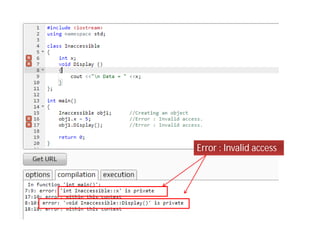
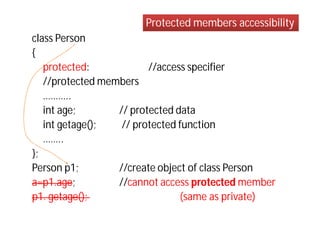
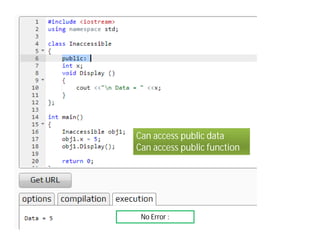
Access specifiers in C++ determine the visibility and accessibility of class members. The four access specifiers are private, public, and protected. Private members can only be accessed by methods within the class, while public members can be accessed by any code. Protected members are like private but can also be accessed by derived classes. If no access specifier is provided, members default to private. The document provides examples demonstrating how to declare access specifiers and the differences between private, protected, and public member accessibility.