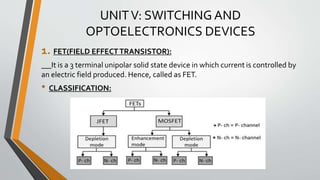
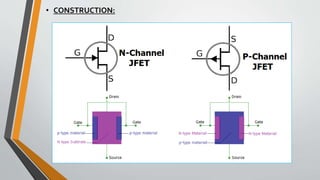
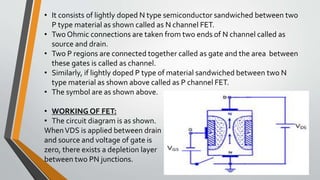
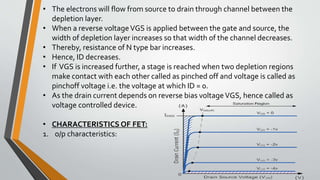
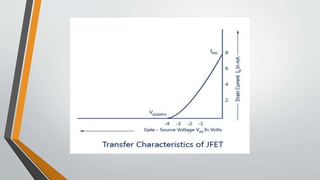
This document discusses three terminal integrated circuit regulators and field effect transistors (FETs). It provides details on the construction, working, characteristics and classification of FETs. Specifically, it describes how a FET is a three terminal solid state device that uses an electric field to control current flow. Applying a reverse voltage between the gate and source depletes the channel, reducing the drain current. The output and transfer characteristics of FETs are also outlined.