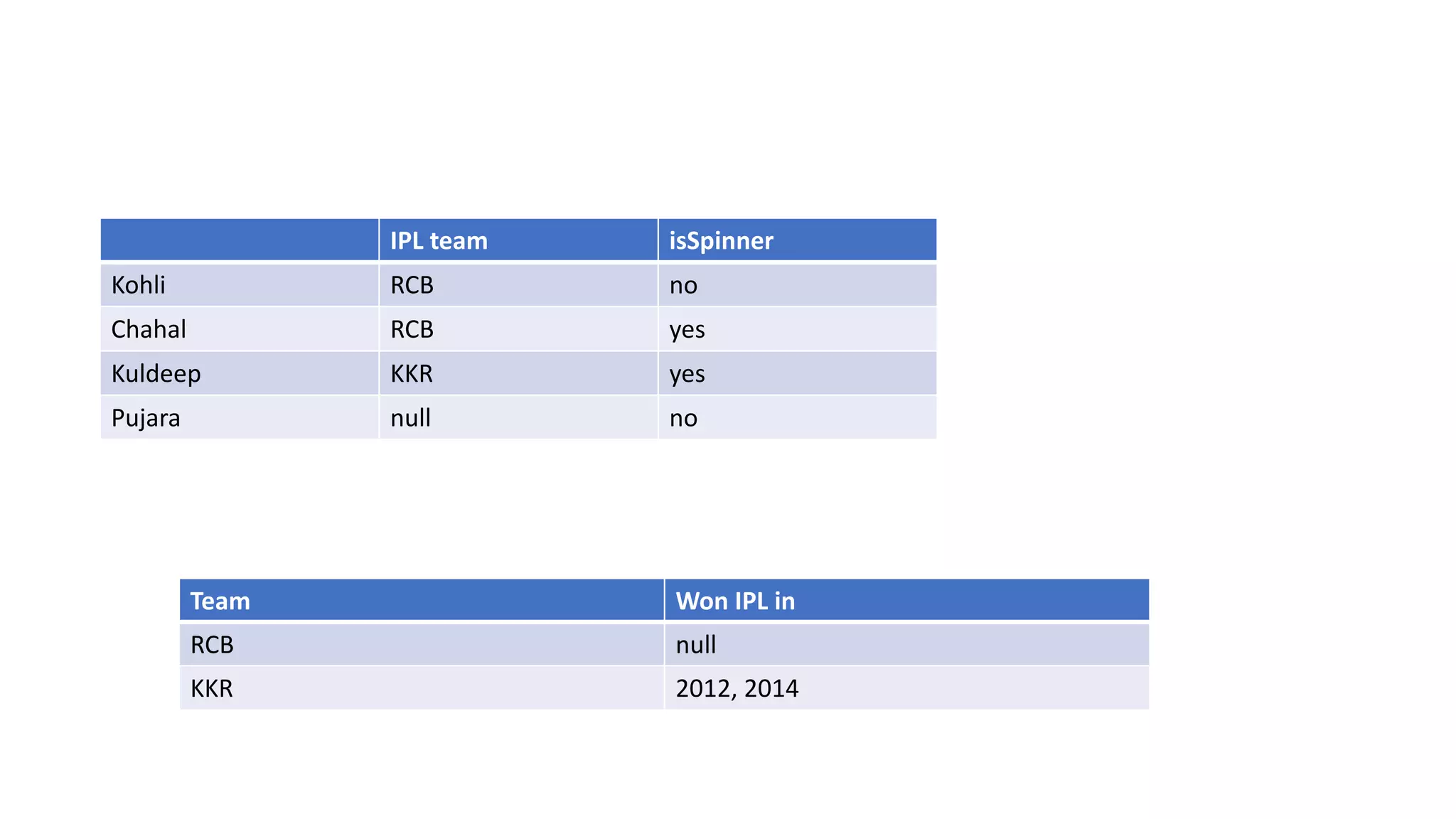
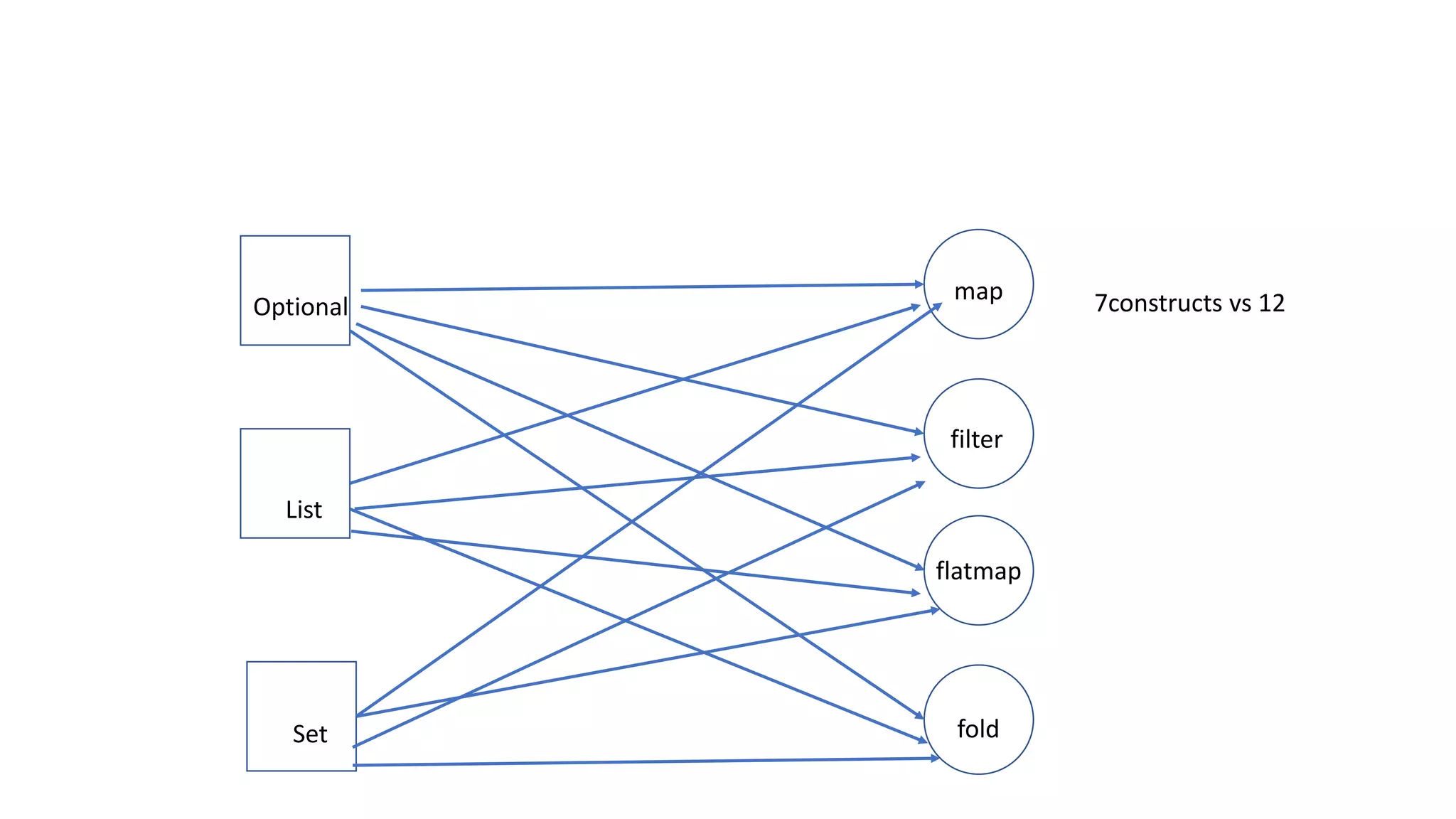
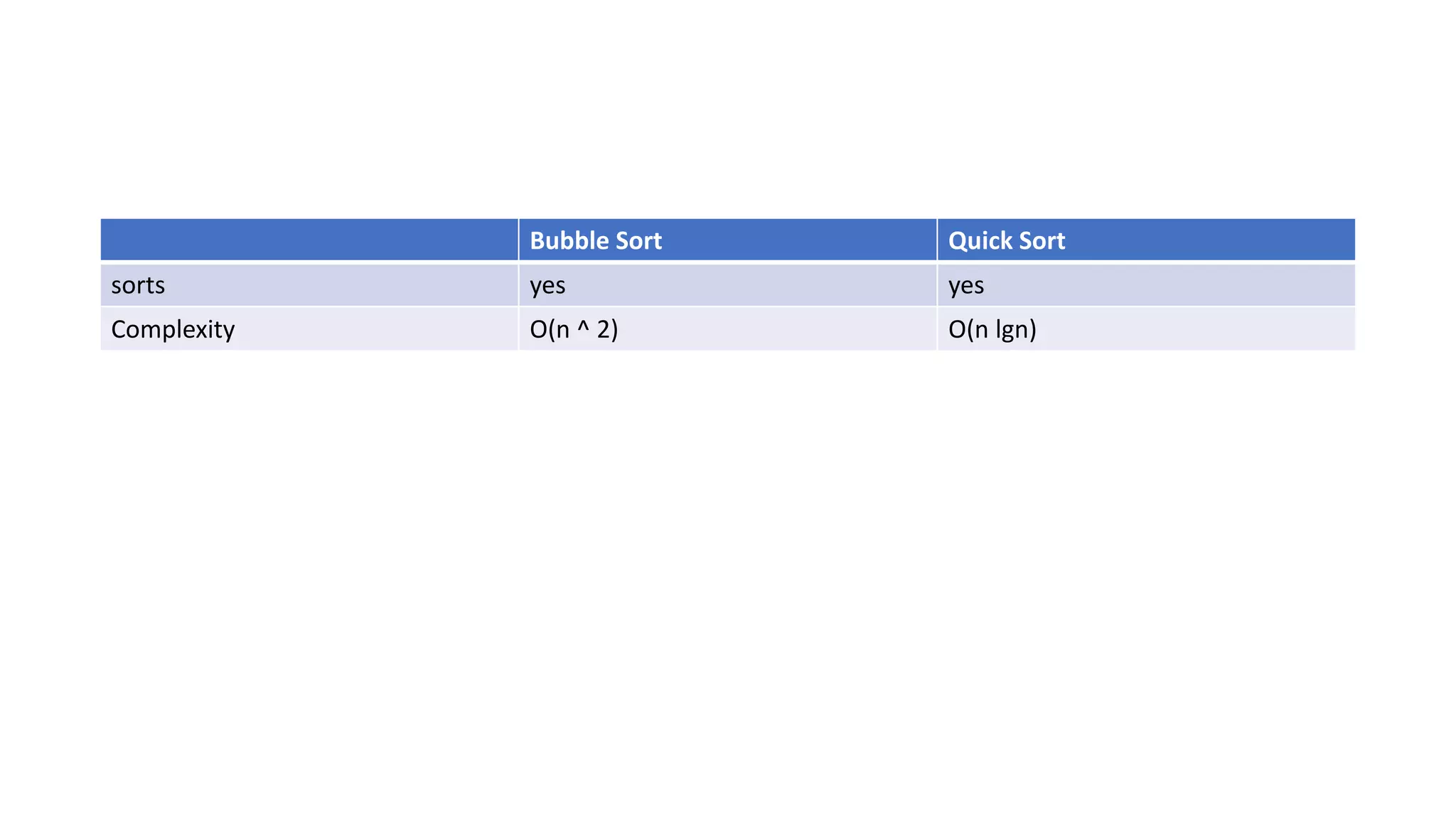
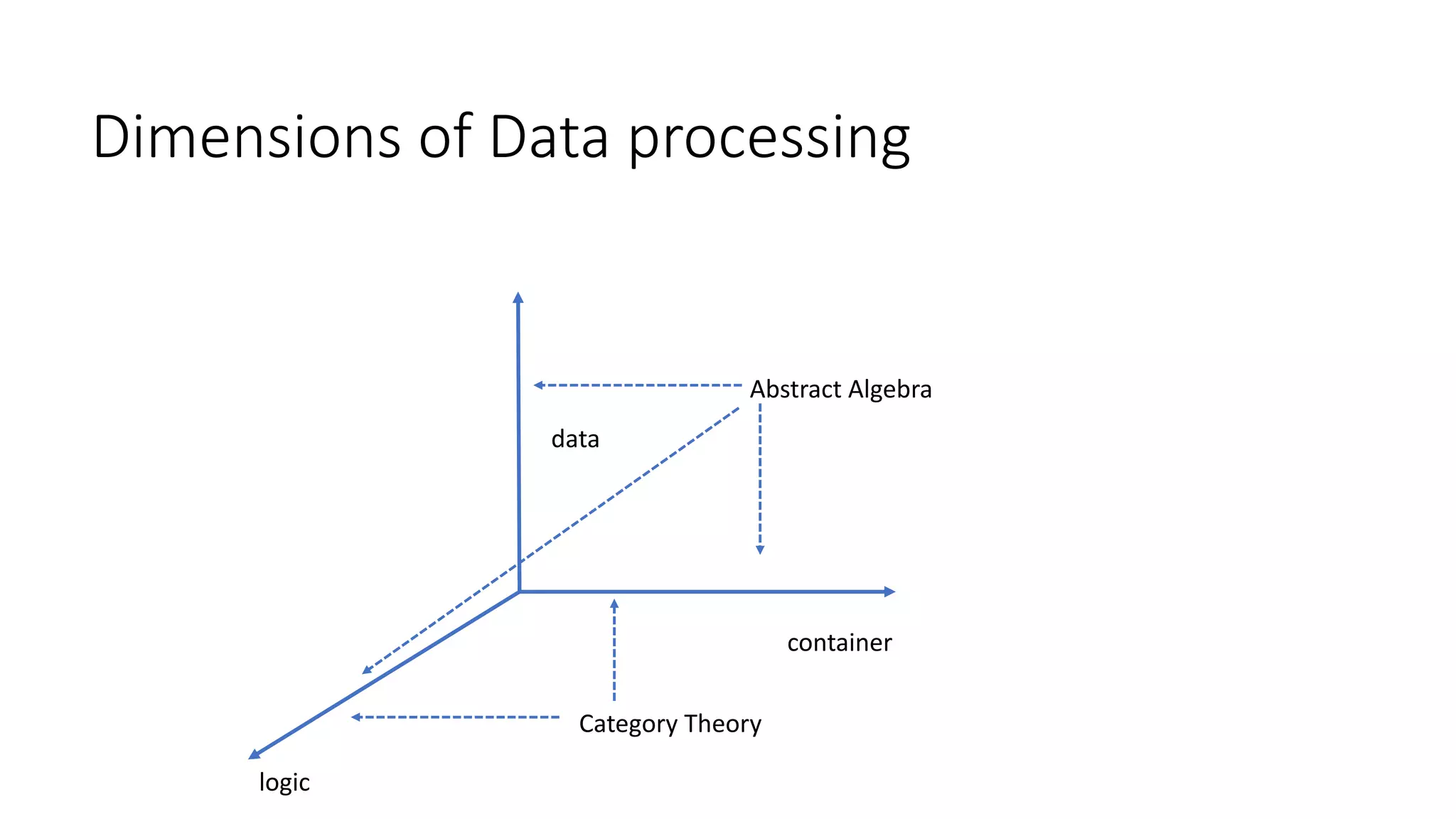
The document discusses data processing concepts including validation, sorting, summarization, aggregation, and analysis, along with their relevance to abstract algebra and category theory. It explains algebraic structures like monoids, semigroups, and functors using code snippets and defines concepts such as type classes and monads in programming. Additionally, it highlights practical applications of these theories in data structures and computational paradigms.





![def sum(list: List[Int]): Int = {
if(list.isEmpty) 0
else list.head + sum(list.tail)
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/paypal-190629095711/75/Abstract-Algebra-and-Category-Theory-9-2048.jpg)


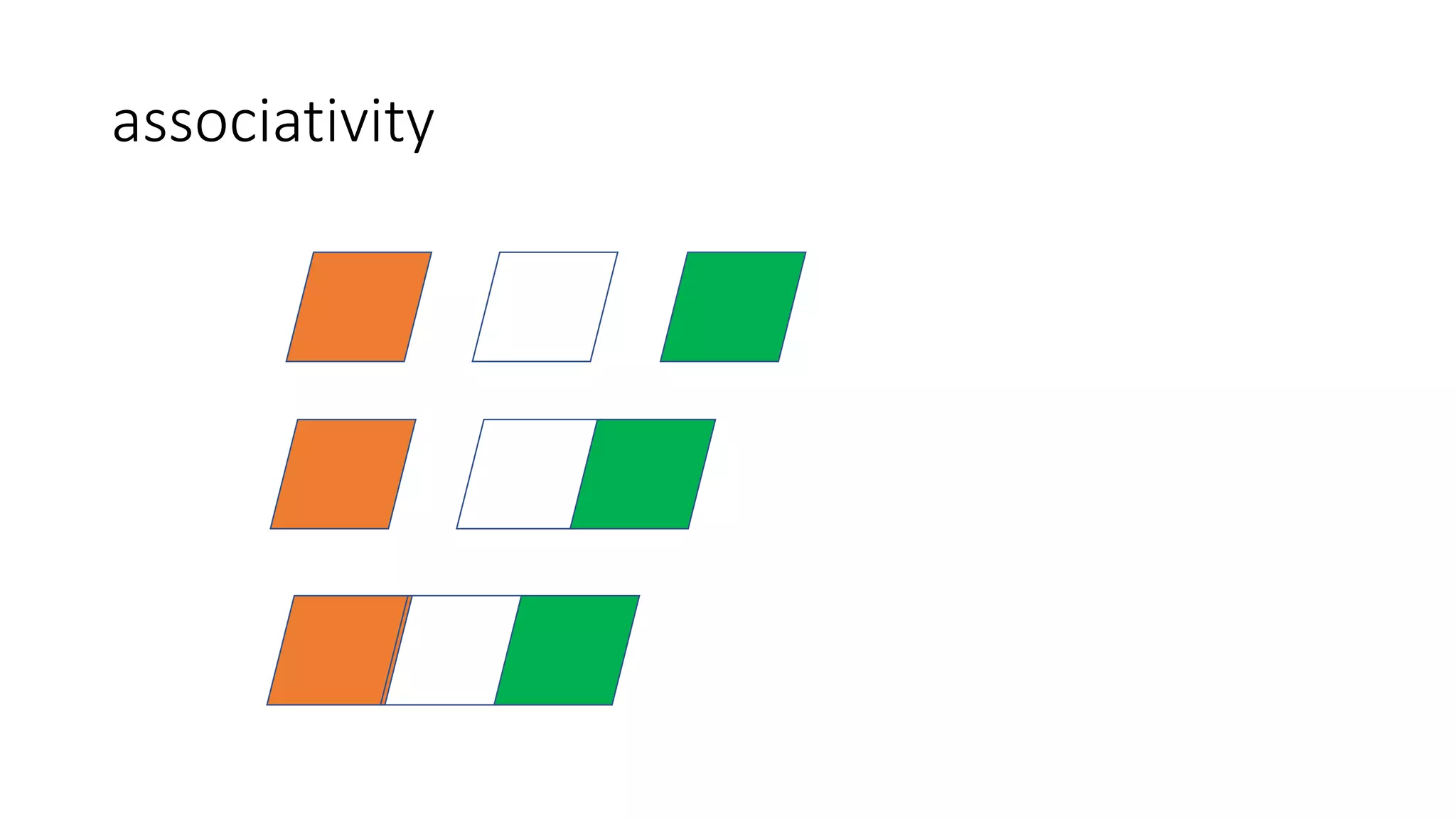

(op: (A1, A1) ⇒ A1): A1
• val l = List(1, 3, 5, 11)
println(l.fold(100) (_ - _));
(1 – 3) – 5 != 1 - (3 – 5)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/paypal-190629095711/75/Abstract-Algebra-and-Category-Theory-16-2048.jpg)

![Loop invariants
int result = 0
for(int index = 0; index < a.length; a++)
result += a[i]
result = sum { a, [0, index)}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/paypal-190629095711/75/Abstract-Algebra-and-Category-Theory-19-2048.jpg)
![• [Int, 0, +] is a monoid](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/paypal-190629095711/75/Abstract-Algebra-and-Category-Theory-20-2048.jpg)
![void mergeSort(List list, int l, int r)
{
if (l < r)
{
// Same as (l+r)/2, but avoids overflow for
// large l and h
int m = l+(r-l)/2;
// Sort first and second halves
mergeSort(list, l, m);
mergeSort(list, m+1, r);
merge(list, l, m, r);
}
}
[SortedList, Merge, Empty List] is a monoid](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/paypal-190629095711/75/Abstract-Algebra-and-Category-Theory-21-2048.jpg)



![trait Monoid[A] {
// an identity element
def id: A
// an associative
operation
def op(x: A, y: A): A
}
implicit val intAddition = new Monoid[Int] {
def id = 0
def op(x:Int, y: Int) = x + y
}
implicit def fold[A](la: List[A])(implicit am: Monoid[A]): A =
la.foldLeft(am.id)(am.op)
fold(List(1, 3, 4)) => 8](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/paypal-190629095711/75/Abstract-Algebra-and-Category-Theory-25-2048.jpg)






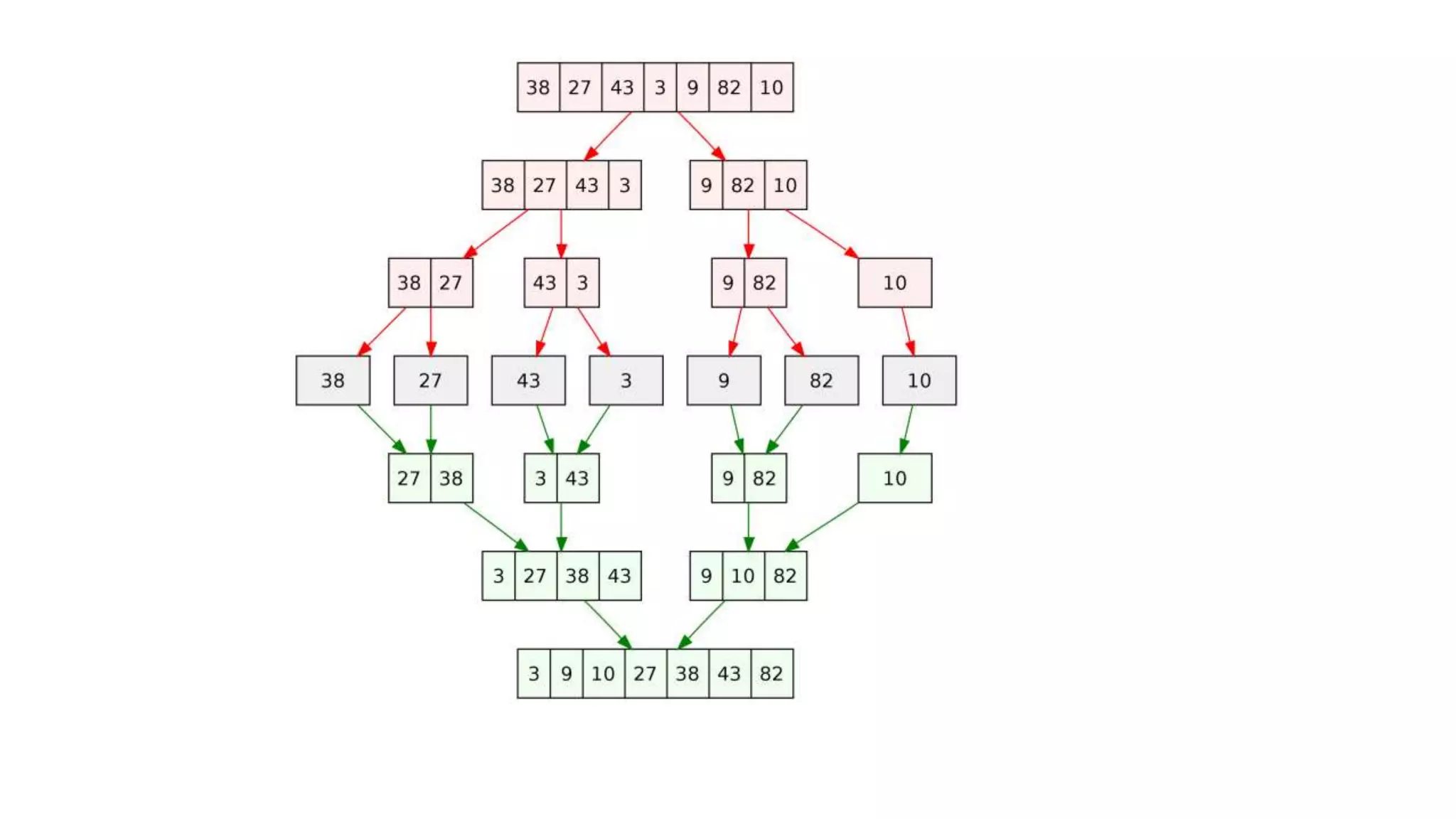
![Find if an element is present in an array
implicit val boolOr = new Monoid[Boolean] {
def id = false;
def op(x: Boolean , y: Boolean) = x || y
}
val list = List(1, 3, 4)
println(fold(list.map(x => x == 2))); The list was converted to a list of Booleans
and then folded over](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/paypal-190629095711/75/Abstract-Algebra-and-Category-Theory-33-2048.jpg)




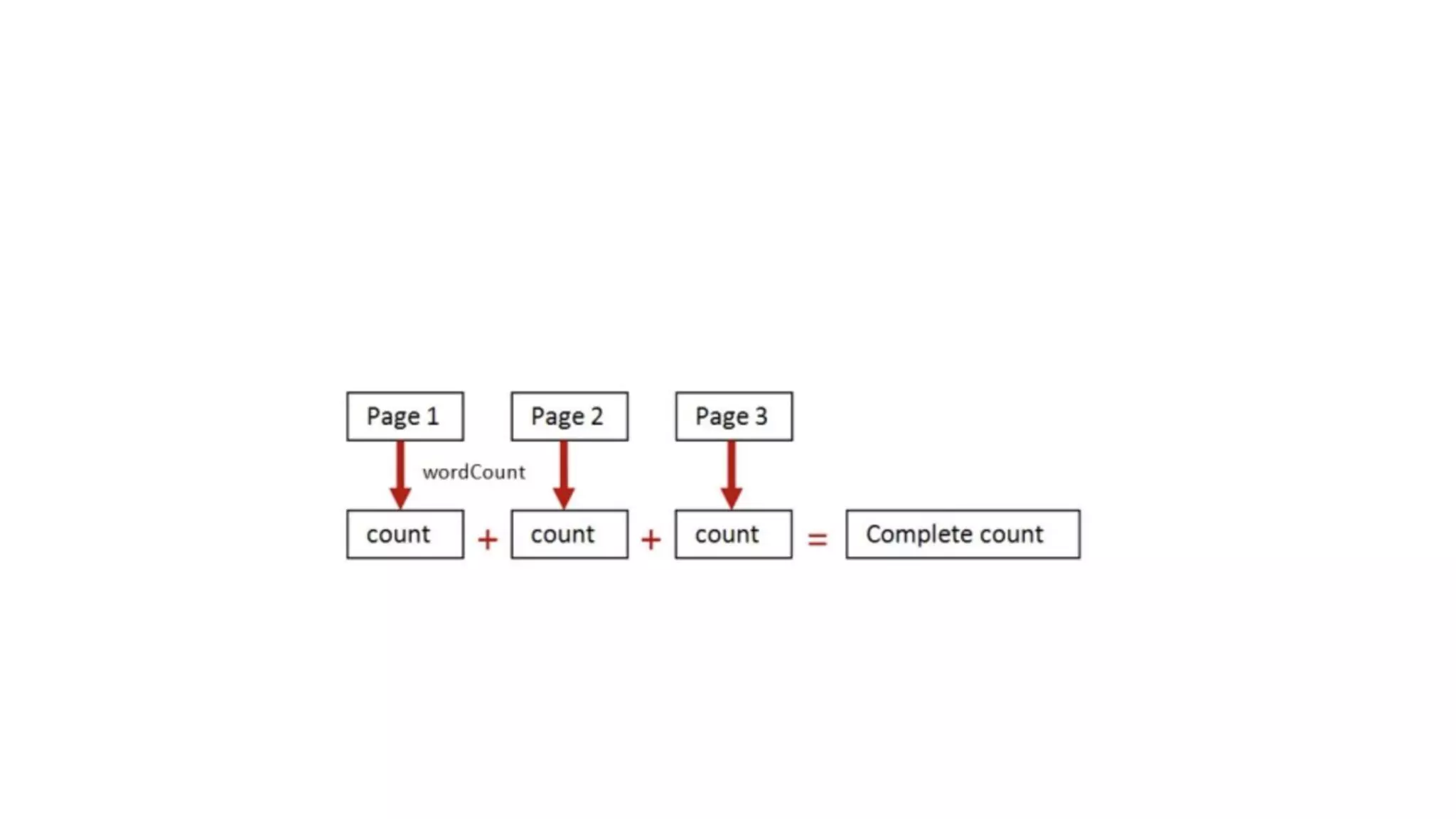




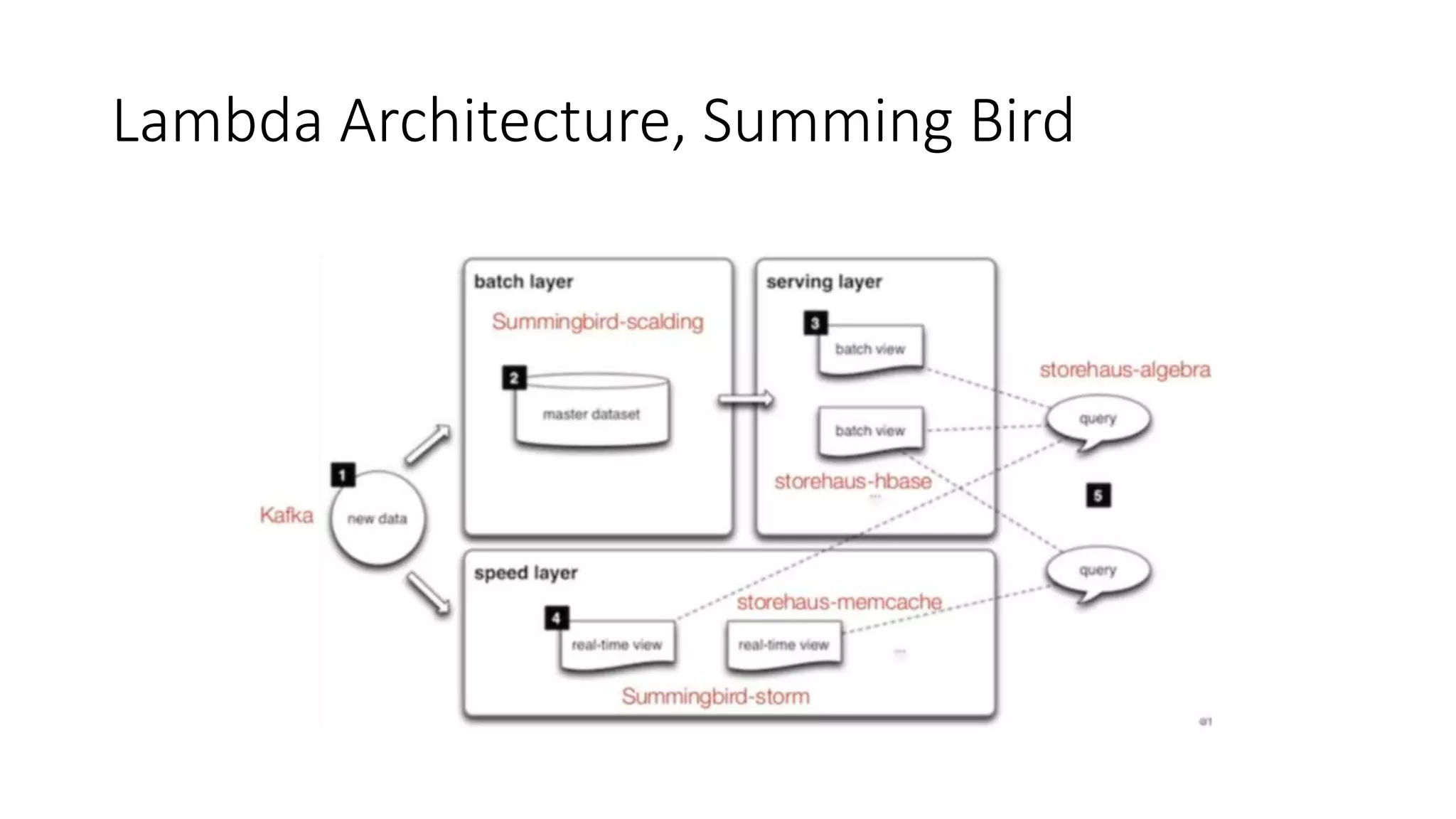

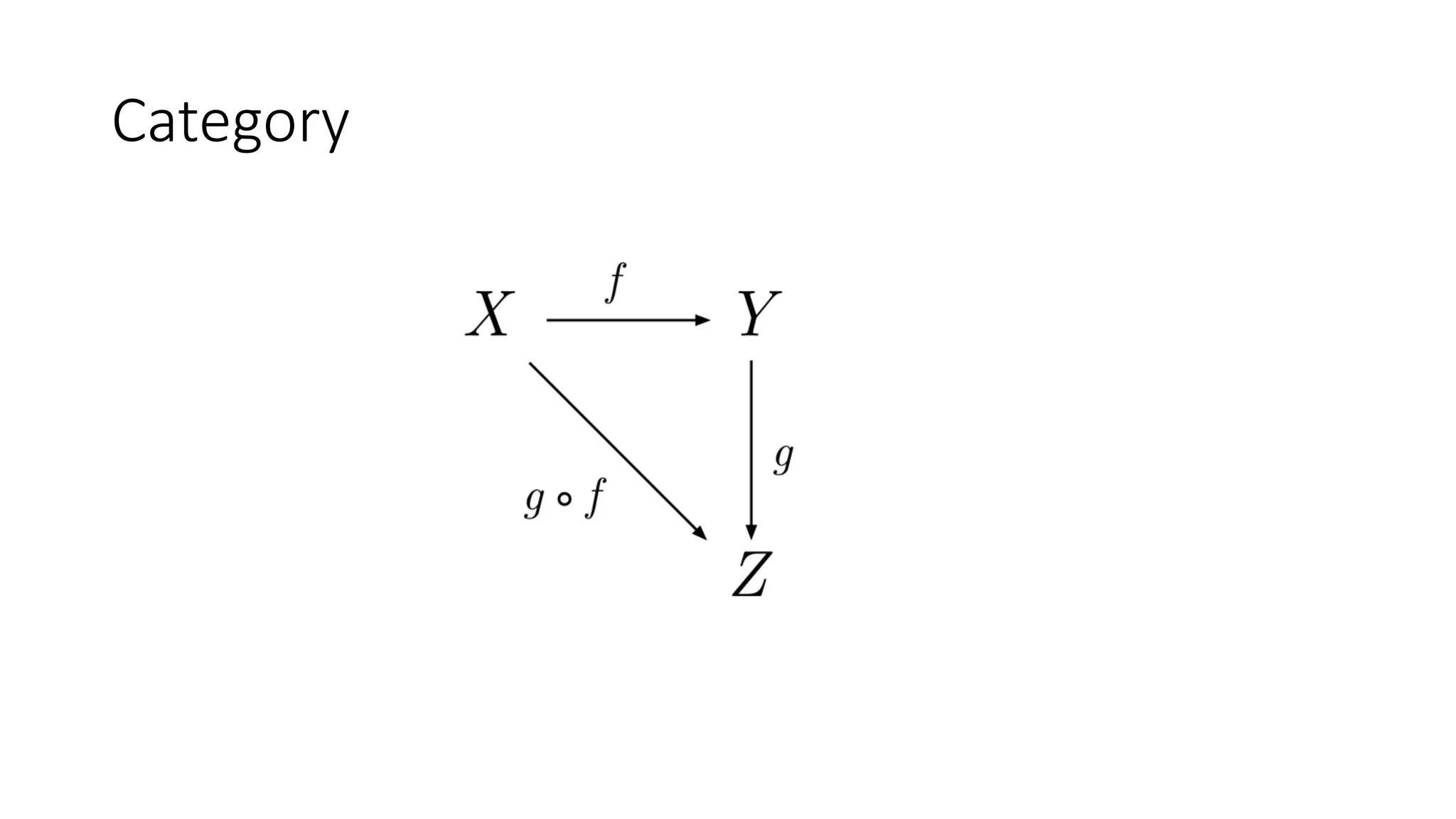





![• trait Functor[F[_]] { def map[A, B](fa: F[A])(f: A => B): F[B] }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/paypal-190629095711/75/Abstract-Algebra-and-Category-Theory-53-2048.jpg)
![Monads
trait Monad[F[_]] {
def flatMap[A, B](fa: F[A])(f: (A) => F[B]):
F[B] def pure[A](x: A): F[A]
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/paypal-190629095711/75/Abstract-Algebra-and-Category-Theory-54-2048.jpg)