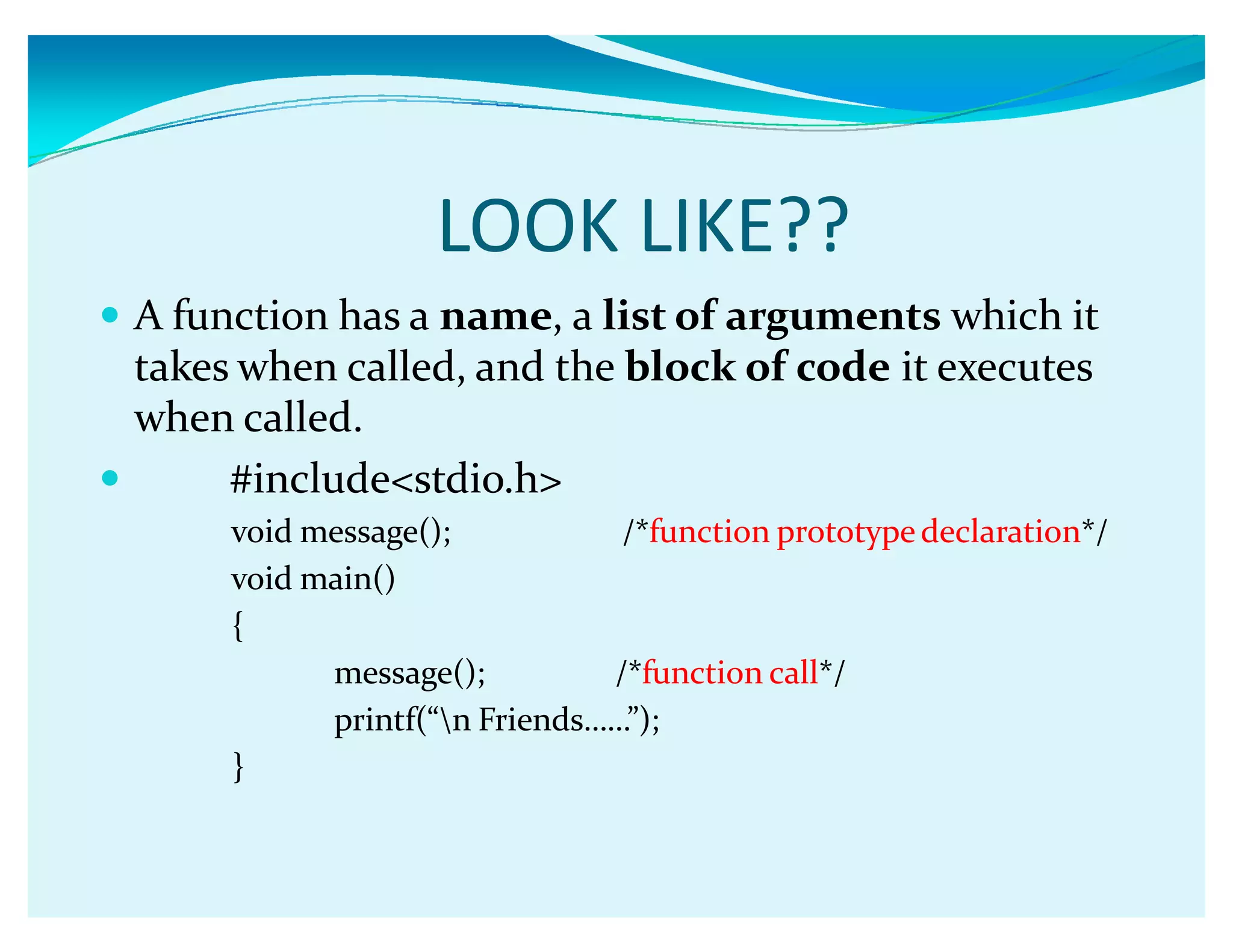
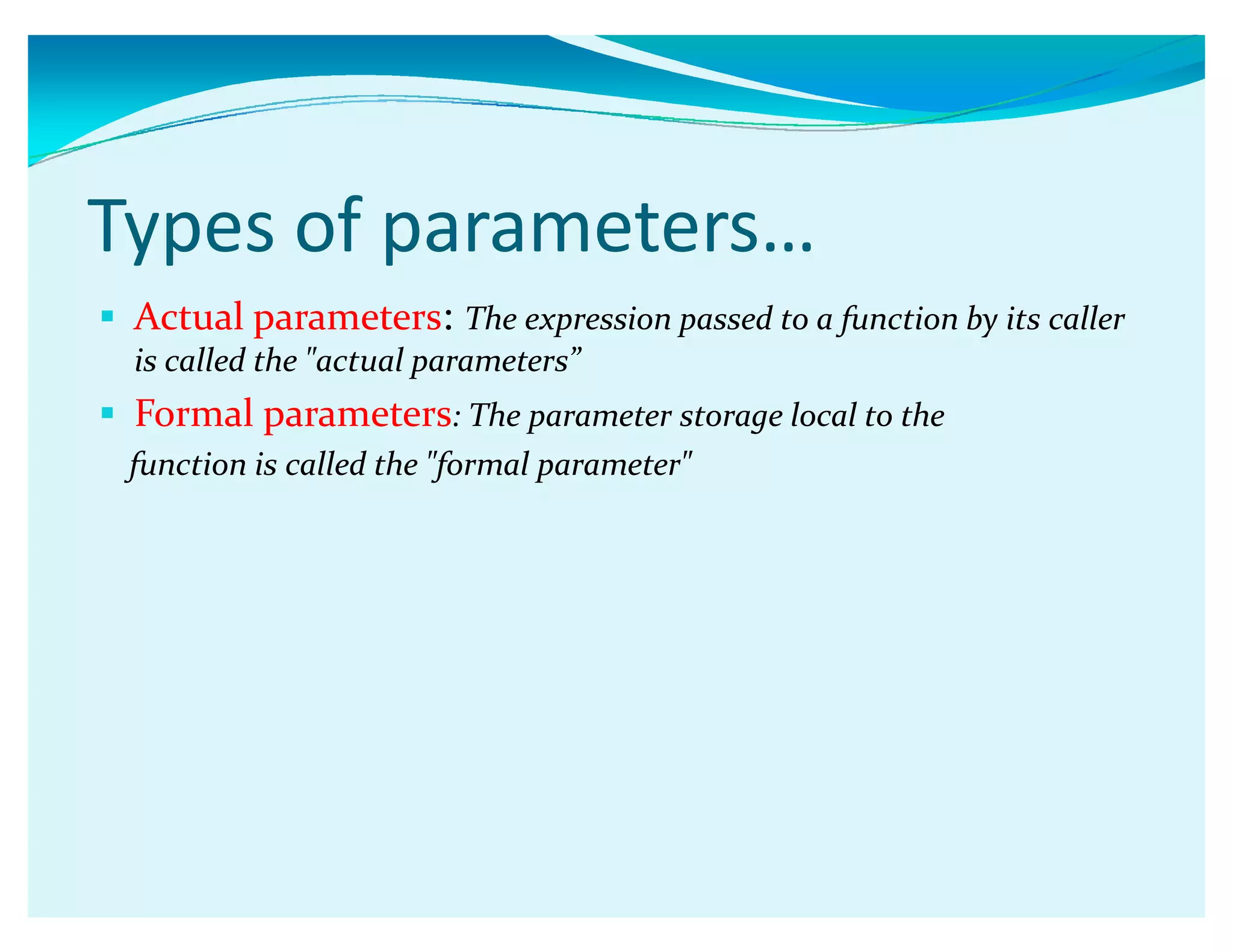
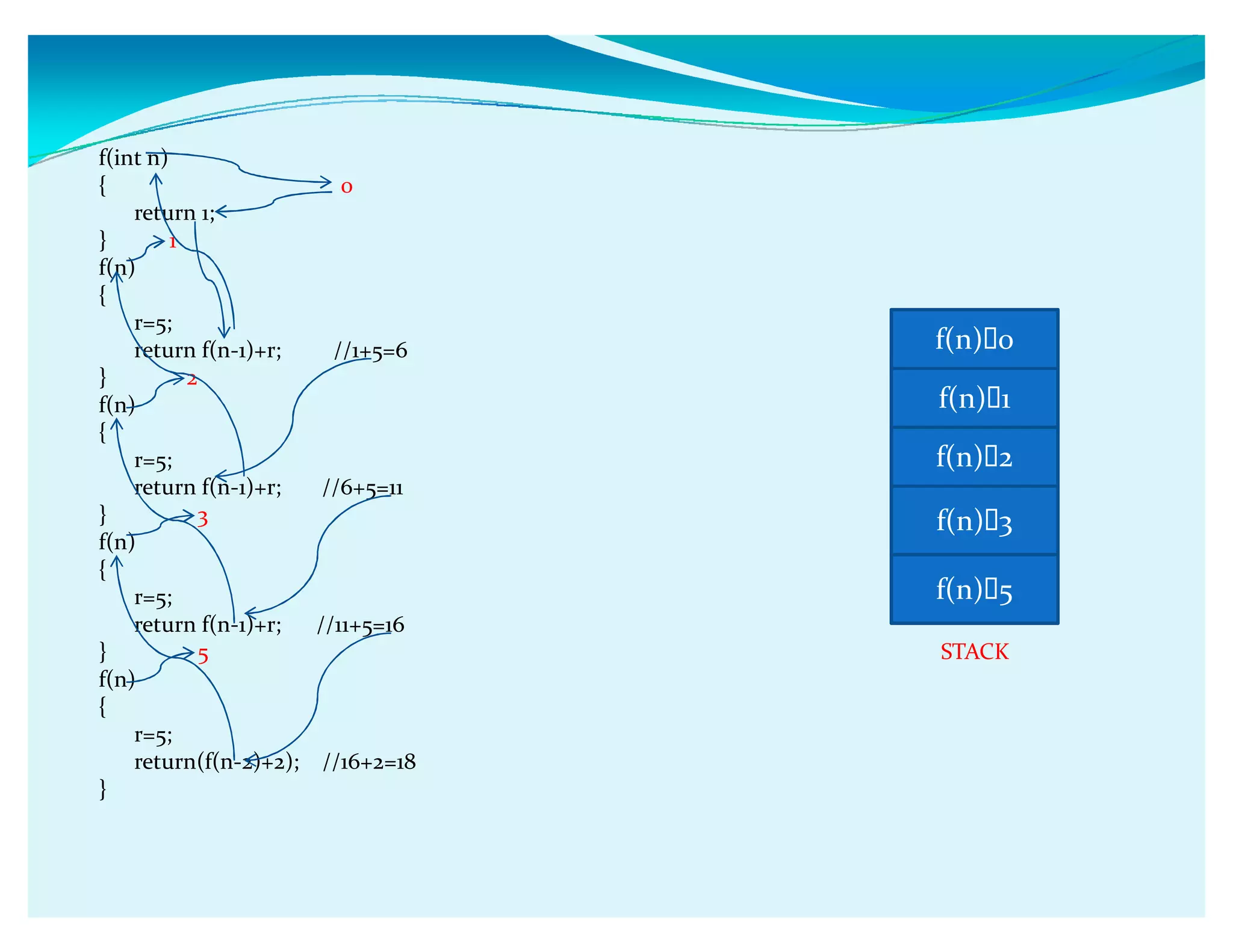
Functions in C allow programmers to package blocks of code that perform tasks. Functions make code reusable and easier to understand by separating code into modular units. A function has a name, list of arguments it takes, and code that is executed when the function is called. Functions can communicate between each other via parameters passed by value or by reference. Parameters passed by value are copied, so changes inside the function don't affect the original variable, while parameters passed by reference allow the function to modify the original variable. Functions can also call themselves recursively.





















![main()
{
int *ptr, i;
int A[]={10,20,30,40,50};
ptr=A+4;
for(i=1;i5;i++)
{
*ptr=*(ptr-1); //*ptr=*ptr--;
*ptr=*ptr-1; //*ptr=*ptr-1;
}
for(i=0;i5;i++)
{
printf(Dz%ddz,A[i]);
}
}
Output is?????
10 20 30 40 39](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/46630497-fun-pointer-1-140612040746-phpapp01/75/46630497-fun-pointer-1-33-2048.jpg)
![Output of the following C program isǥǥǥǥǥǥ?
main()
{
char s[]={'a','b','c','n','c','0'};
char *p,*str,*str1;
p=s[3];
str=p;
str1=s;
printf(%d,++*p + ++*str1-32);
}
NOTE:ASCII value of n(10),0(0)
Output:: 77(ǮMǯ)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/46630497-fun-pointer-1-140612040746-phpapp01/75/46630497-fun-pointer-1-34-2048.jpg)
![main()
{
int a[2][2][2] = { {10,2,3,4}, {5,6,7,8} };
int *p,*q;
p=a[2][2][2];
*q=***a;
printf(%d----%d,*p,*q);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/46630497-fun-pointer-1-140612040746-phpapp01/75/46630497-fun-pointer-1-35-2048.jpg)
![y Output: some garbage valueǥǥ
y Explanation:p=a[2][2][2] you declared only two 2D
arrays, but you are trying to access the third 2D(which
you are not declared) it will print garbage values.
*q=***a ǥstarting address of Ǯaǯ is assigned to integer
pointer. Now q is pointing to starting address of a. If
you print *q, it will print first element of 3D array..](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/46630497-fun-pointer-1-140612040746-phpapp01/75/46630497-fun-pointer-1-36-2048.jpg)


![main()
{
static char names[5][20]={pascal,ada,cobol,fortran,perl};
int i;
char *t;
t=names[3];
names[3]=names[4];
names[4]=t;
for (i=0;i=4;i++)
printf(%s,names[i]);
}
Ans ::Compiler error: Lvalue required in function main
Explanation::Array names are pointer constants. So it cannot be
modified..](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/46630497-fun-pointer-1-140612040746-phpapp01/75/46630497-fun-pointer-1-39-2048.jpg)


![main()
{
char name[10],s[12];
scanf(Dz %[^],s);
}
How scanf will execute?
Ans :First it checks for the leading white space and
discards it. Then it matches with a quotation mark and
then it reads all character upto another quotation
mark..](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/46630497-fun-pointer-1-140612040746-phpapp01/75/46630497-fun-pointer-1-42-2048.jpg)




![void main()
{
static char *s[3]={math,phy,che};
typedef char *( *ppp)[3];
static ppp p1=s,p2=s,p3=s;
char * (*(*array[3]))[3]={p1,p2,p3};
char * (*(*(*ptr)[3]))[3]=array;
p2+=1;
p3+=2;
printf(%s,(***ptr[0])[2]);
}
Output isǥǥǥ.???](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/46630497-fun-pointer-1-140612040746-phpapp01/75/46630497-fun-pointer-1-47-2048.jpg)
![y Ans: che
y Explanation: Here
ptr: is pointer to array of pointer to string.
P1, p2, p3: are pointers to array of string.
array[3]: is array which contain pointer to array of string.
As we know p[i]=*(p+i)
(***ptr[0])[2]=(*(***ptr+0))[2]=(***ptr)[2]
=(***(array))[2] //ptr=array
=(**array)[2] //From rule *p=p
=(**(p1))[2] //array=p1
=(*p1)[2]
=(*s)[2] //p1=s
=s[2]=dzchedz](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/46630497-fun-pointer-1-140612040746-phpapp01/75/46630497-fun-pointer-1-48-2048.jpg)
![What will be output if you will compile and execute the following c code?
#includeconio.hDz
int display();
int(*array[3])();
int(*(*ptr)[3])();
void main()
{
array[0]=display;
array[1]=getch;
ptr=array;
printf(%d,(**ptr)());
(*(*ptr+1))();
}
int display()
{
int x=5;
return x++;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/46630497-fun-pointer-1-140612040746-phpapp01/75/46630497-fun-pointer-1-49-2048.jpg)
![y Ans: 5
y Explanation:
In this example: array []: It is array of pointer to such function which
parameter is void and return type is int data type.
ptr: It is pointer to array which contents are pointer to such function which
parameter is void and return type is int type data.
(**ptr)() = (** (array)) () //ptr=array
= (*array) () // from rule *p=p
=array [0] () //from rule *(p+i)=p[i]
=display () //array[0]=display
(*(*ptr+1))() =(*(*array+1))() //ptr=array
=*(array+1) () // from rule *p=p
=array [1] () //from rule *(p+i)=p[i]
=getch () //array[1]=getch](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/46630497-fun-pointer-1-140612040746-phpapp01/75/46630497-fun-pointer-1-50-2048.jpg)






