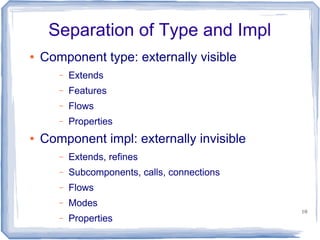
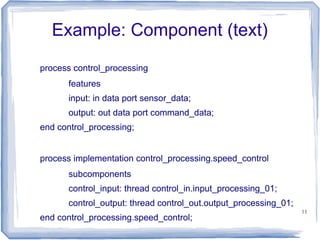
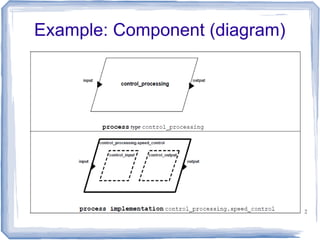
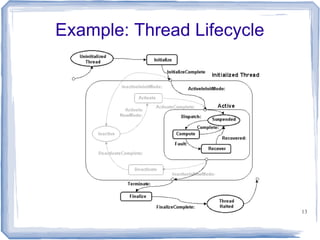
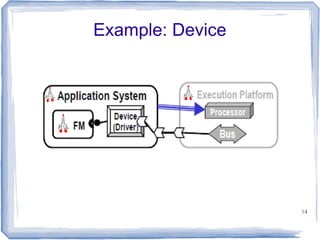
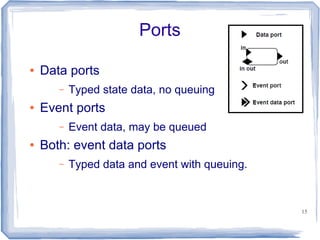
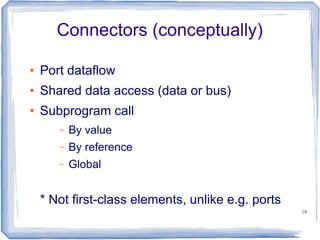
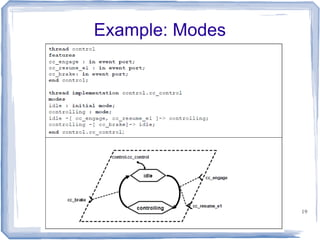
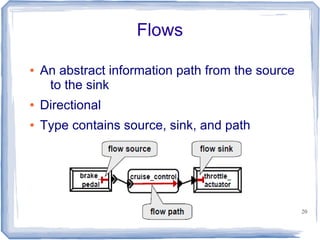
This document provides an overview of the Architecture Analysis and Design Language (AADL). AADL is a text-based language used to model embedded systems. It separates system architecture into software and hardware components, and separates component types from their implementations. AADL models can be used to generate code, perform analysis, and capture system topology, properties, and modes. Key features include different component types, ports, connectors, bindings, flows, and annexes for extensions.