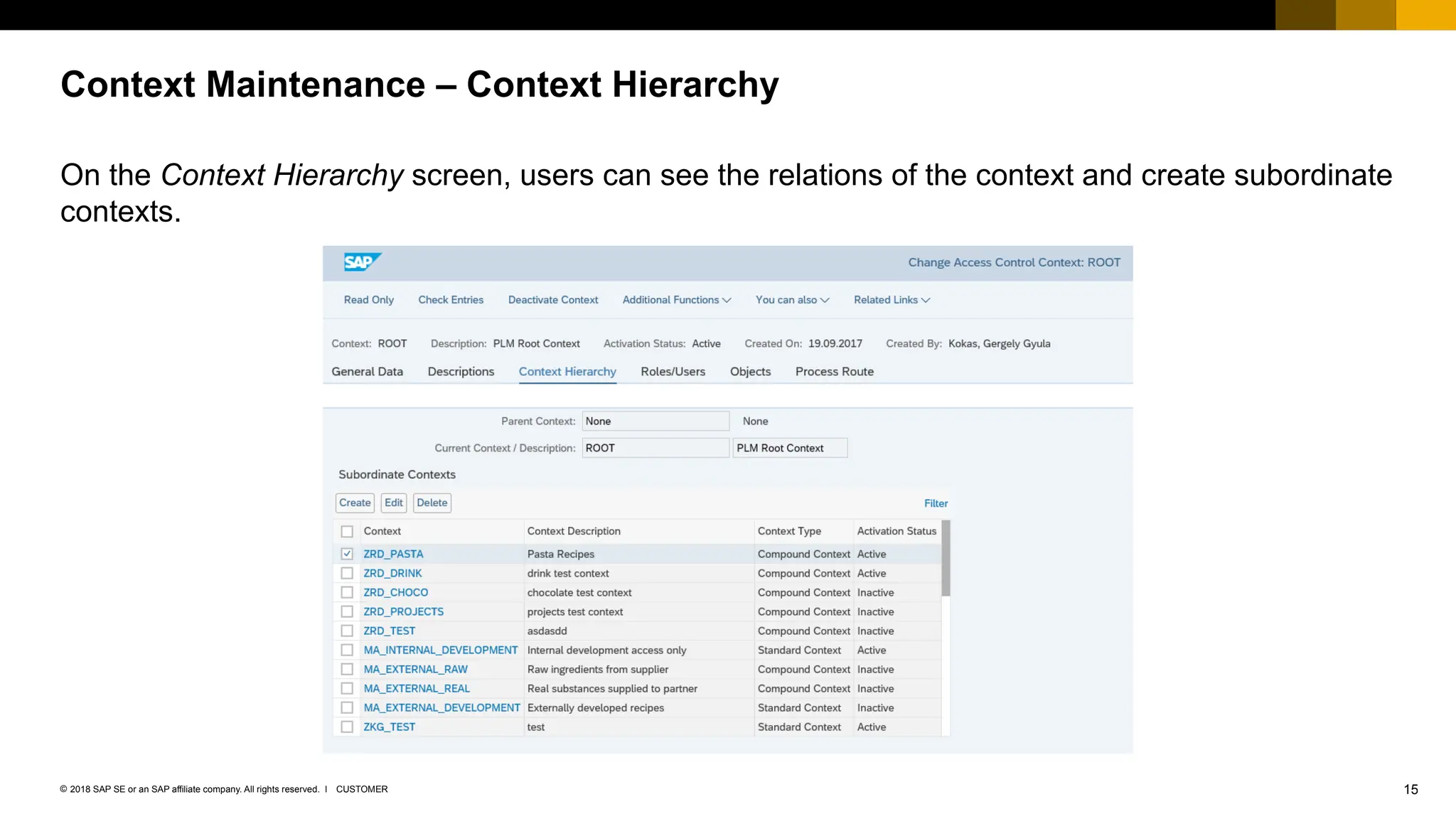
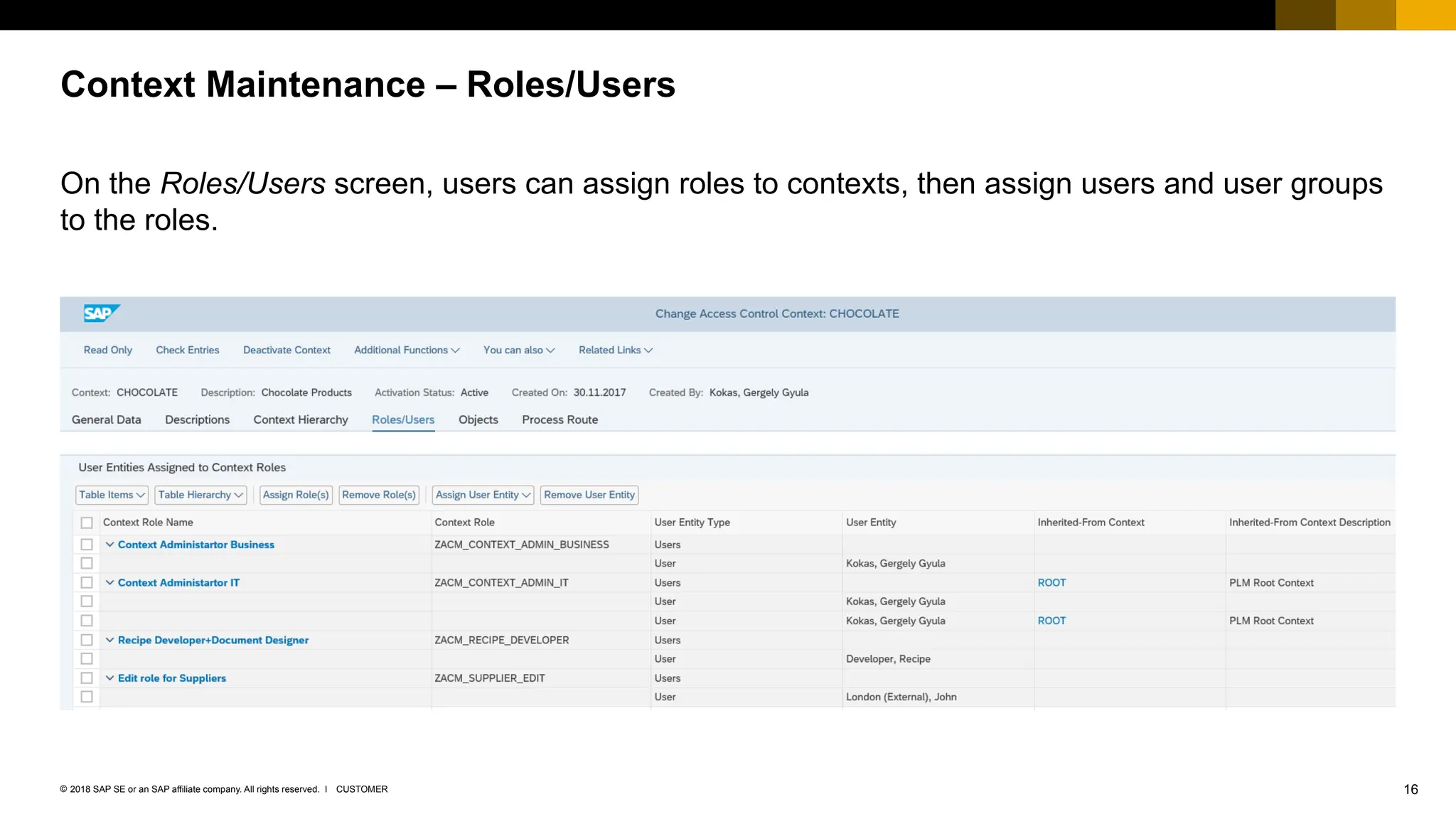
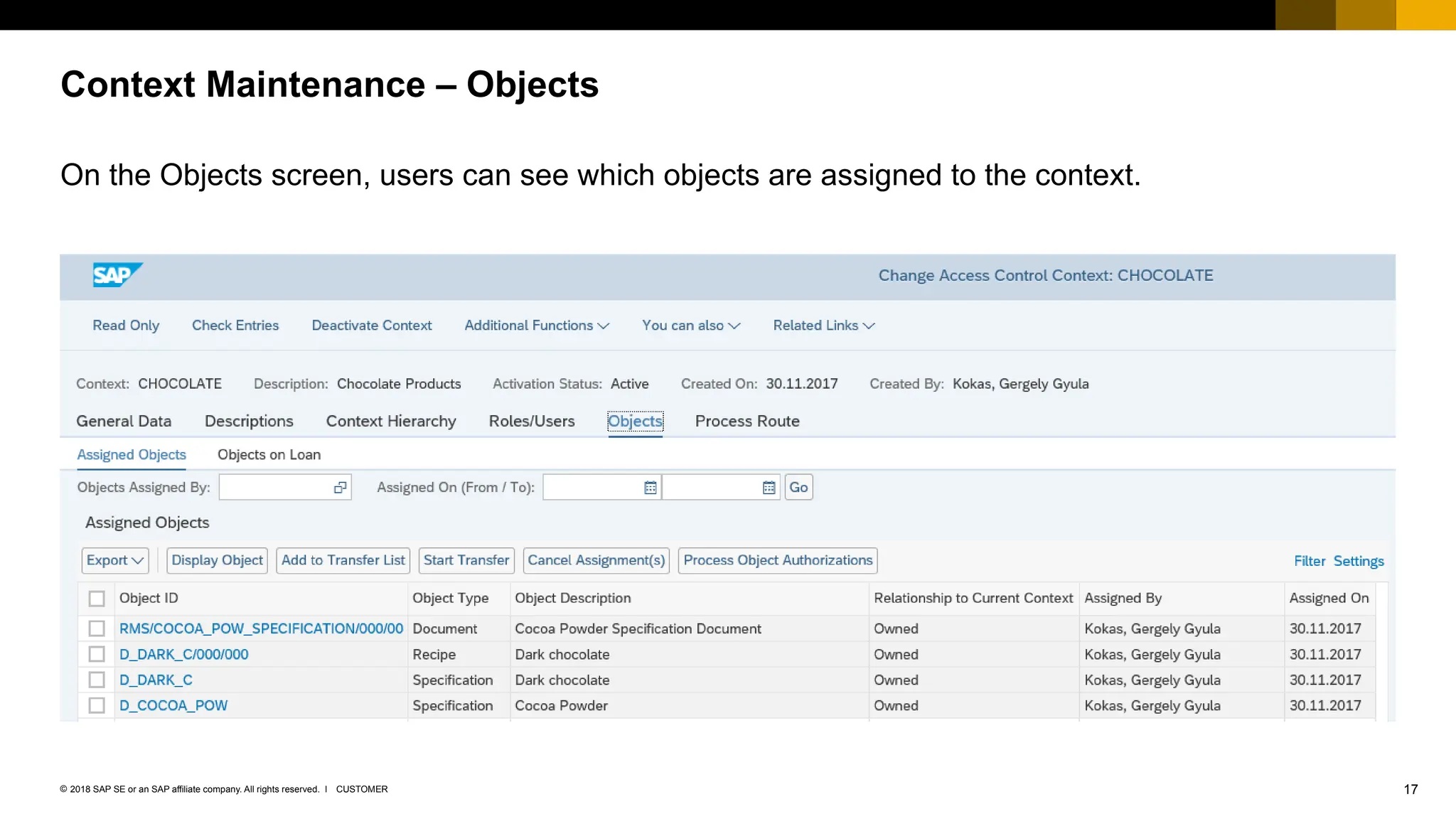
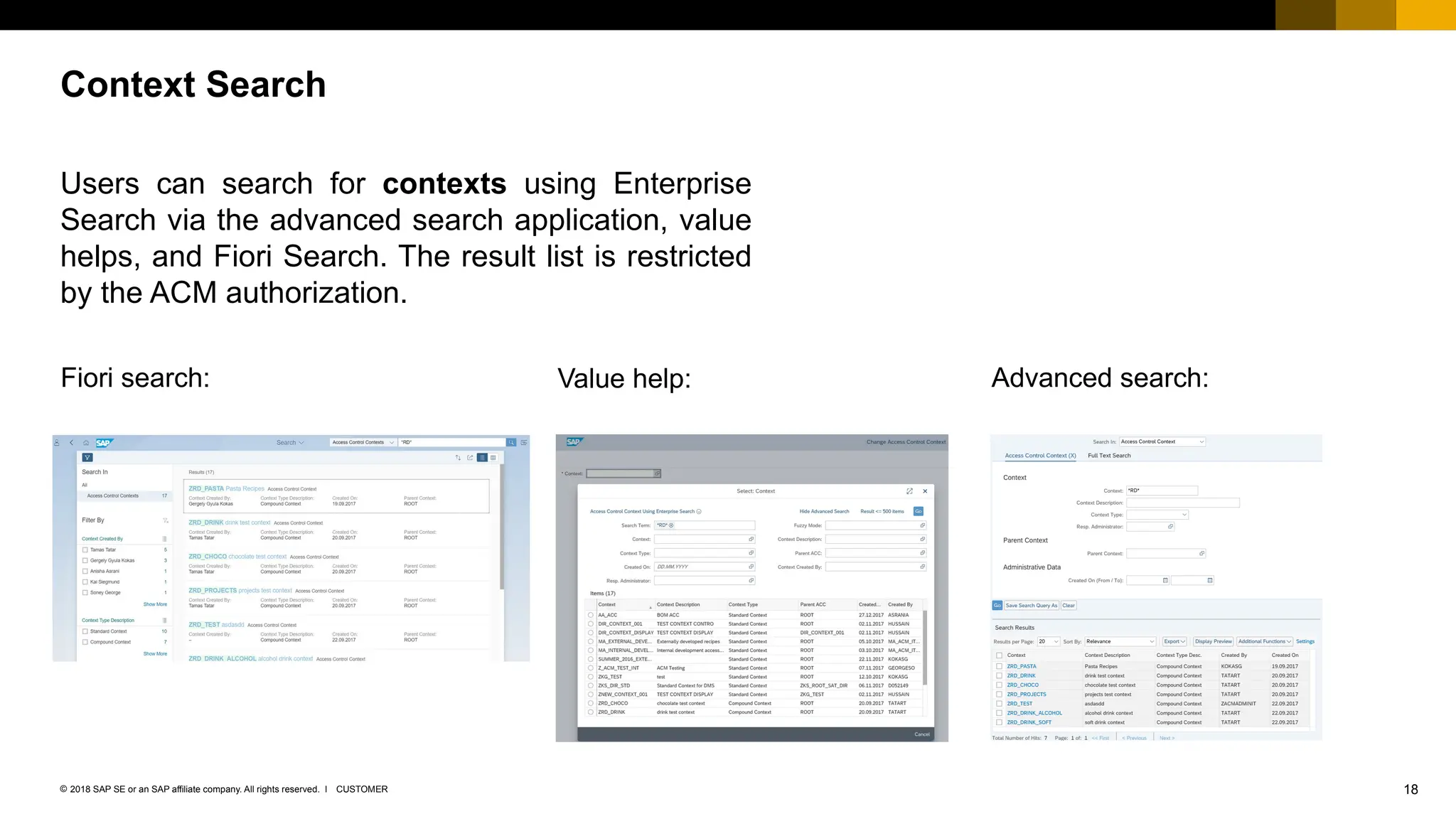
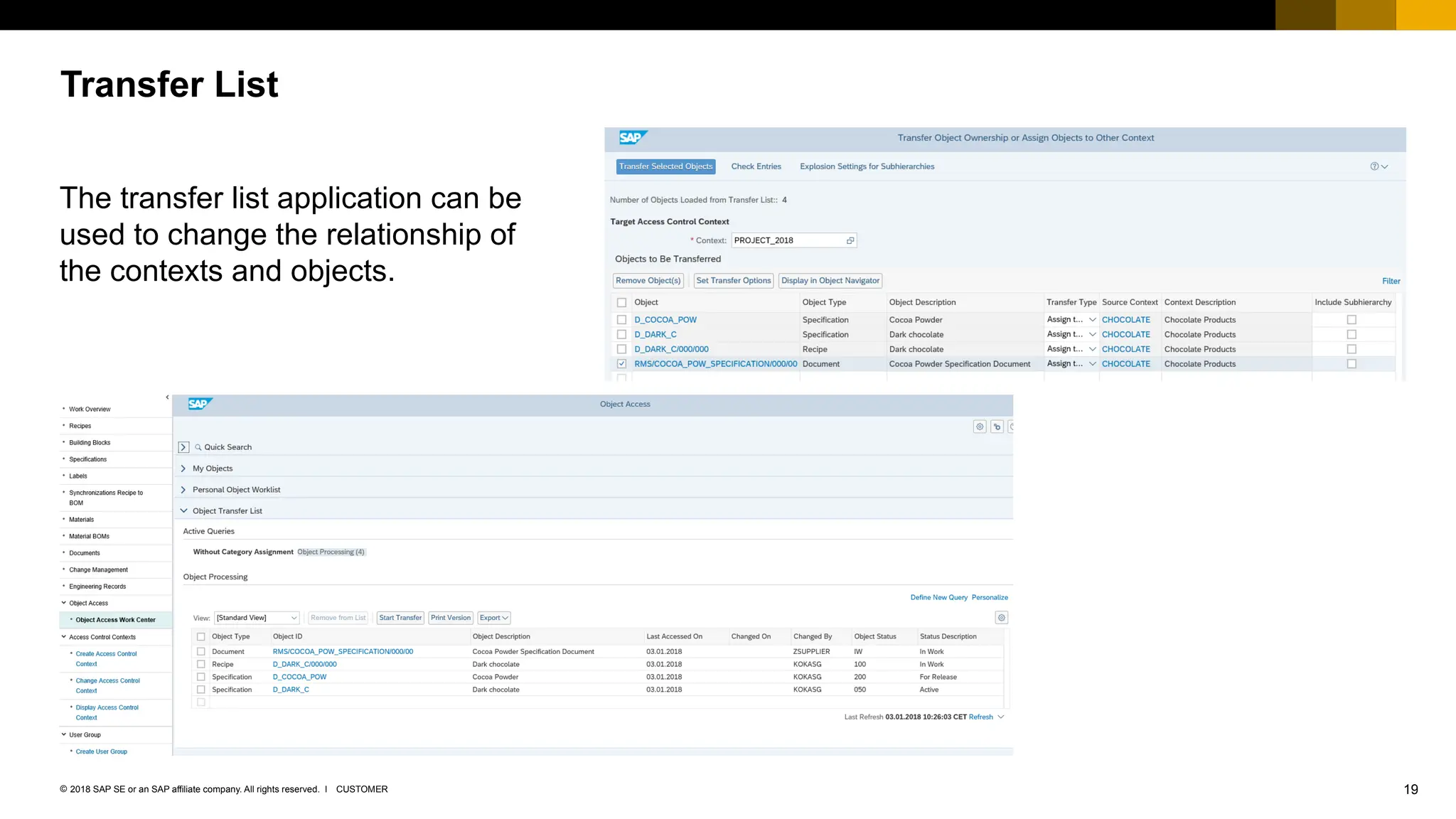
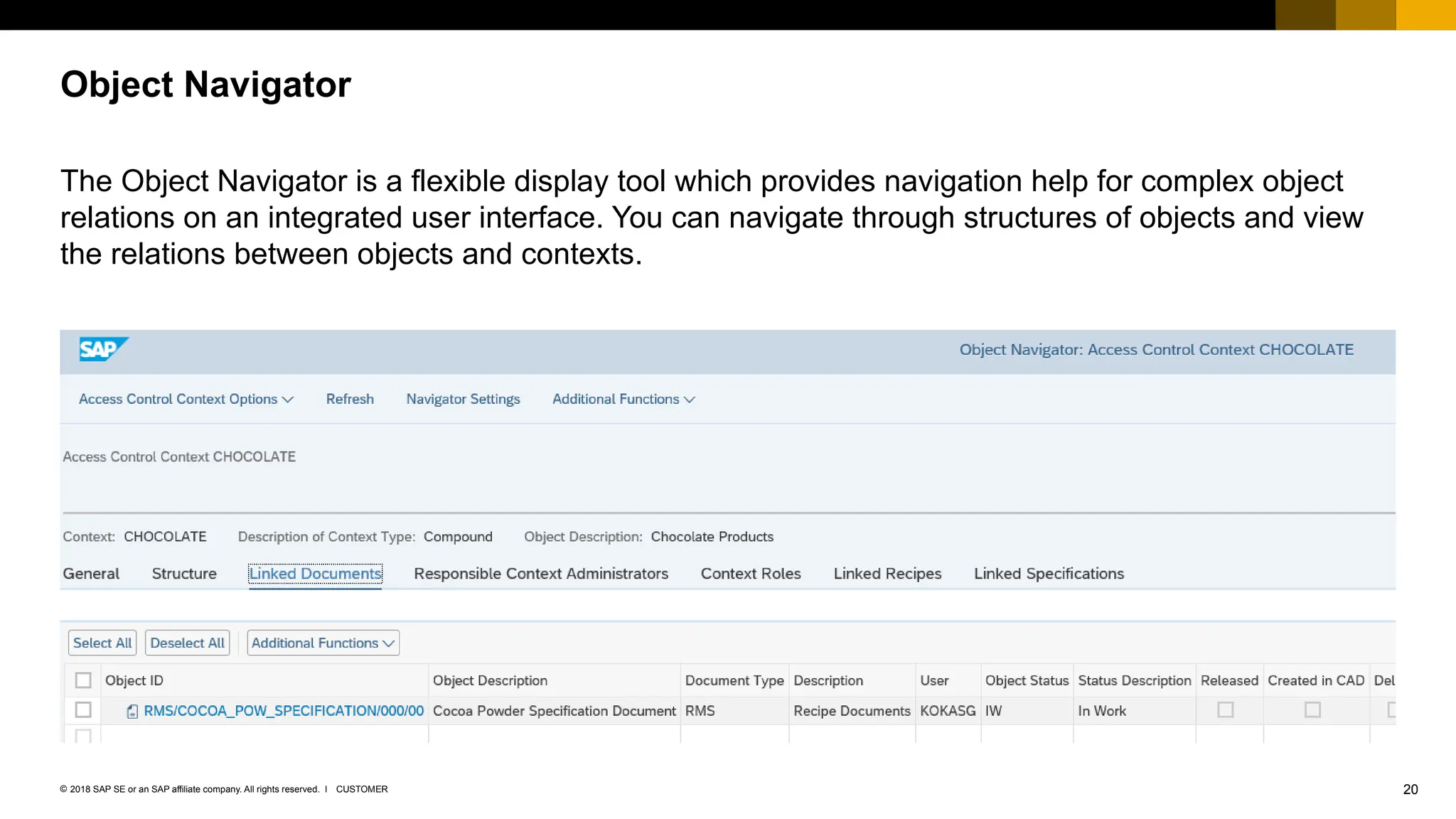
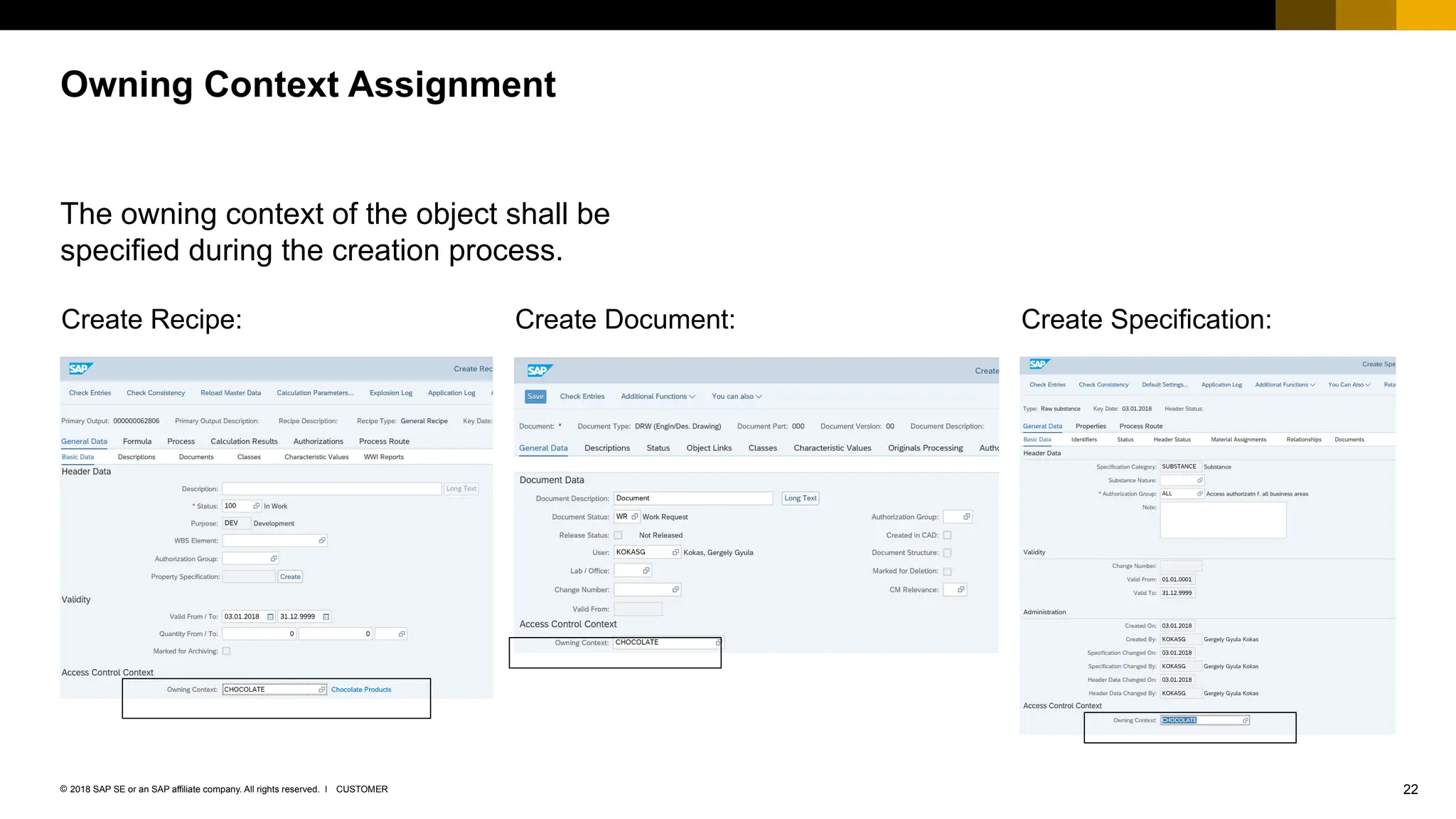
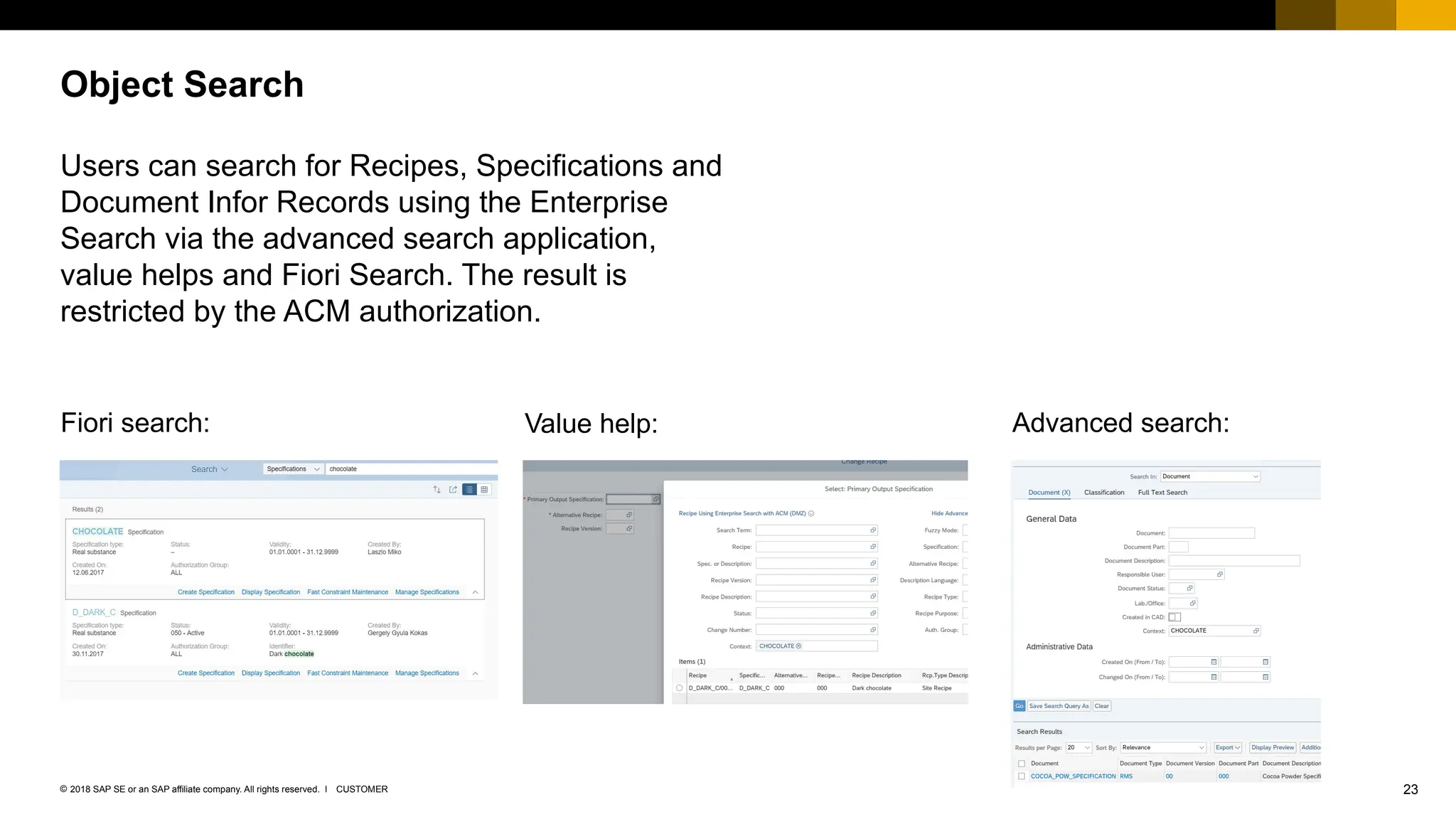
The document provides an overview of Access Control Management (ACM) in SAP S/4HANA, detailing its key features, usage scenarios, and functionalities. It explains how ACM controls access to business objects and integrates with roles and authorization objects, including the super and trusted user concepts. Additionally, it outlines customizing activities and maintenance tasks necessary for effective ACM implementation.