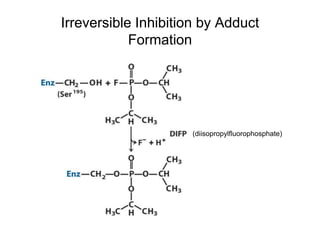
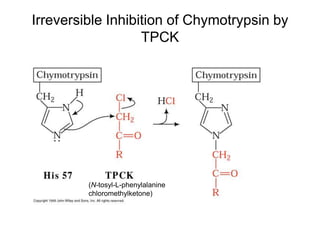
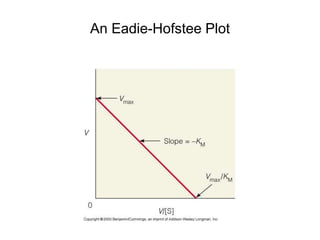
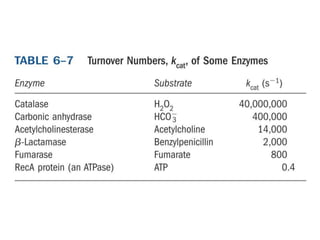
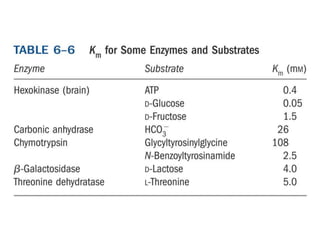
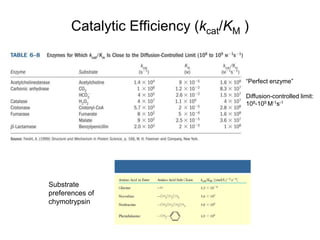
Enzymes catalyze biochemical reactions with great specificity and efficiency under mild conditions. Enzyme kinetics follows defined rate laws that can be modeled using Michaelis-Menten equations. The Michaelis-Menten equation relates reaction velocity to substrate concentration and defines kinetic parameters like Vmax and KM. Reaction rates are influenced by factors like temperature, pH, and the presence of inhibitors or activators. Different types of inhibition - competitive, uncompetitive, mixed - affect kinetic parameters in characteristic ways. Irreversible inhibitors permanently inactivate the enzyme through covalent modification.



![Irreversible First-Order Reactions
A B
v = d[B]/dt = -d[A]/dt = k[A]
(k = first-order rate constant (s-1))
Change in [A] with time (t):
[A]= [A]o e –kt or
[A]/[A]o = e –kt
ln([A]/[A]o) = –kt
([A]o = initial concentration)
k](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/9392189-230725175526-781f4953/85/9392189-ppt-4-320.jpg)
![Reversible First-Order Reactions
A B
v = -d[A]/dt = k1[A] - k-1[B]
At equilibrium: k1[A]eq - k-1[B]eq = 0
[B]eq/[A]eq = k1/k-1 = Keq
k1
k-1
](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/9392189-230725175526-781f4953/85/9392189-ppt-5-320.jpg)
![Second-Order Reactions
2A P
v = -d[A]/dt = k[A]2
Change in [A] with time:
1/[A] = 1/[A]o + kt
A + B P
v = -d[A]/dt = -d[B]/dt = k[A][B]
(k = second-order rate constant (M-1s-1))
k
k
Note: third-order reactions rare, fourth- and higher-order reactions unknown.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/9392189-230725175526-781f4953/85/9392189-ppt-6-320.jpg)
![Free Energy Diagrams
Keq = e –∆Gº/RT
For A A‡
[A]‡/[A]o = e –∆Gº‡/RT
[A]‡ = [A]o e –∆Gº‡/RT
Keq = equilibrium constant
[A]‡ = concentration of molecules having the activation energy
[A]o = total concentration of A
–∆Gº‡ = standard free energy change of activation (activation energy)
](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/9392189-230725175526-781f4953/85/9392189-ppt-7-320.jpg)
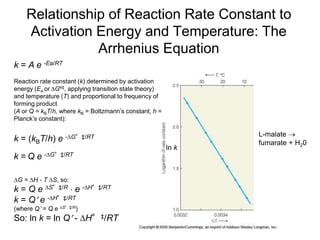

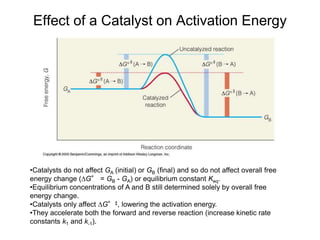
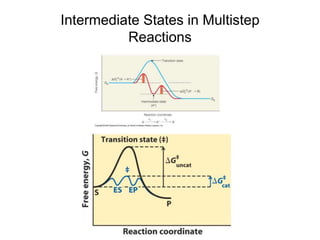

![Michaelis-Menten Kinetics (1)
v = k2[ES]
(Note: k2 also referred to as kcat)
[Enzyme]total = [E]t = [E] + [ES]
How to solve for [ES]?
1. Assume equilibrium, if k-1 >> k2:
KS = k-1/k1 = [E][S]/[ES]
or
2. Assume steady state:
d[ES]/dt = 0
(Michaelis and
Menten, 1913)
(Briggs and
Haldane, 1925)
E = enzyme, S = substrate,
ES = enzyme-substrate complex,
P = product](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/9392189-230725175526-781f4953/85/9392189-ppt-14-320.jpg)
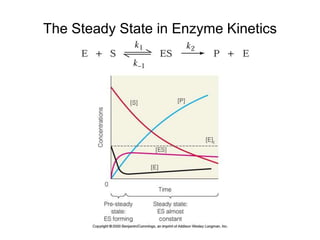
![Michaelis-Menten Kinetics Continued (2)
Rate of formation of ES complex = k1[E][S]
Rate of breakdown of ES complex = k-1[ES] + k2[ES]
Because of steady state assumption:
k1[E][S] = k-1[ES] + k2[ES]
Rearranging: [ES] = (k1/(k-1 + k2))[E][S]
Substituting Michaelis constant = KM = (k-1 + k2)/k1) = KS + k2/k1:
[ES] = ([E][S])/KM
So: KM[ES] = [E][S]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/9392189-230725175526-781f4953/85/9392189-ppt-16-320.jpg)
![Michaelis-Menten Kinetics Continued (3)
Substituting [E] = [E]t - [ES]:
KM[ES] = [E]t[S] - [ES][S]
Rearranging: [ES](KM + [S]) = [E]t[S]
So: [ES] = [E]t[S]/(KM + [S])](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/9392189-230725175526-781f4953/85/9392189-ppt-17-320.jpg)
![Michaelis-Menten Kinetics Continued (4)
Now we can substitute for [ES] in the rate equation
vo = k2[ES].
But first note that the velocity in v = k2[ES] we use is the initial
velocity, vo, the velocity of the reaction after the pre-steady state
and in the early part of the steady state, i.e., before ~10% of
substrate is converted to product. This is because at this stage of
the reaction, the steady-state assumption is reasonable ([ES] is still
approximately constant). Also, since not much P has yet
accumulated, we can approximate the kinetics for even reversible
reactions with this equation if we limit ourselves to vo.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/9392189-230725175526-781f4953/85/9392189-ppt-18-320.jpg)
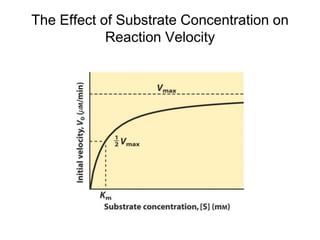
![The Michaelis-Menten Equation
vo = k2[E]t[S]/(KM + [S])
or
vo = Vmax[S]/(KM + [S])
(since Vmax = k2[E]t when [S] >> KM)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/9392189-230725175526-781f4953/85/9392189-ppt-19-320.jpg)
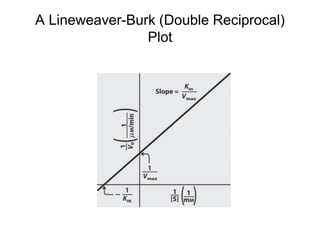
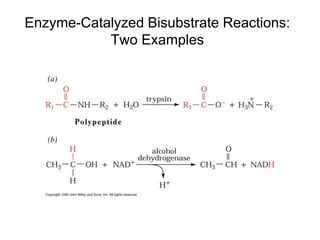
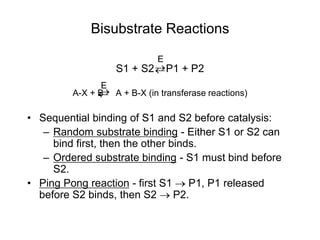
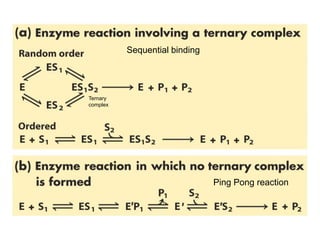
![Multistep Reactions
E + S ES ES E + P
vo = kcat[E]t[S]/(KM + [S])
k2 k3
k1
k-1
kcat = empirical rate constant that reflects rate-
determining component. Mathematically, for the
reaction above,
kcat = k2k3/(k2 + k3).
However, k2 and k3 often very hard to establish
with precision as individual rate constants.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/9392189-230725175526-781f4953/85/9392189-ppt-22-320.jpg)

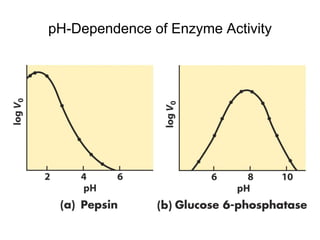
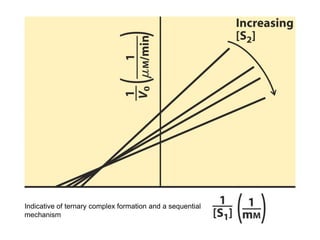
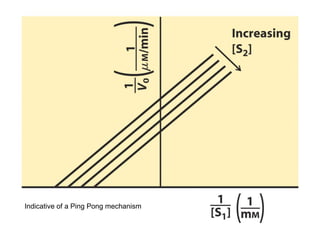


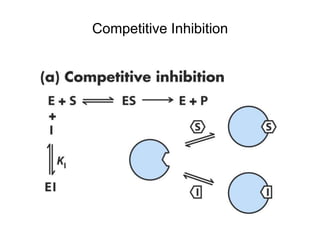
![Effects of Competitive Inhibitor on
Enzyme Kinetics
Kapp
M = KM(1 + [I]/KI) > KM
Vapp
max = Vmax
KI (inhibitor dissociation
constant) = koff/kon](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/9392189-230725175526-781f4953/85/9392189-ppt-36-320.jpg)
![a = 1 + [I]/KI](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/9392189-230725175526-781f4953/85/9392189-ppt-37-320.jpg)

![Relationship of KI to Half-Maximal
Inhibitory Concentration (IC50)
For a competitive inhibitor of an enzyme that follows
Michaelis-Menton kinetics:
vI/v0 = (Vmax[S]/(KMa + [S]))/(Vmax[S]/(KM + [S])) = (KM +
[S])/(KMa + [S])
vI = initial velocity with inhibitor
v0 = initial velocity without inhibitor
a = 1 + [I]/KI
When vI/v0 = 0.5, [I] = IC50 = KI(1 + [S]/KM)
If measurement made when [S] << KM, IC50 = KI](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/9392189-230725175526-781f4953/85/9392189-ppt-40-320.jpg)
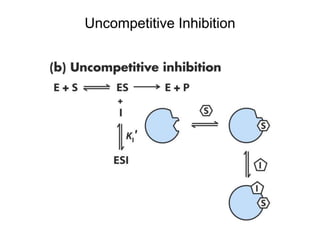
![Effects of Uncompetitive Inhibitor on
Enzyme Kinetics
Kapp
M = KM/(1 + [I]/KI) < KM
Vapp
max = Vmax/(1 + [I]/KI) < Vmax](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/9392189-230725175526-781f4953/85/9392189-ppt-42-320.jpg)
![a = 1 + [I]/KI](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/9392189-230725175526-781f4953/85/9392189-ppt-43-320.jpg)
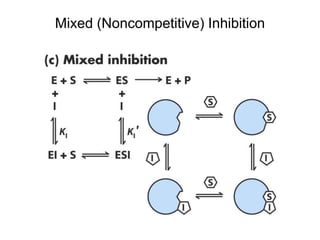
![Effects of Mixed (Noncompetitive)
Inhibitor on Enzyme Kinetics
Kapp
M = (1 + [I]/KI)KM/(1 + [I]/KI)
(= KM, when KI = KI, which is often the case.)
Vapp
max = Vmax/(1 + [I]/KI) < Vmax
k1
k-1
•Not the same as uncompetitive inhibition.
•In mixed inhibition, inhibitor can bind E or
ES.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/9392189-230725175526-781f4953/85/9392189-ppt-45-320.jpg)
![a = 1 + [I]/KI
a = 1 + [I]/KI](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/9392189-230725175526-781f4953/85/9392189-ppt-46-320.jpg)
![a = 1 + [I]/KI
a = 1 + [I]/KI
(For mixed inhibitor,
generally, ~ KM)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/9392189-230725175526-781f4953/85/9392189-ppt-47-320.jpg)
![Irreversible Inhibition
k1
k-1
k2
E + I E·I E-I
Plot:
ln(residual enzyme activity) vs. time
If [I]>>[E], conditions are pseudo-first
order and slope is -kobs (pseudo-first
order inactivation rate constant)
kinact (second-order inactivation constant)
= k1k2/k-1 = kobs/[I]
Slope = -kobs](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/9392189-230725175526-781f4953/85/9392189-ppt-48-320.jpg)