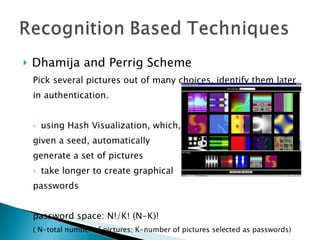
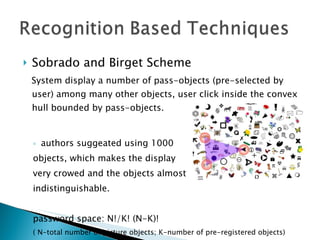
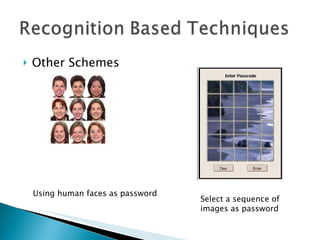
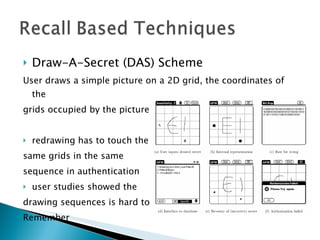
The document discusses and compares various authentication methods, including recognition-based, recall-based, and graphical password techniques. It provides an overview of common techniques such as Dhamija and Perrig's picture selection scheme, Sobrado and Birget's pass-object selection scheme, and Jermyn et al.'s Draw-A-Secret scheme. While graphical passwords may be easier for users to remember than text passwords, they have limitations such as taking longer to create and register, requiring more storage space, and not being very mature yet compared to traditional text-based passwords. The document evaluates the security and usability of different authentication methods.