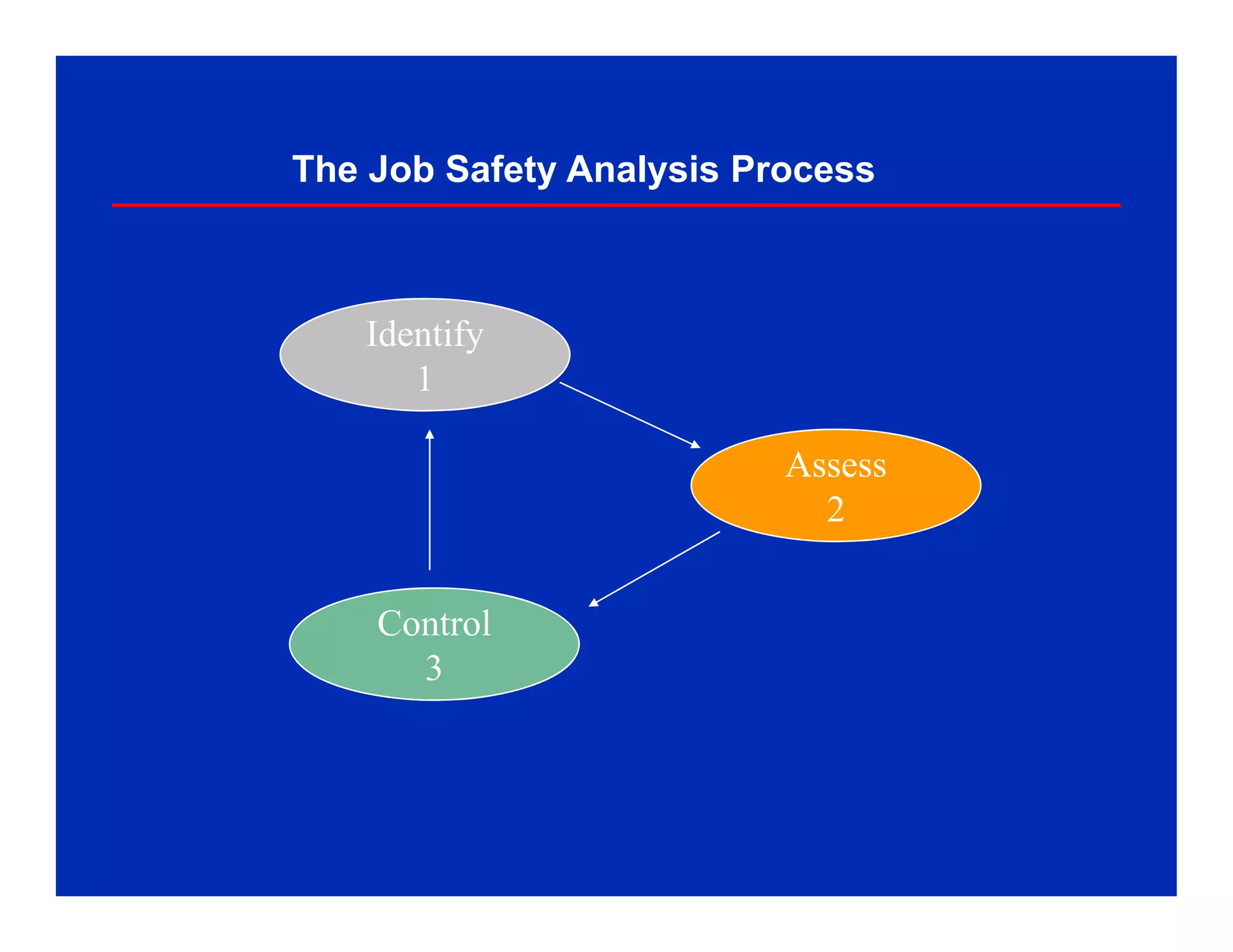
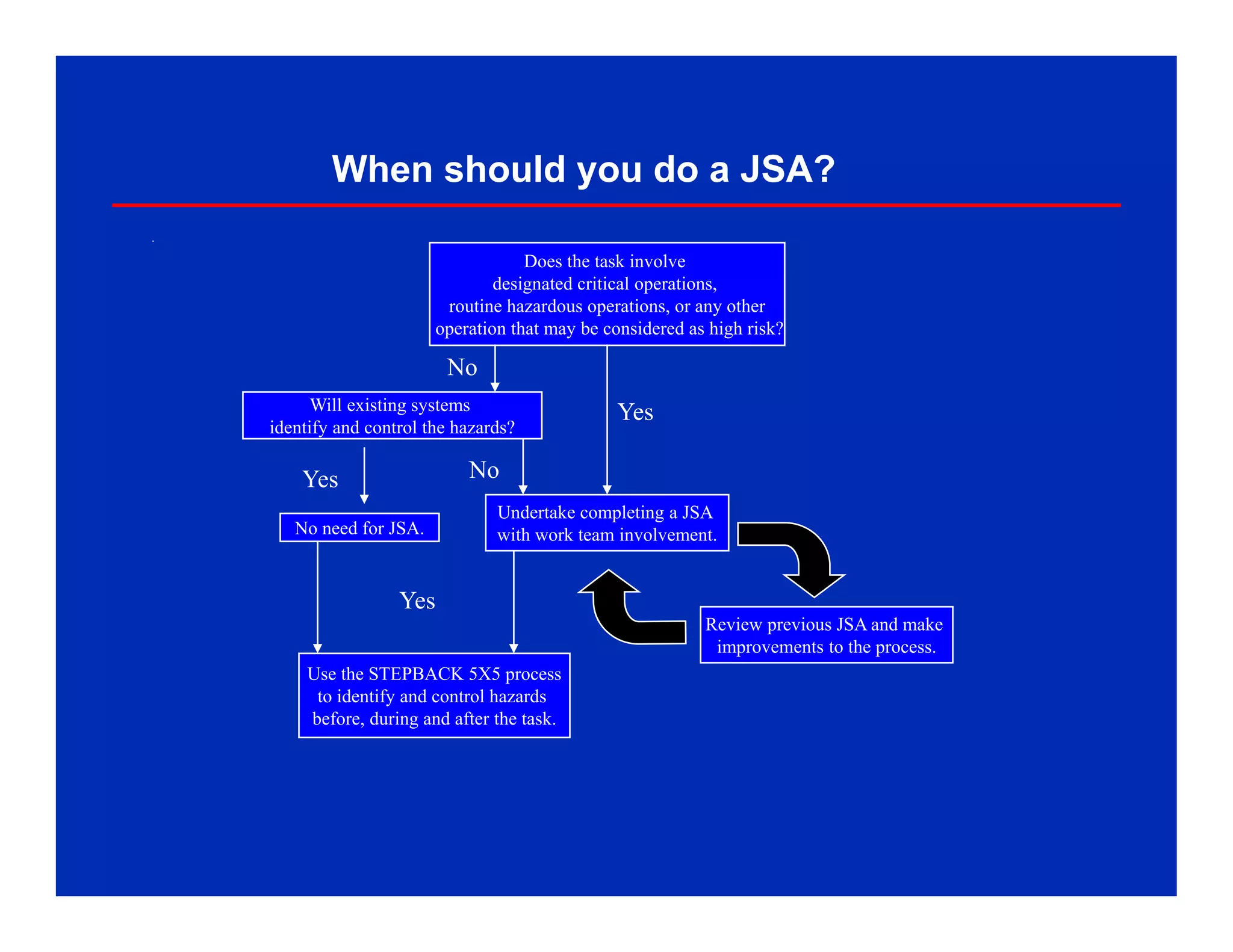
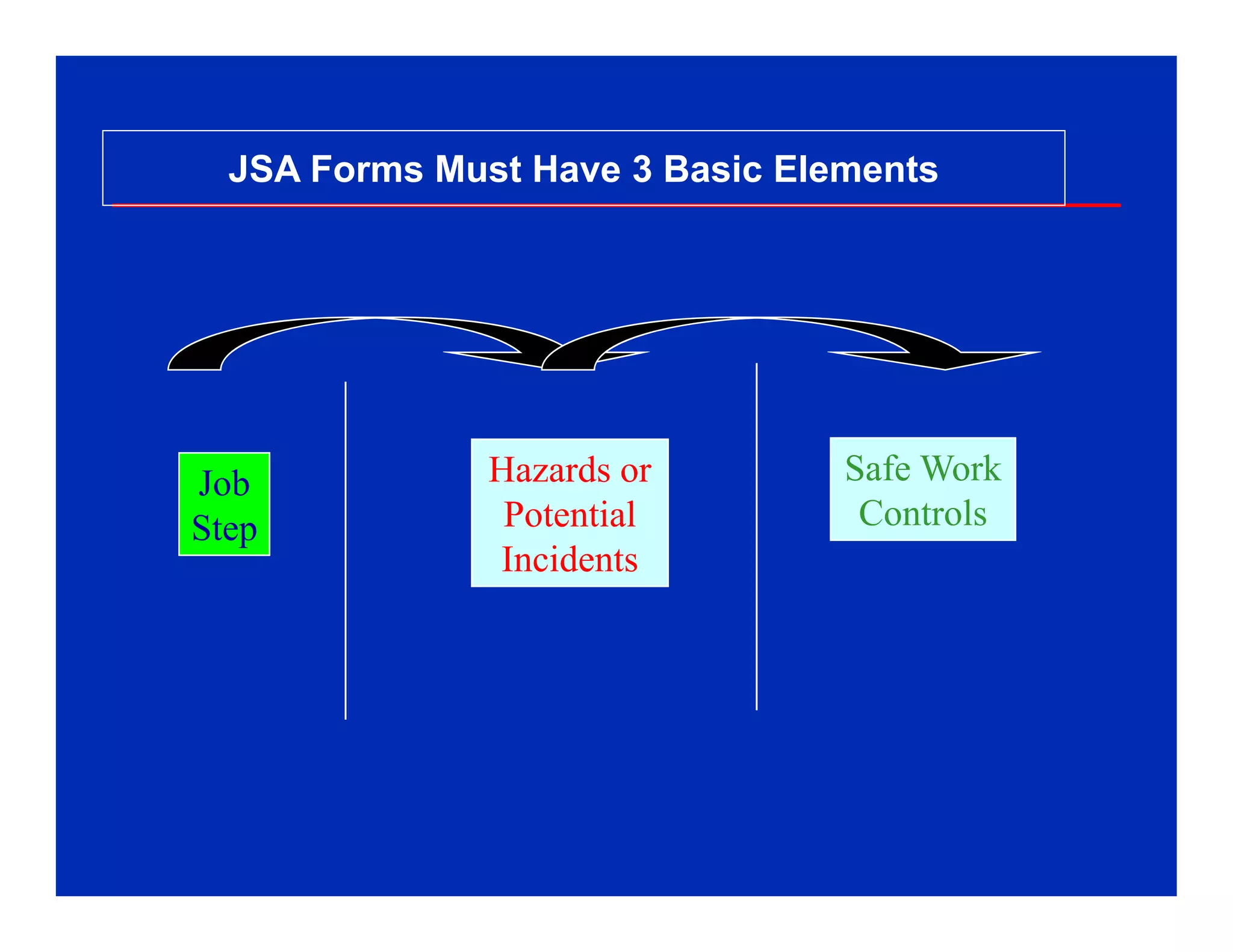
The document discusses Job Safety Analysis (JSA), which is a process to identify hazards and implement controls for each job step. It involves identifying hazards for each step, then developing safe work practices to eliminate or reduce potential incidents. JSAs should be done for high-risk tasks and whenever existing controls won't sufficiently manage risks. The key elements are separating the job into steps, identifying hazards for each step, then establishing controls. JSAs help ensure safety, gain commitment to safe practices, and identify more efficient work methods.