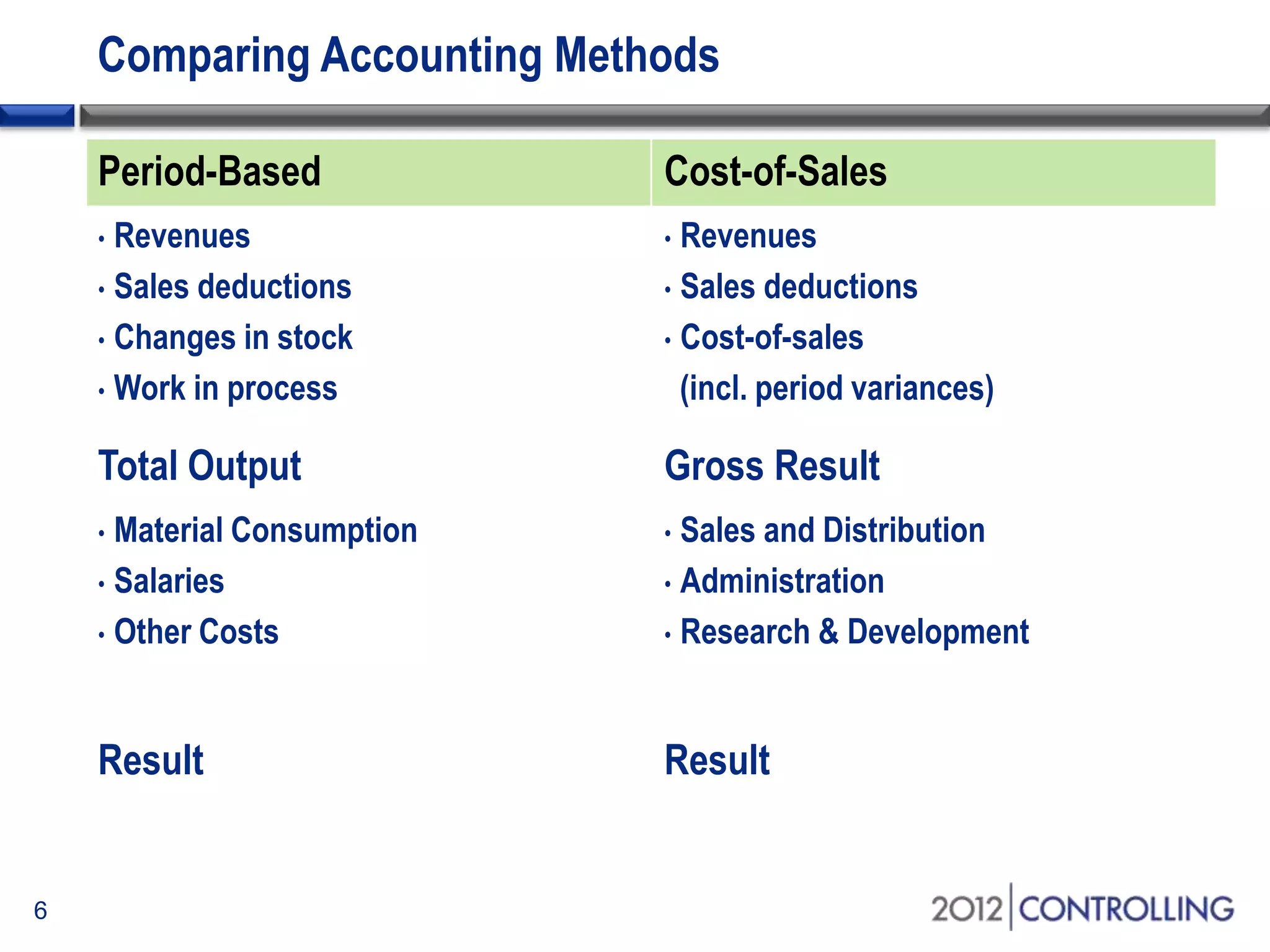
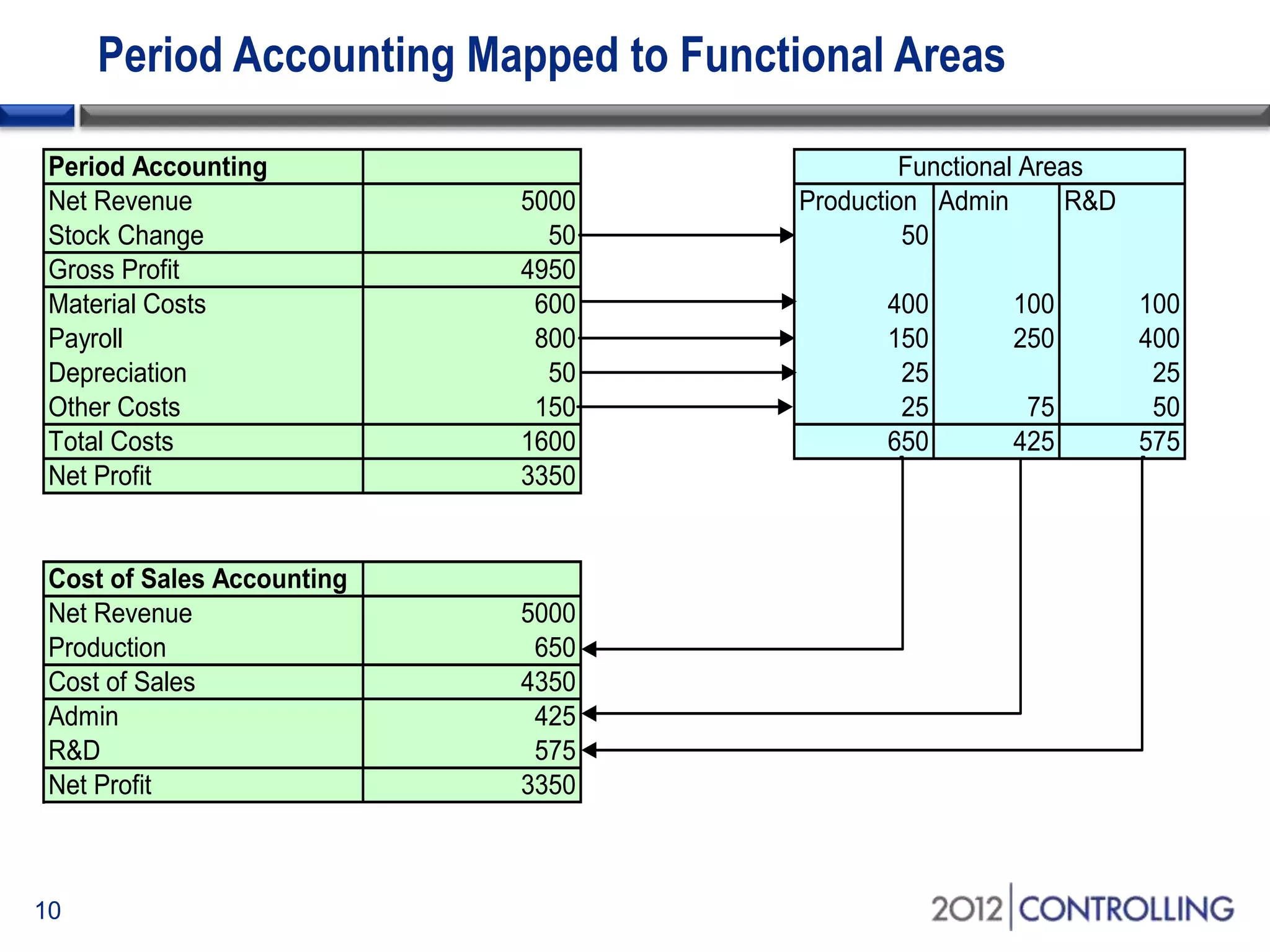
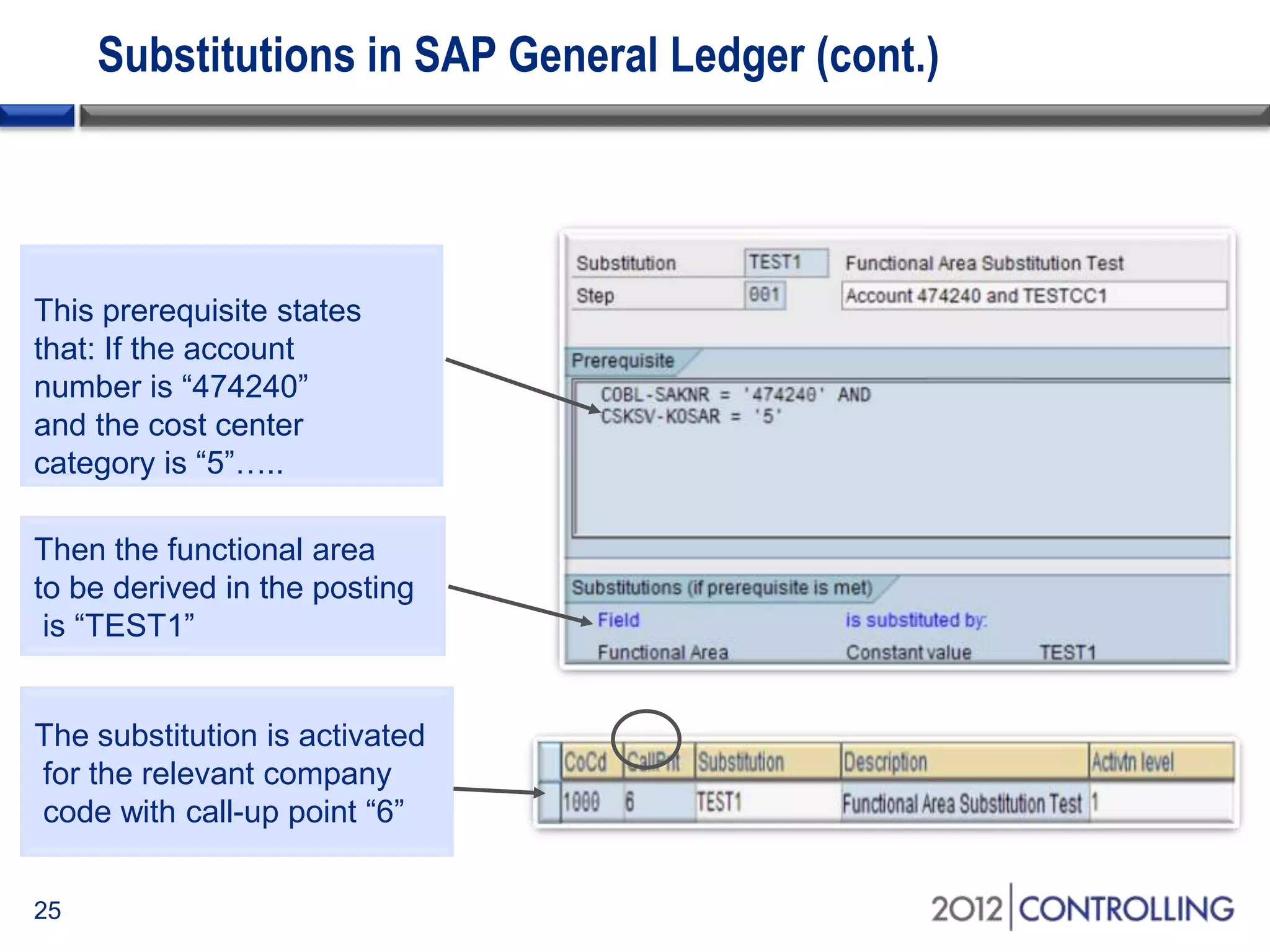
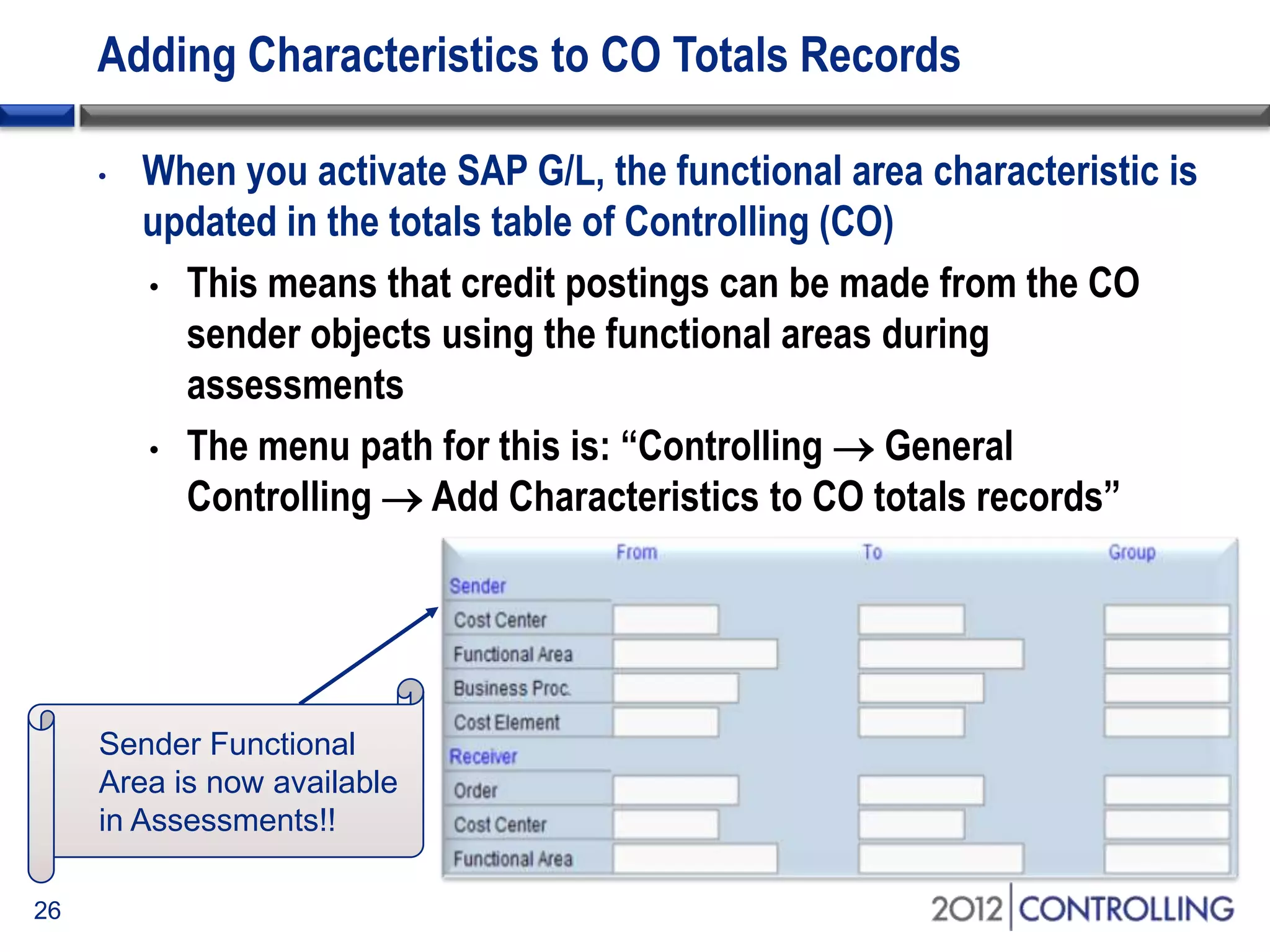
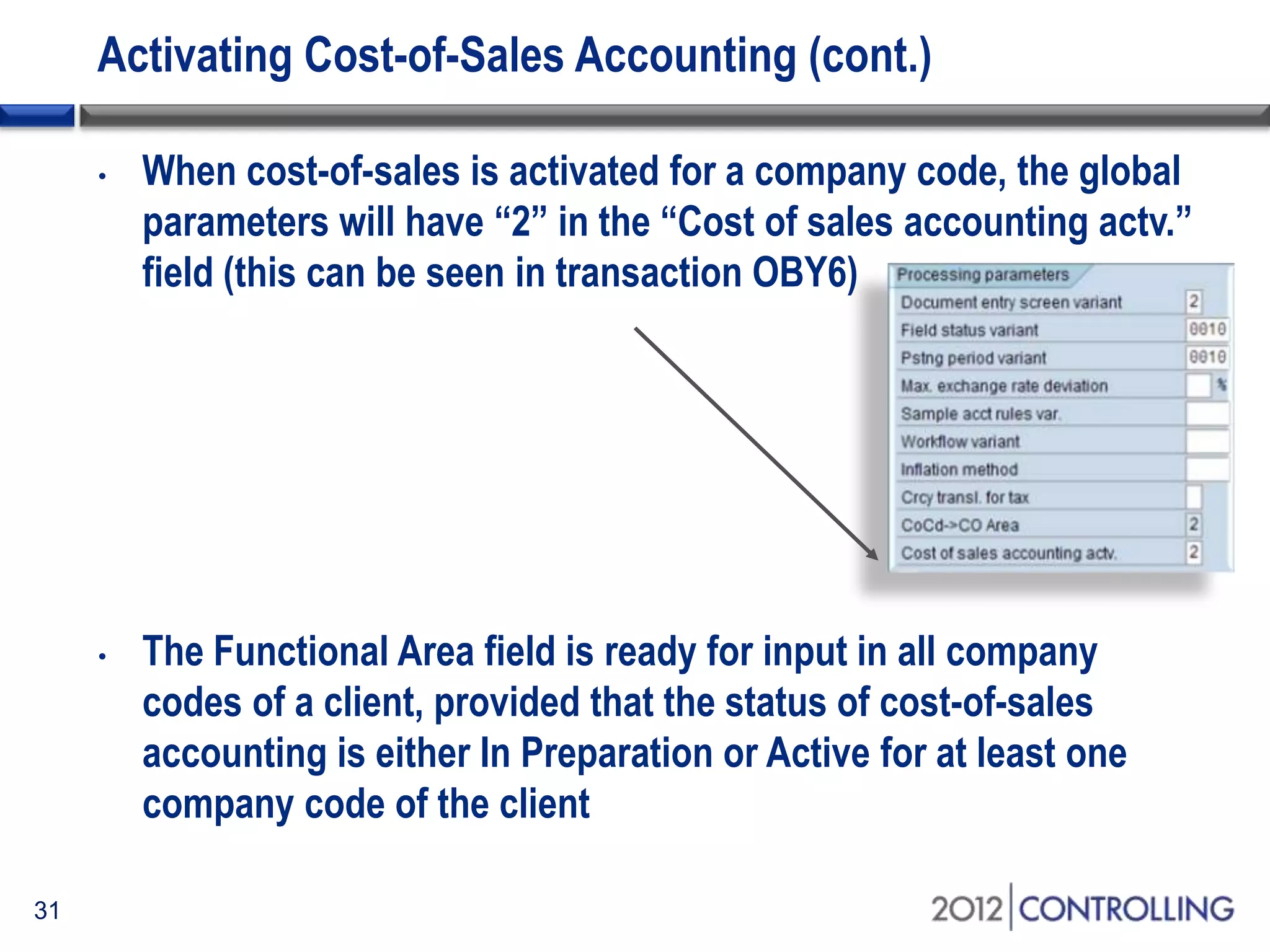
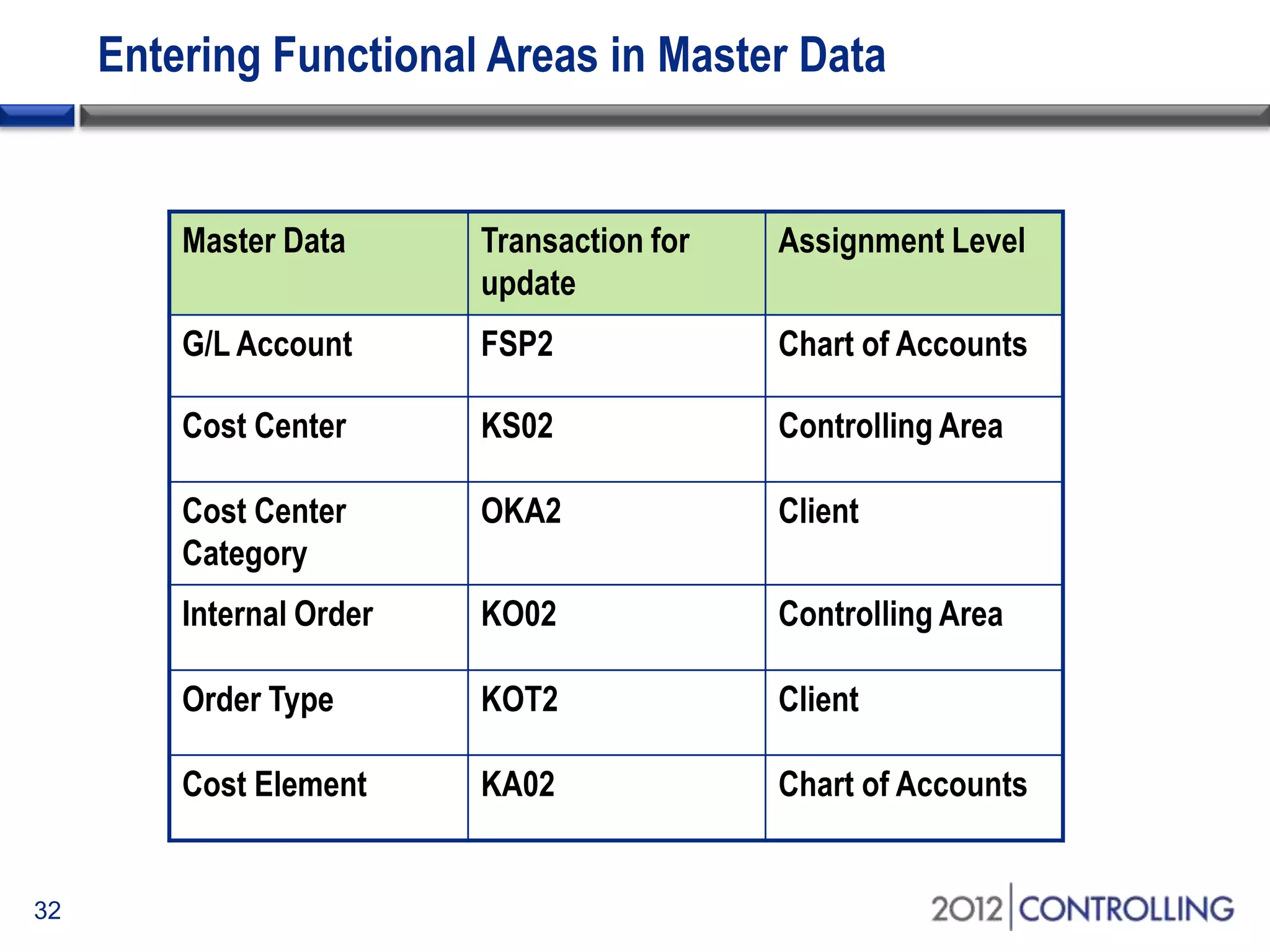
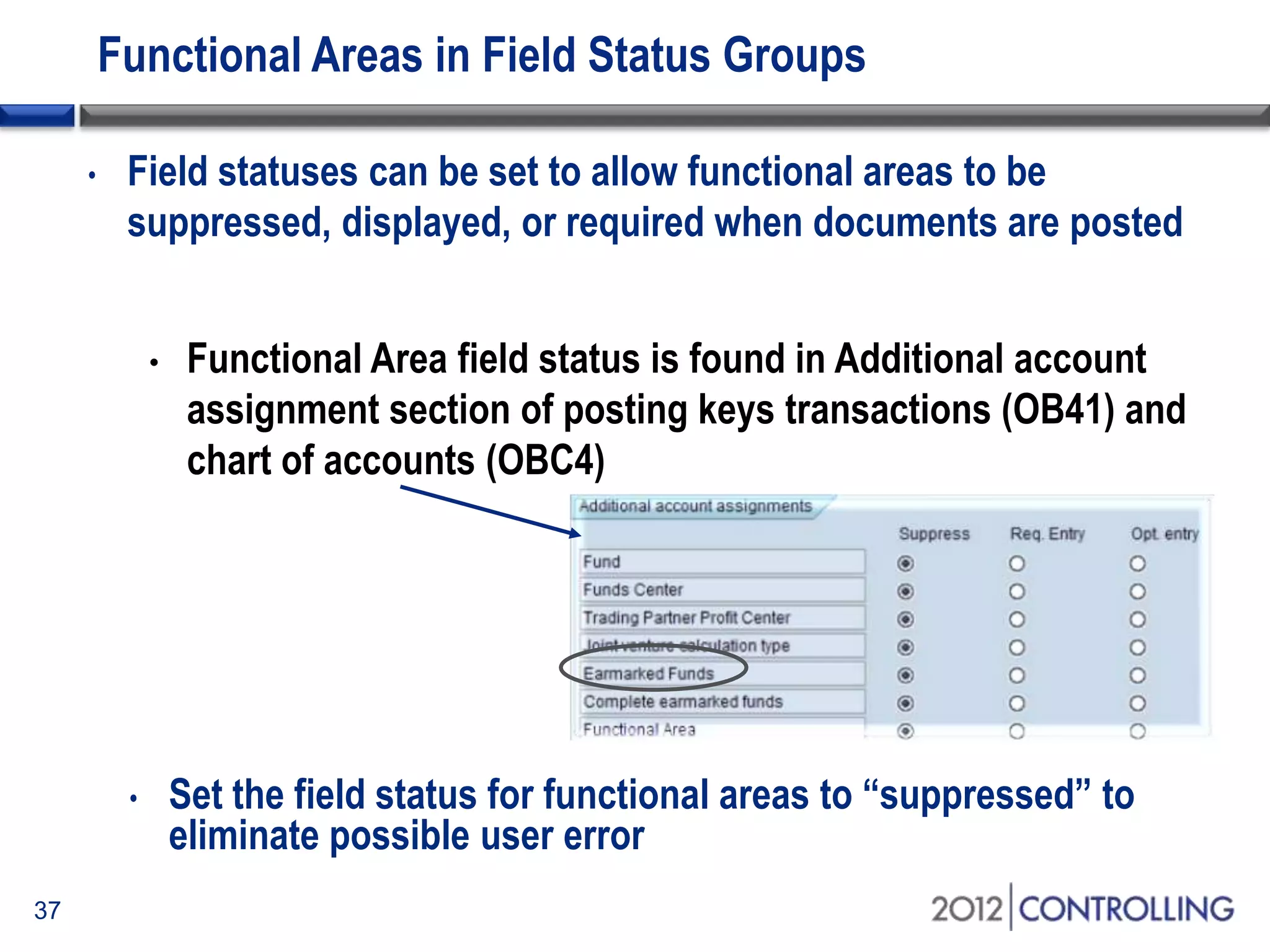
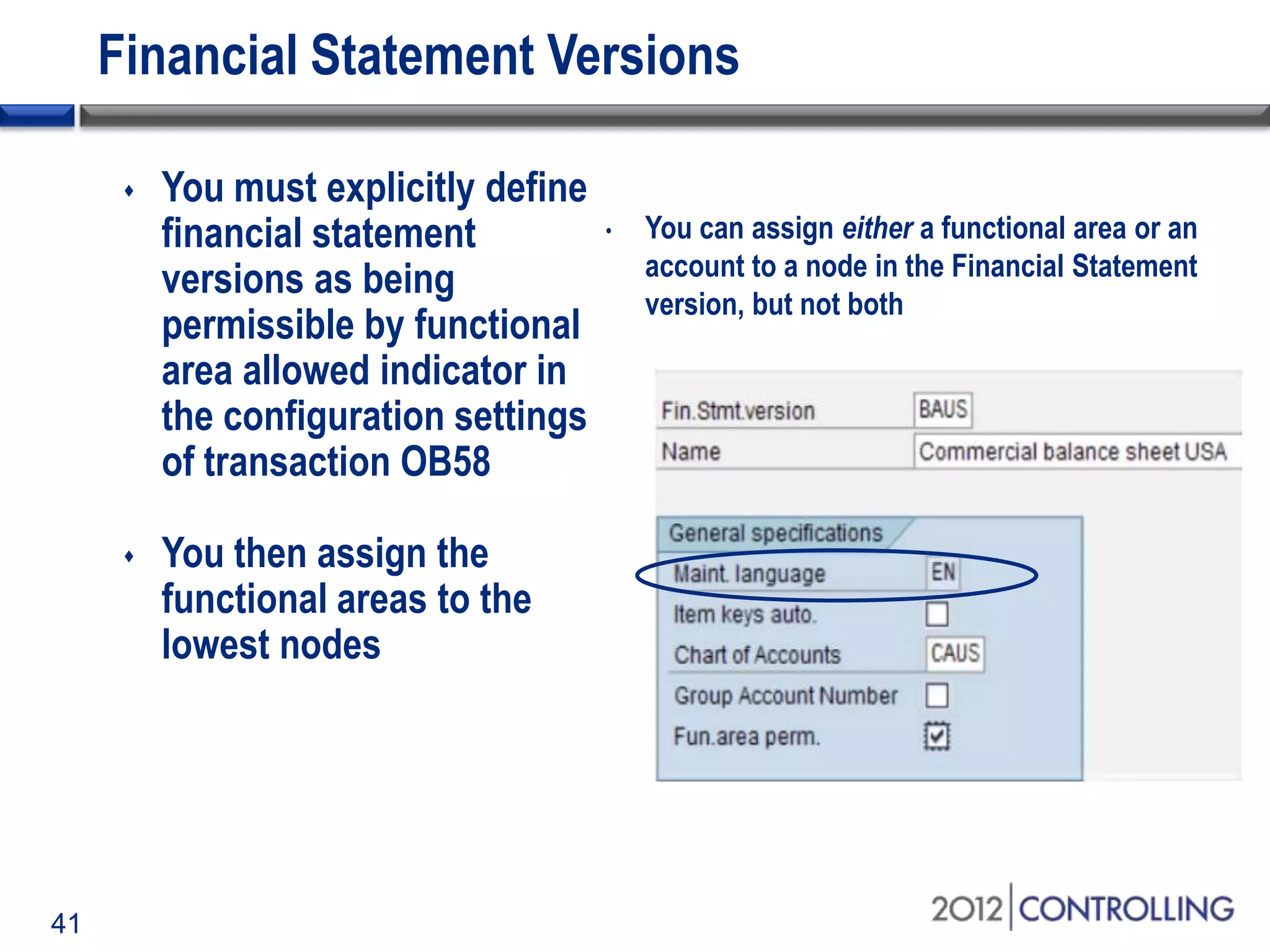
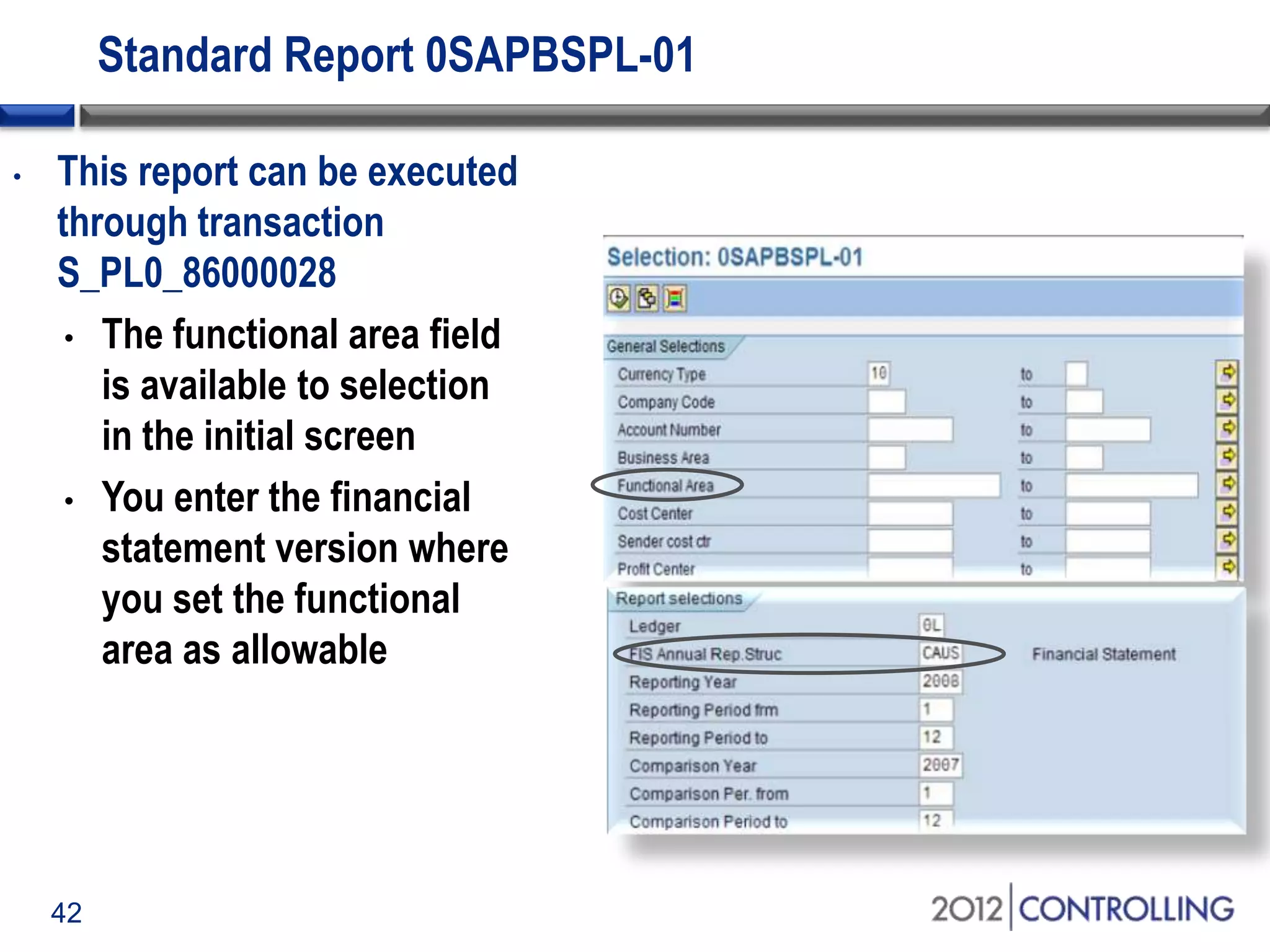
- The document provides guidance on using functional areas for cost-of-sales accounting in SAP General Ledger, including how to activate cost-of-sales functionality, define functional areas in master records, and create cost-of-sales financial statements by functional area using standard reports.
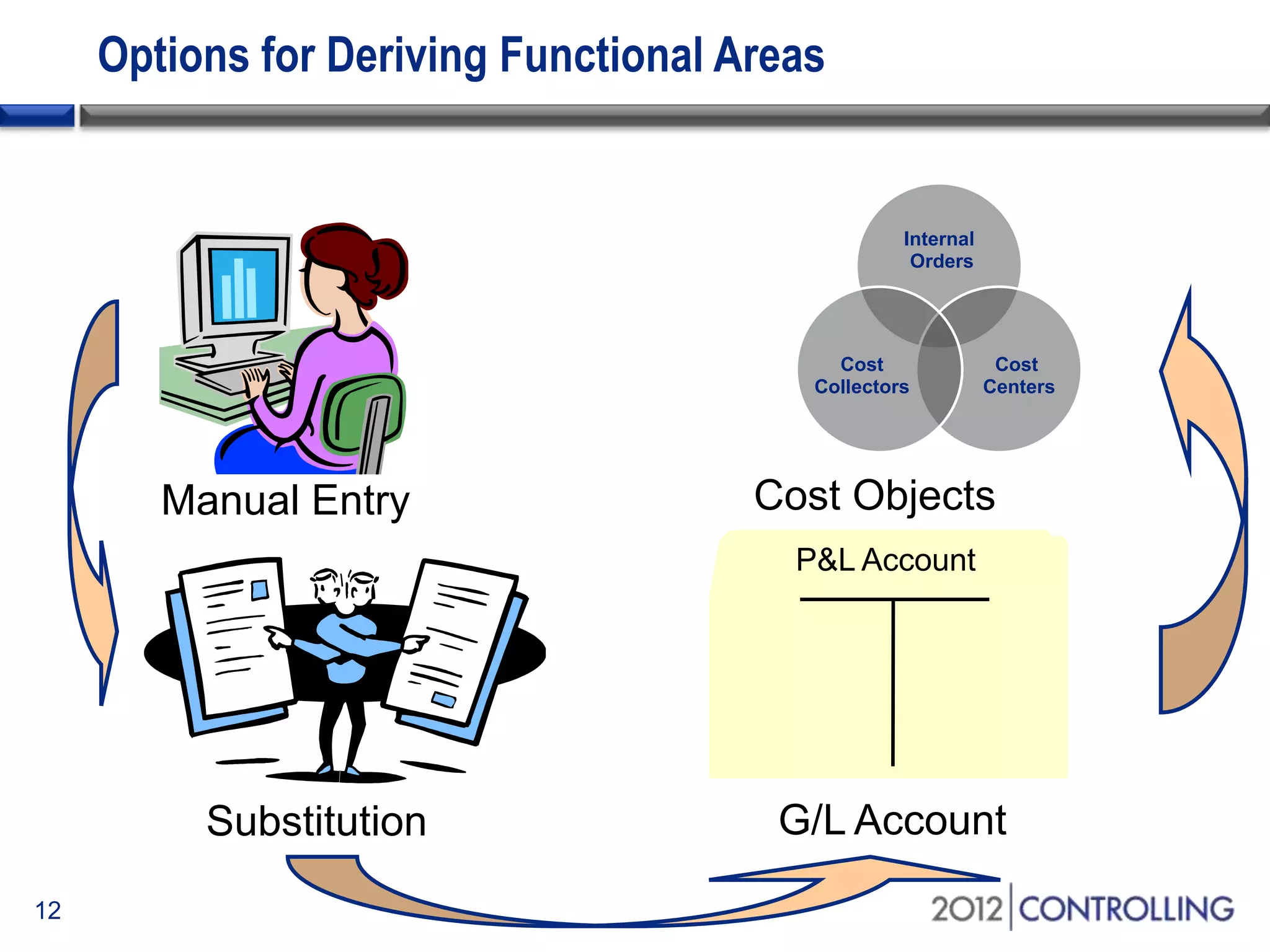
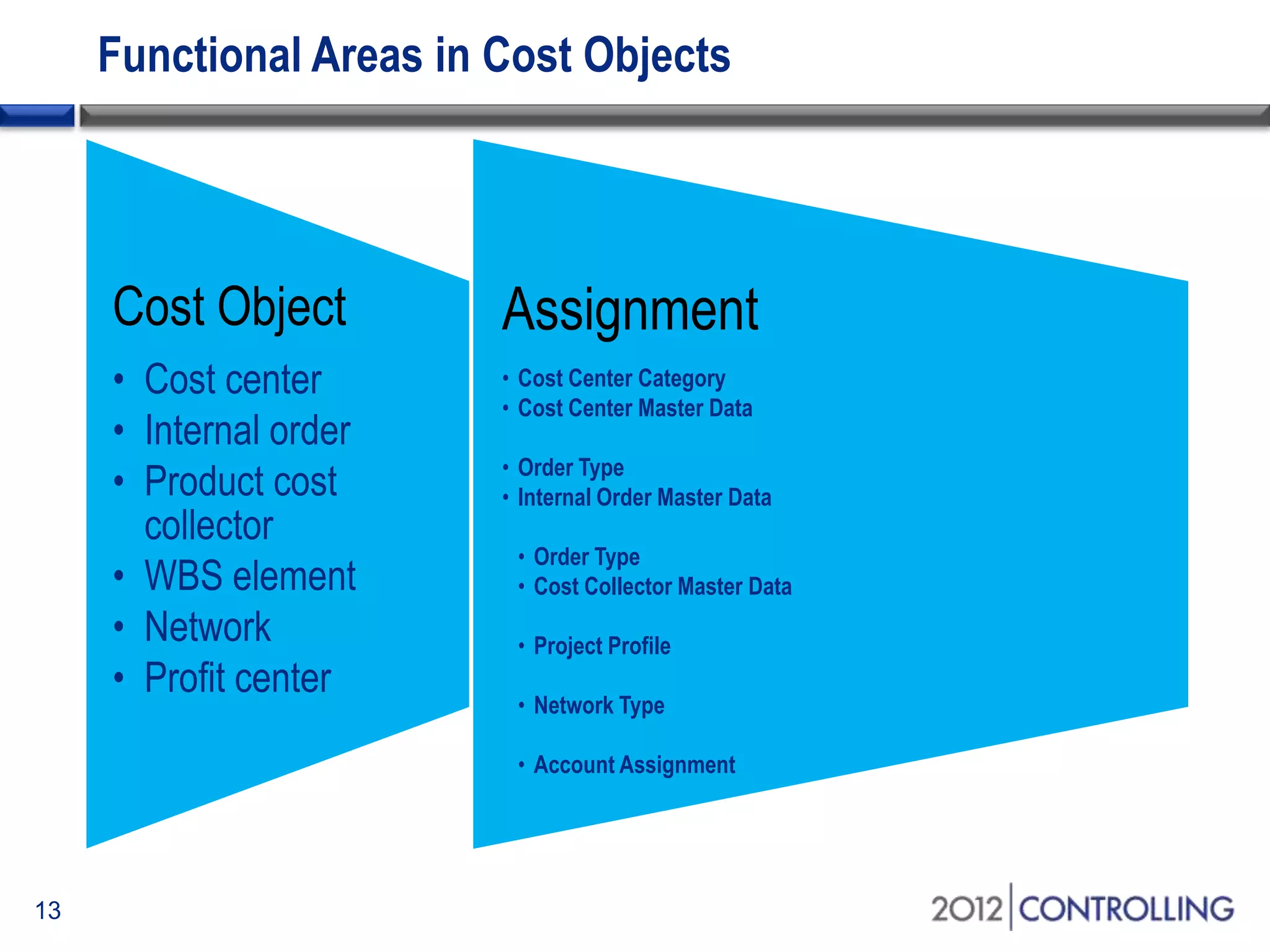
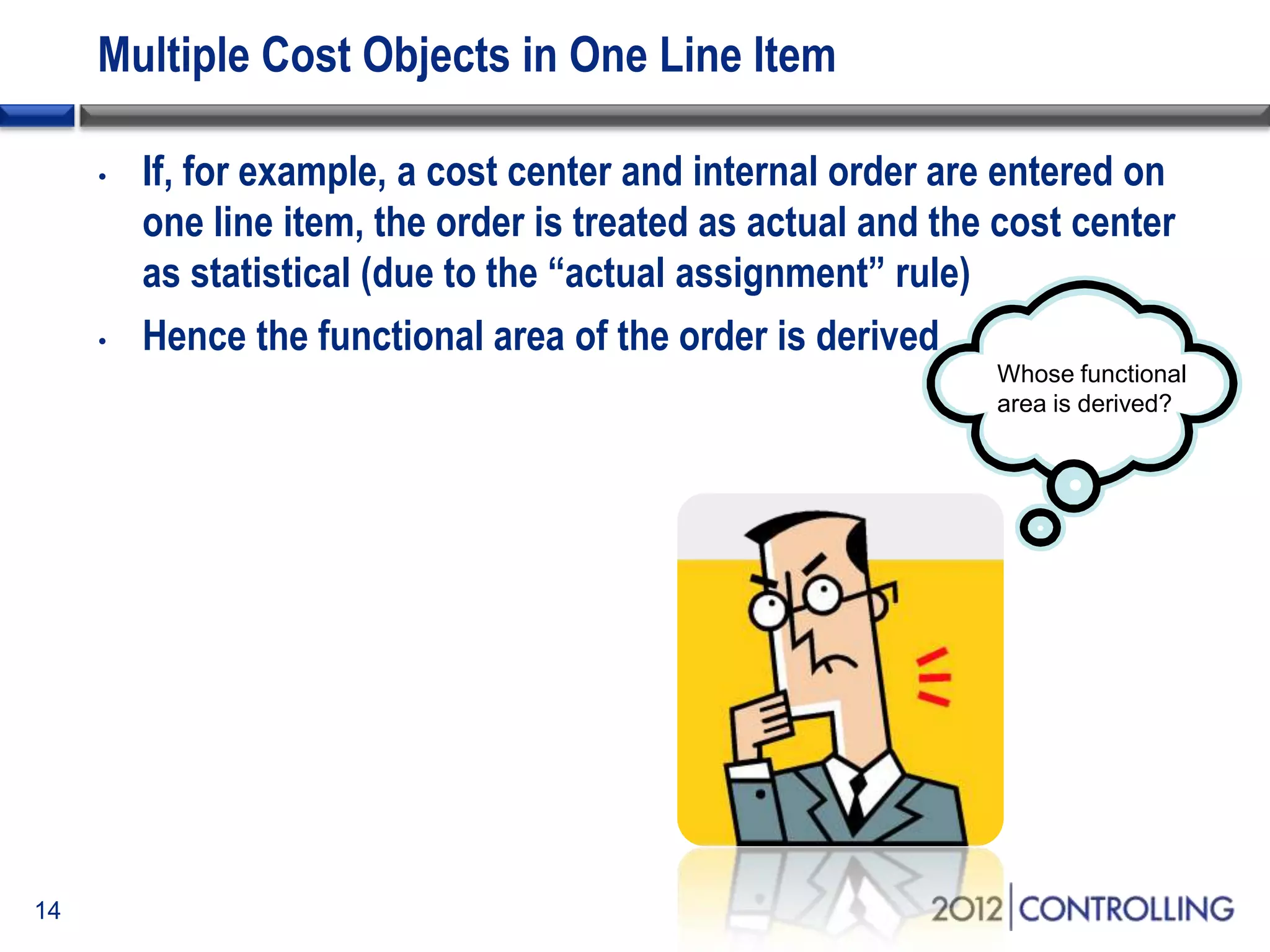
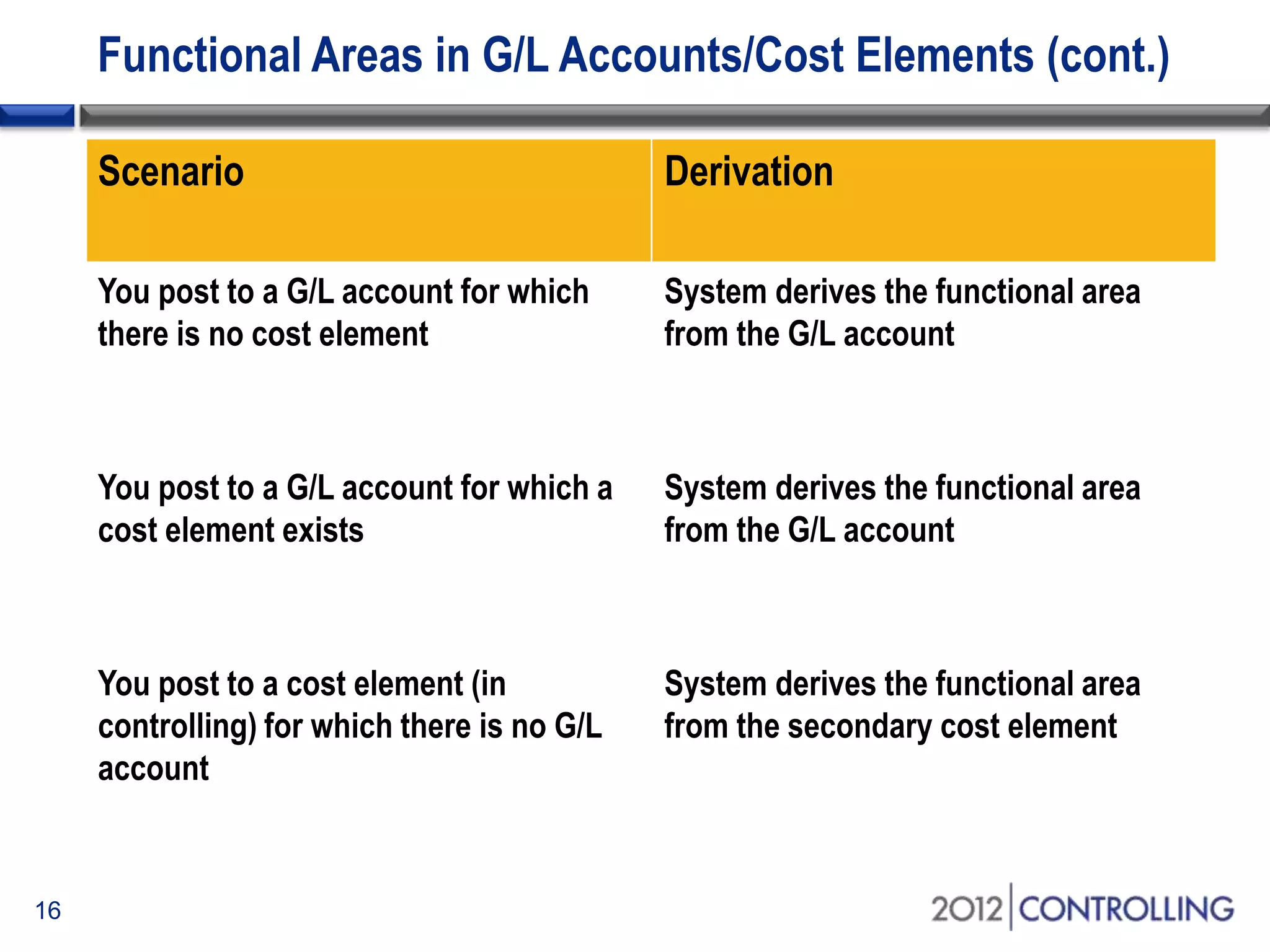
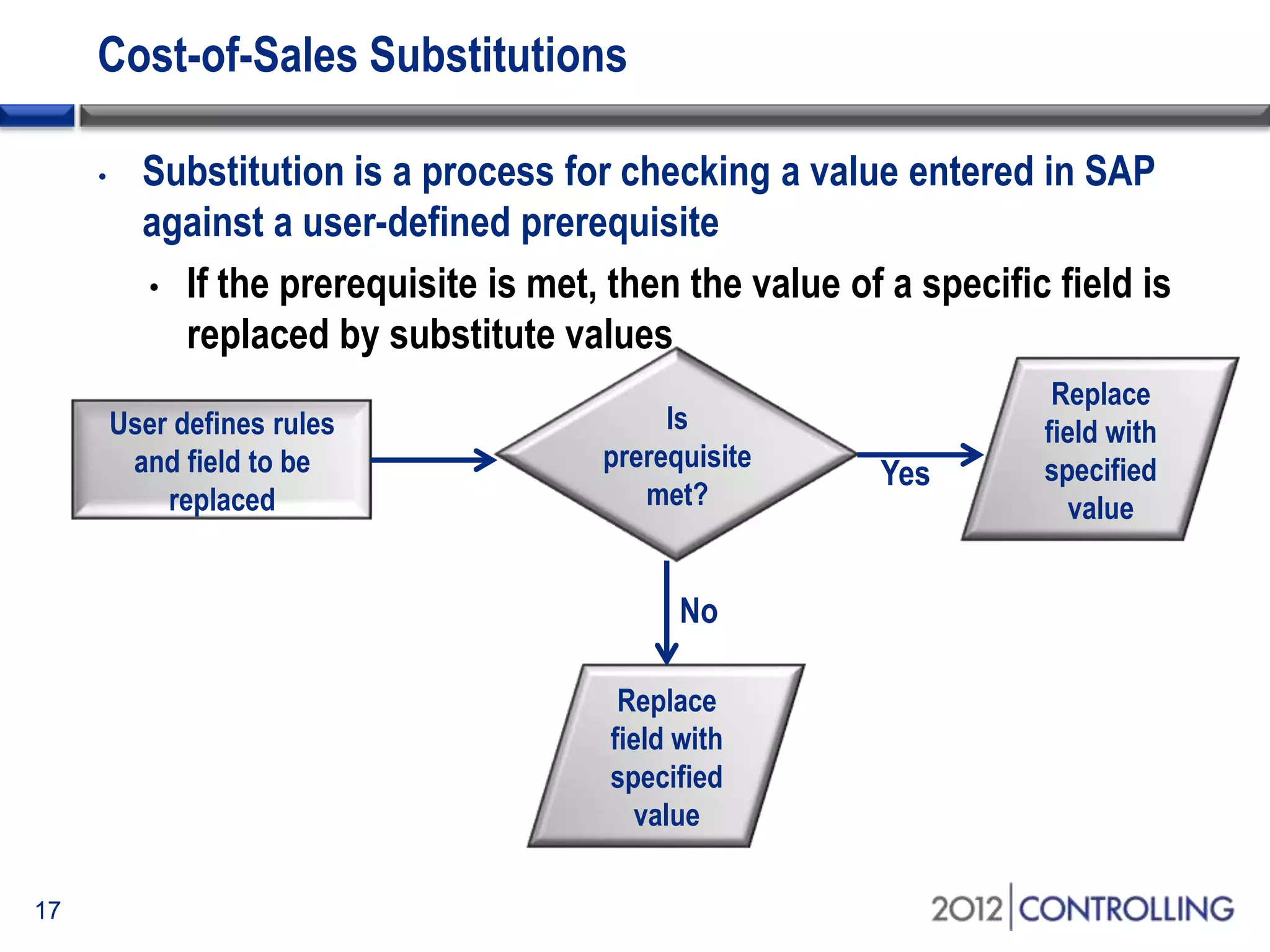
- It discusses approaches for deriving functional areas from cost objects, G/L accounts, substitutions, and manual entry. Activating the cost-of-sales scenario updates the functional area field for postings.
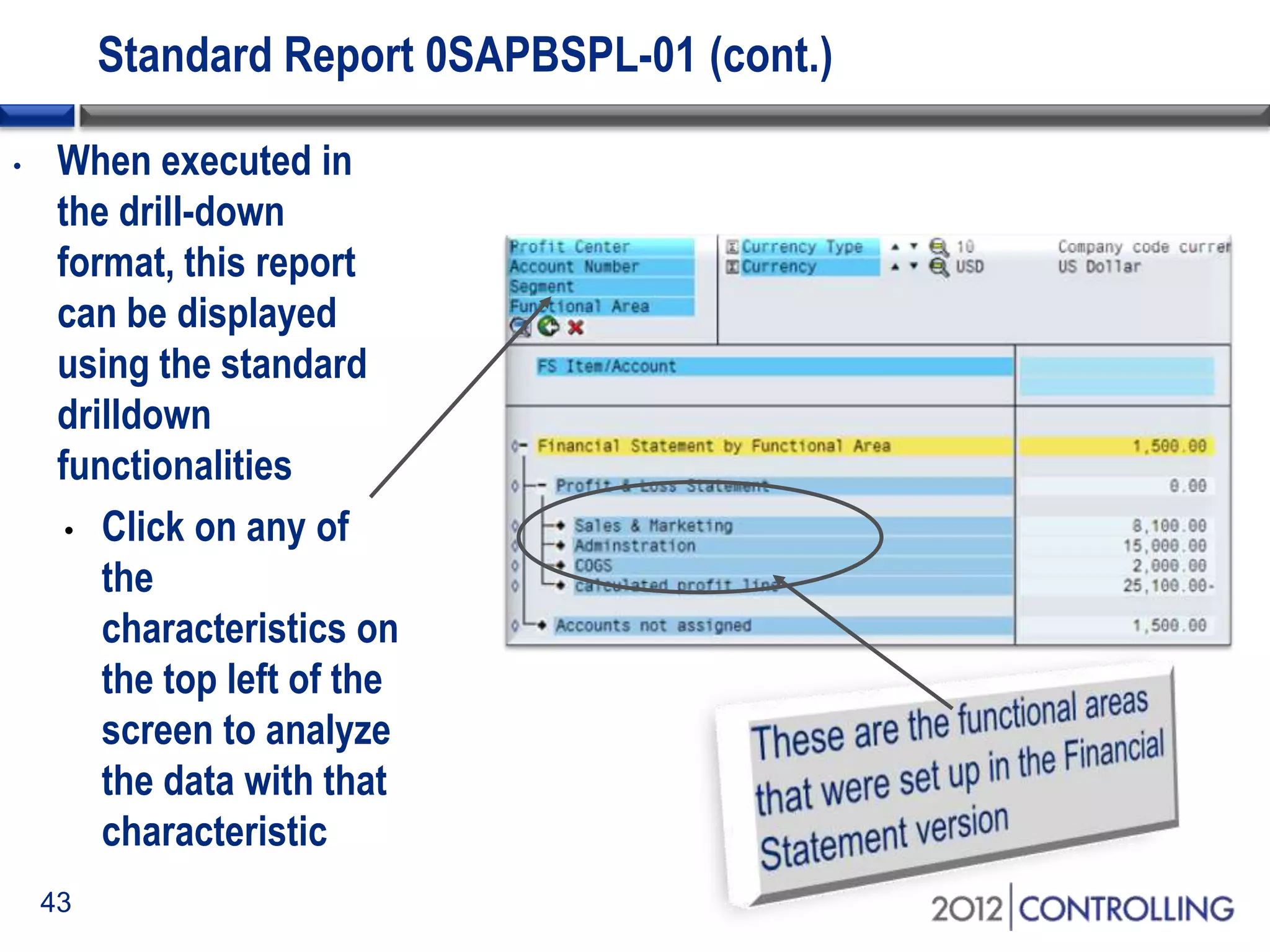
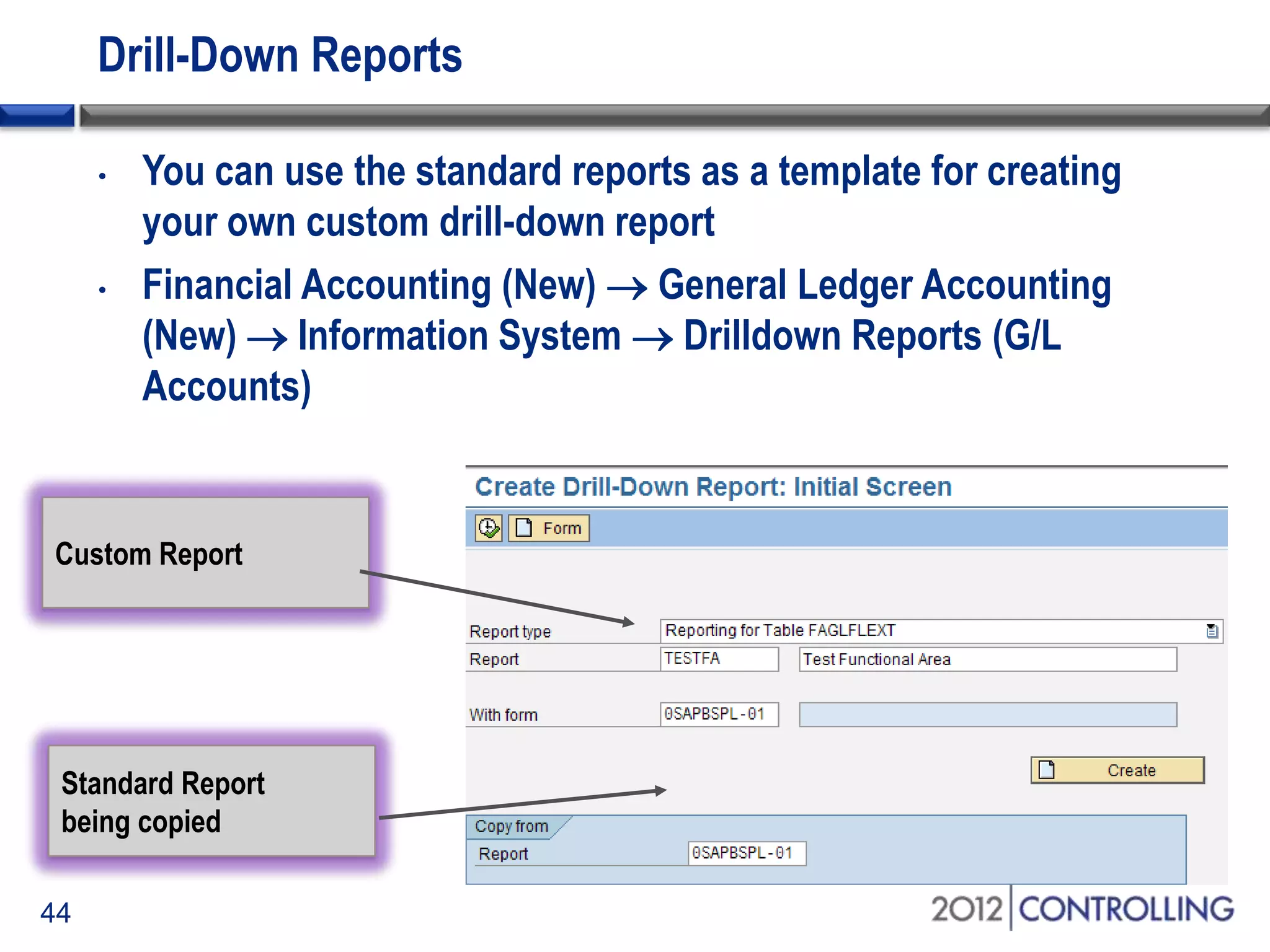
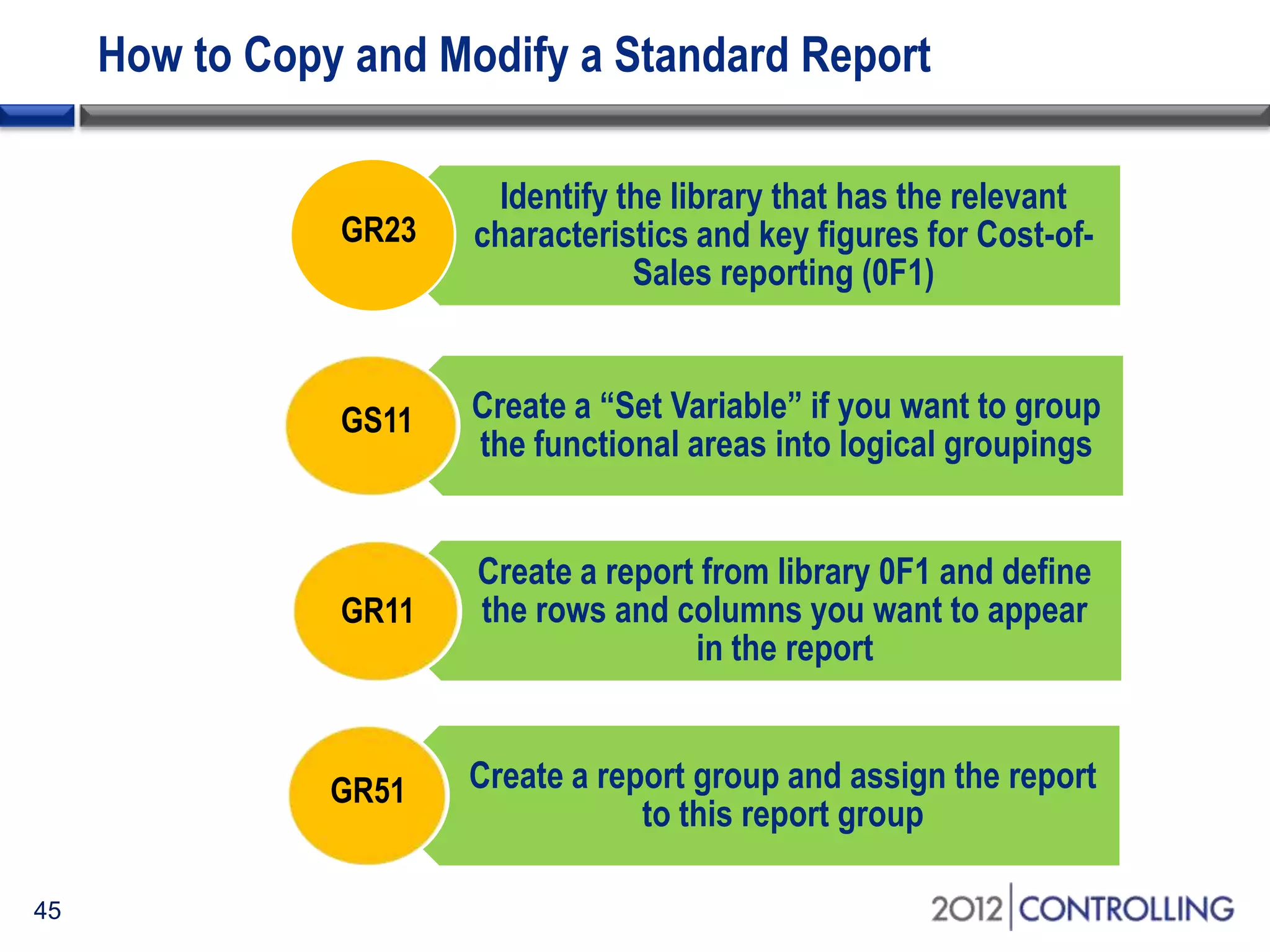
- The document demonstrates how to generate cost-of-sales reports by functional area using the standard report 0SAPBSPL-01 and drilling down by characteristics for analysis.