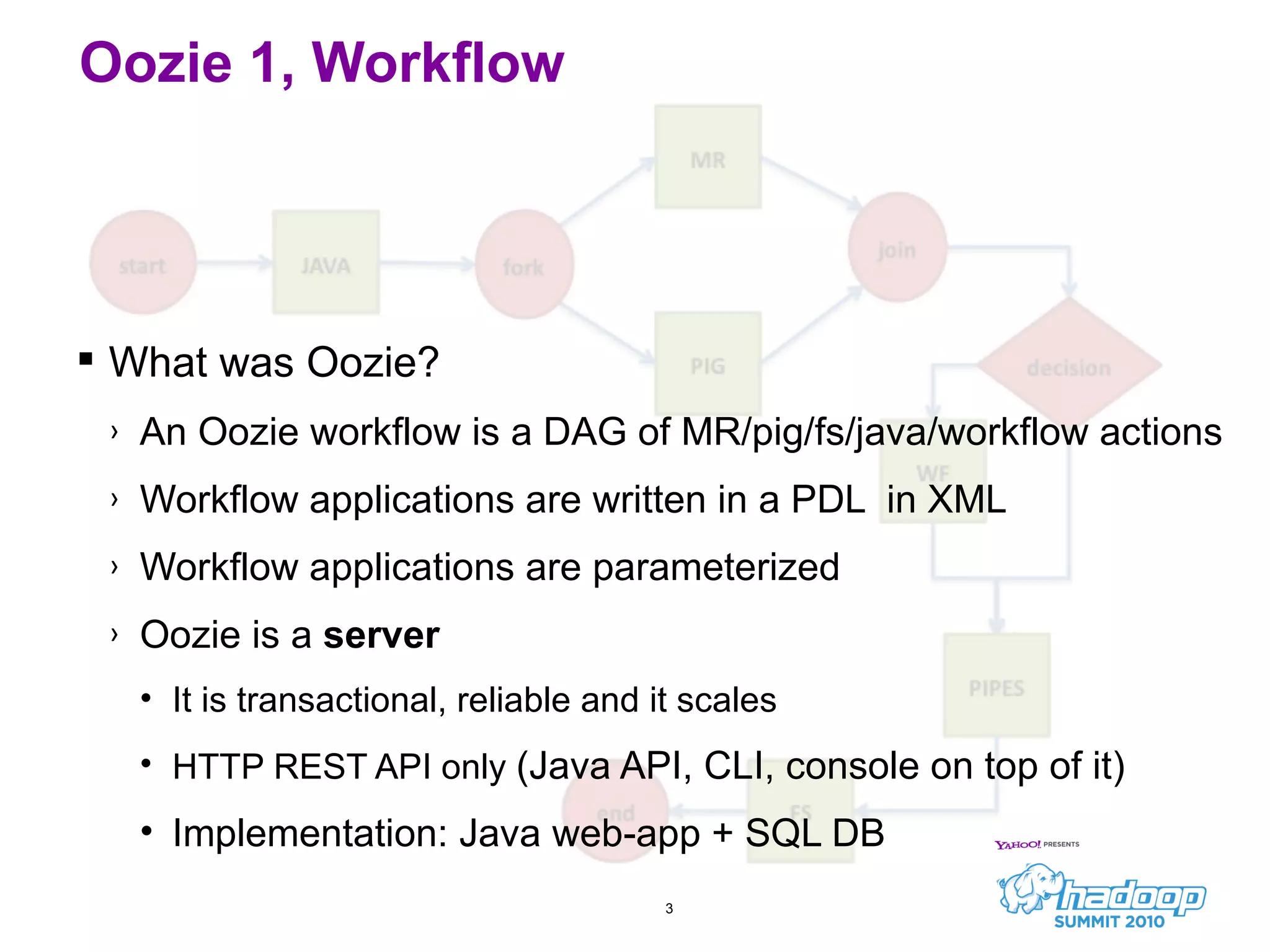
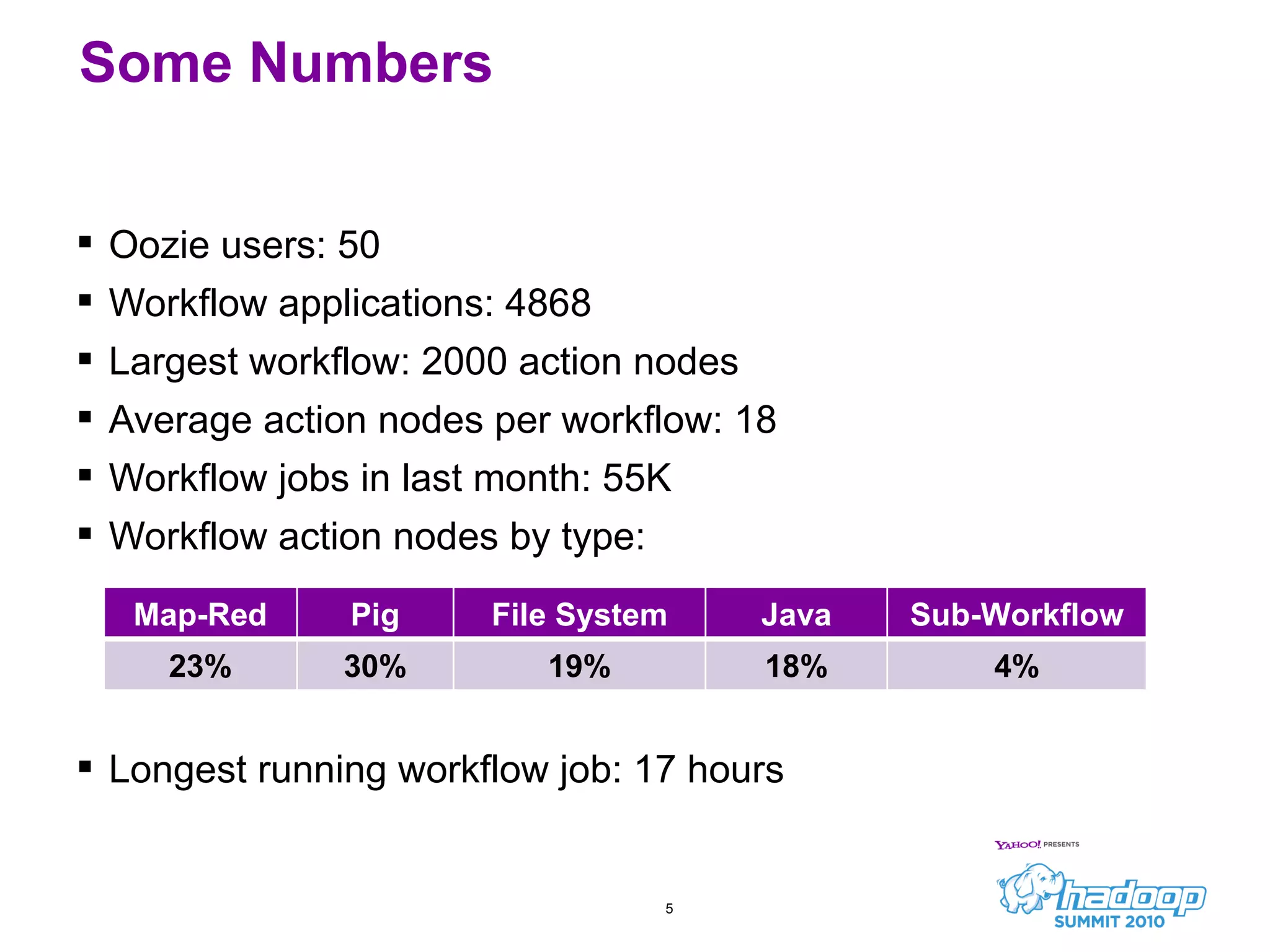
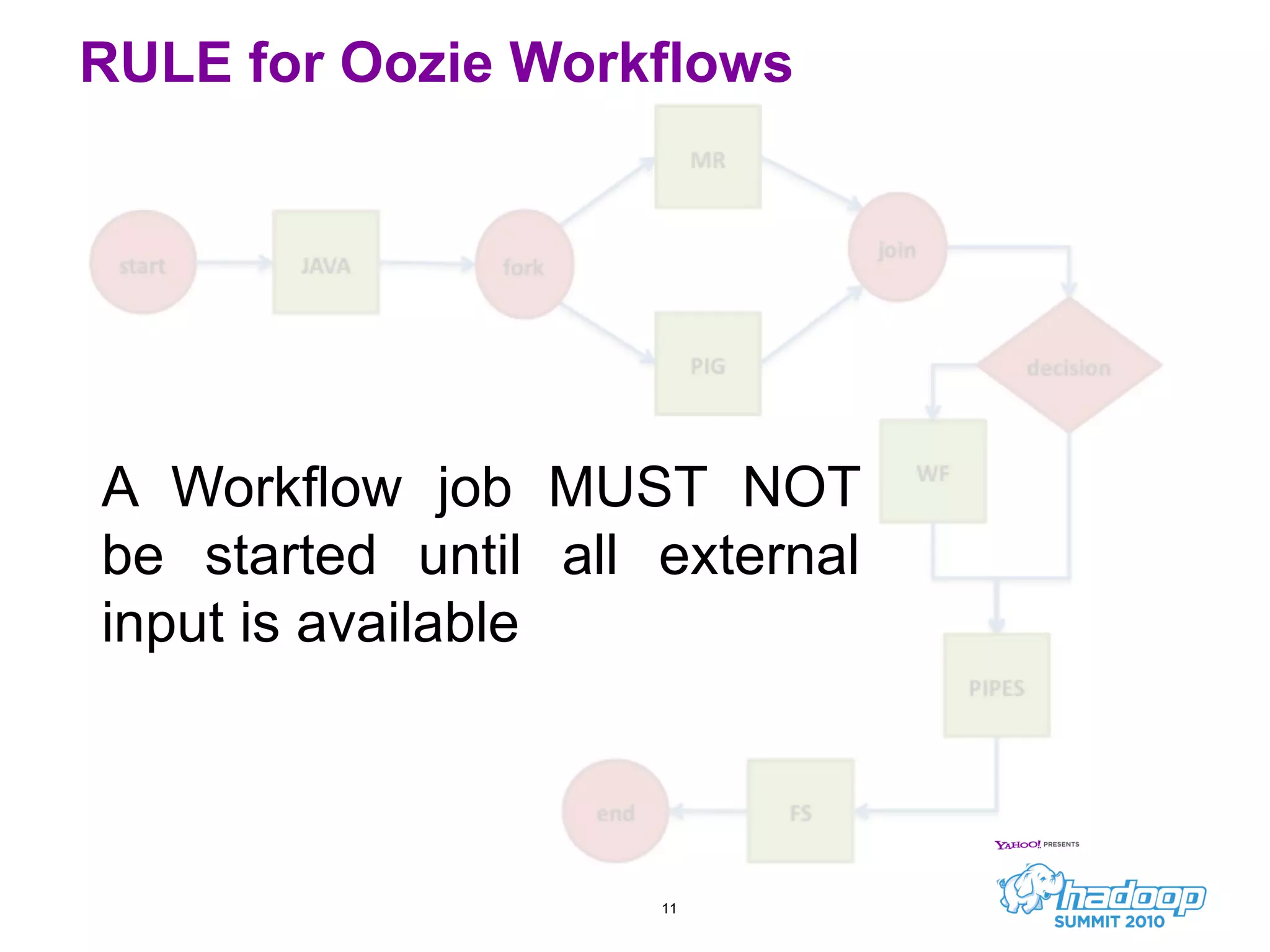
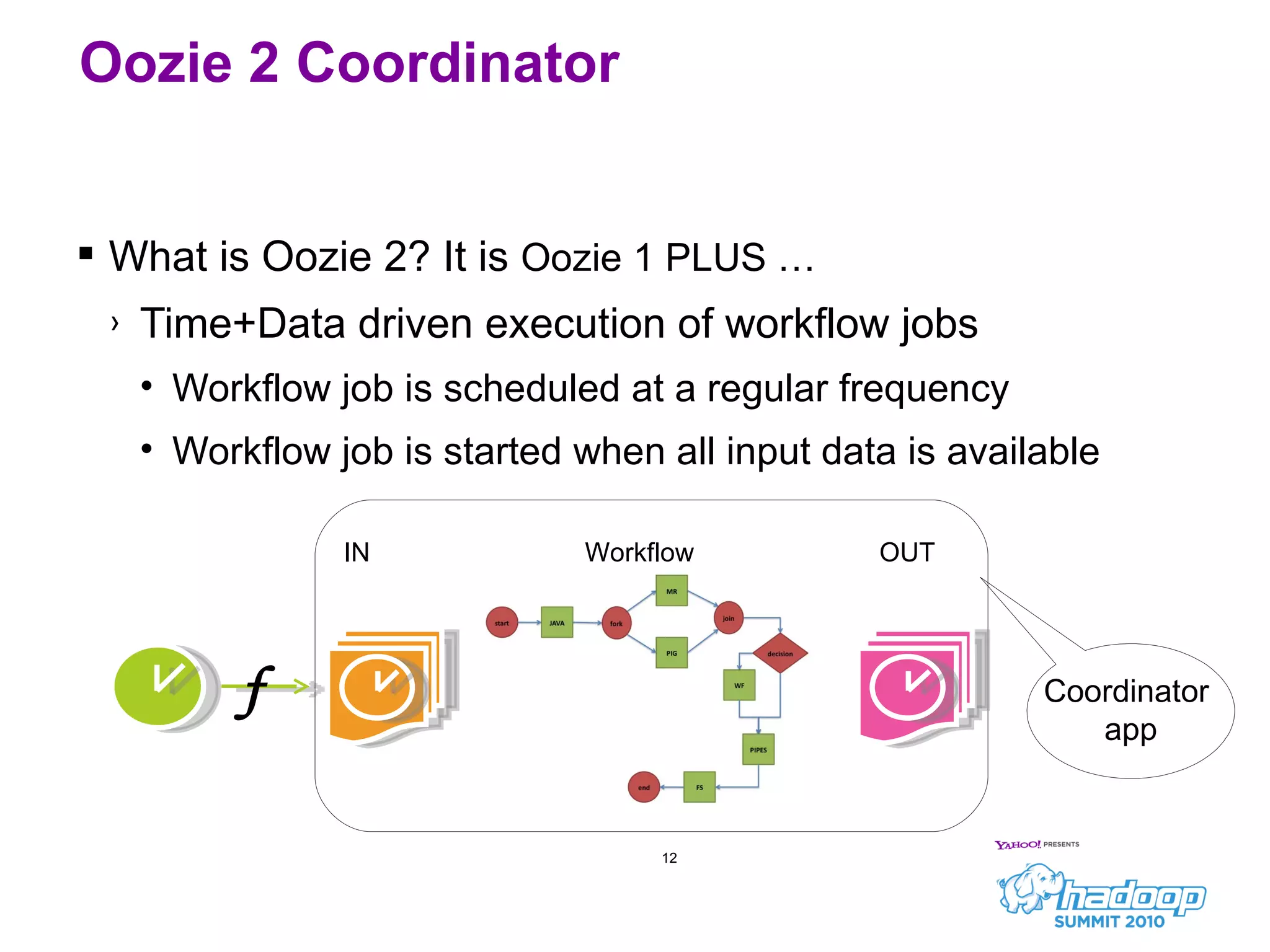
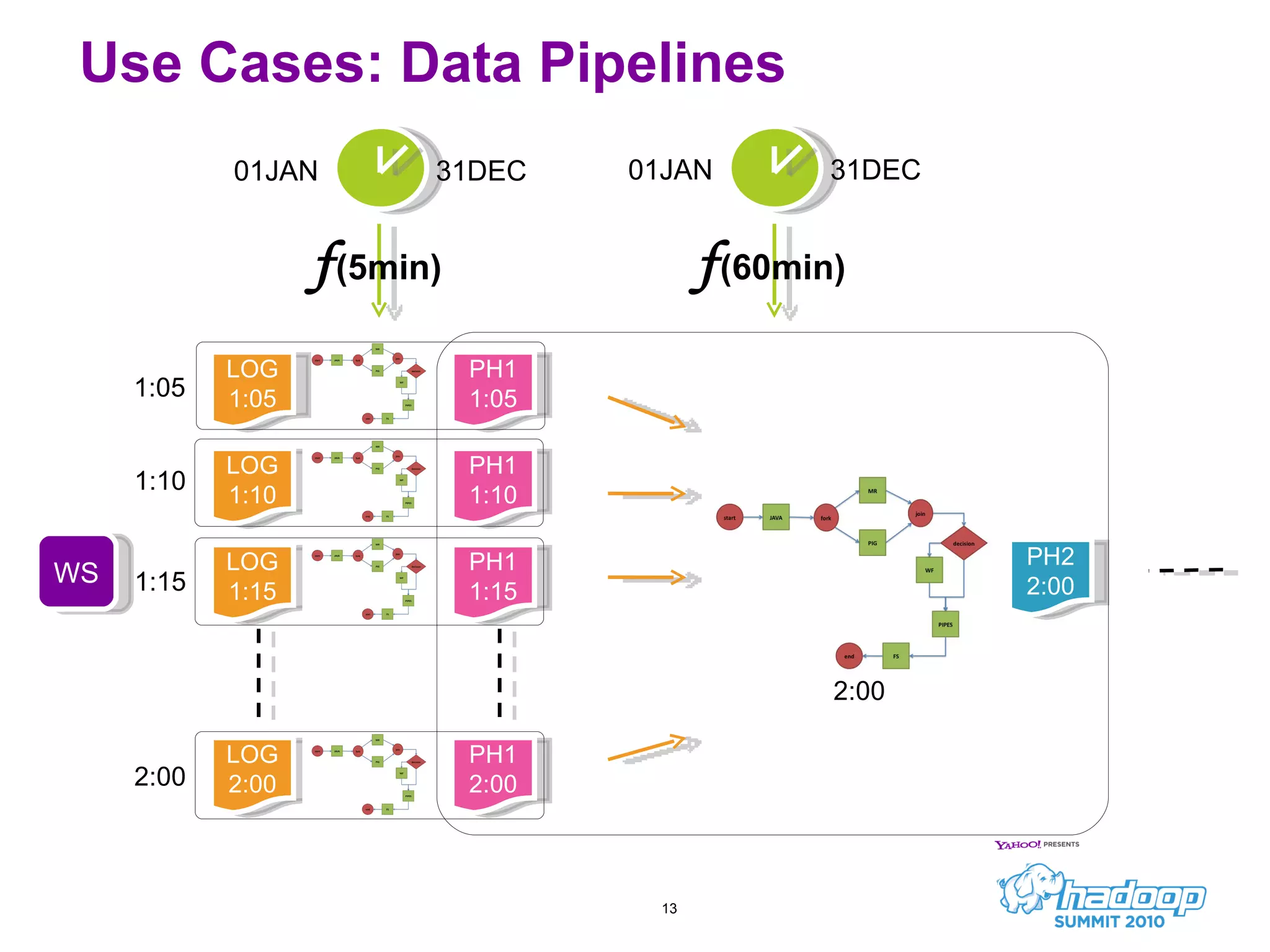
Oozie is a workflow scheduler system for managing Hadoop jobs. It allows users to create workflows as directed acyclic graphs (DAGs) of Hadoop jobs such as MapReduce, Pig, and Hive. Oozie 1 focused on workflow scheduling, while Oozie 2 added coordinator capabilities to schedule workflows based on time and data availability. In its first year, Oozie saw significant usage at Yahoo and helped automate many complex workflows and data pipelines.







![Questions? Alejandro Abdelnur [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/5ooziehadoopsummit2010-100630134430-phpapp02/75/Workflow-on-Hadoop-Using-Oozie__HadoopSummit2010-19-2048.jpg)