1) SEJ is the leading convenience store chain in Japan, operating over 12,000 stores with annual profits of $30 billion.
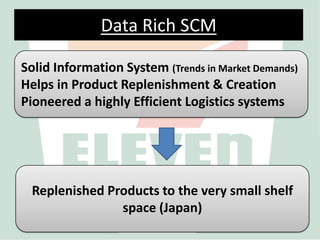
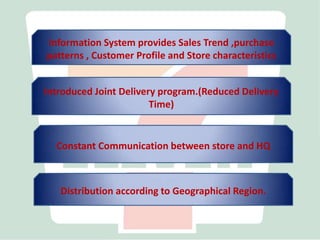
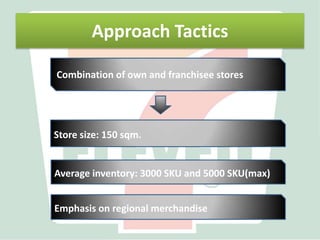
2) SEJ has pioneered highly efficient logistics and supply chain management systems using data collected from every transaction to continuously replenish products and understand customer demand.
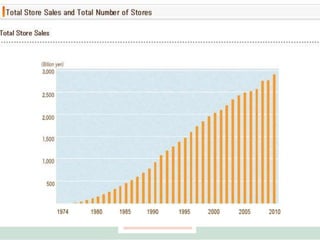
3) By analyzing detailed sales data collected through its integrated IT systems, SEJ is able to precisely replenish inventory, develop new products, and achieve strong financial performance despite economic challenges through its customer-focused operations.