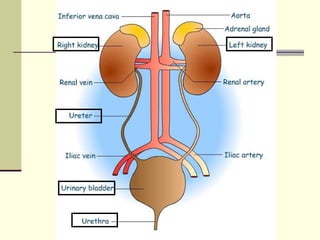
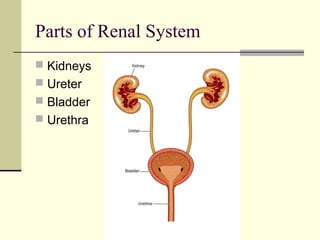
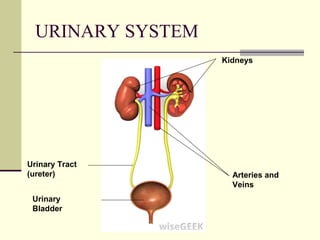
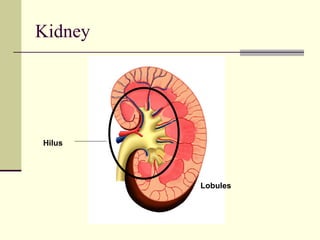
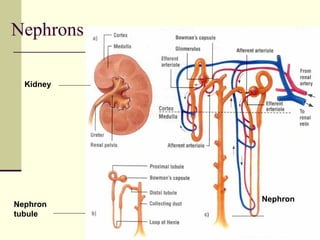
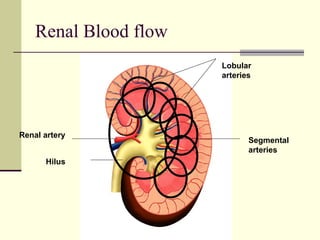
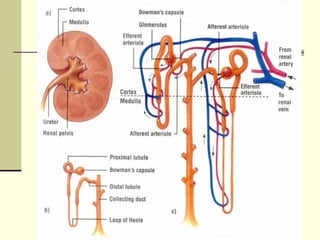
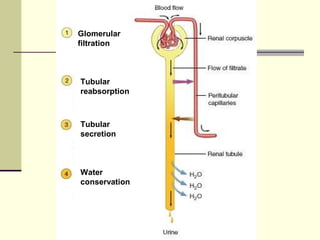
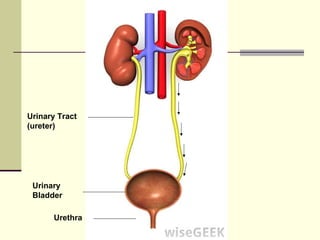
The urinary system is responsible for filtering blood and producing urine. The kidneys filter waste from the blood to form urine, while regulating water and electrolyte levels. Urine travels from the kidneys through ureters to the bladder, where it is stored until excreted through the urethra. The key parts are the kidneys, which contain nephrons that filter blood and reabsorb necessary substances; ureters, which transport urine from kidneys to bladder; and bladder, which stores urine until excretion. Together this system eliminates wastes and regulates fluid and electrolyte balance in the body.