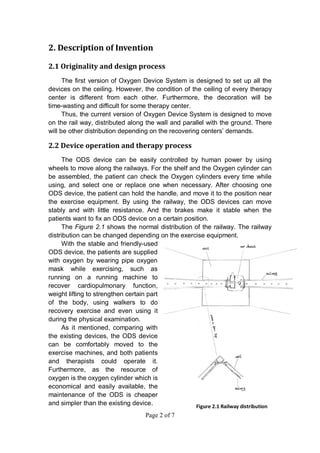
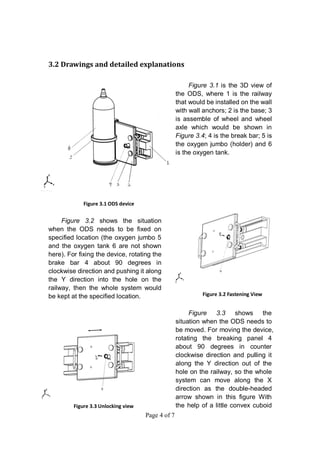
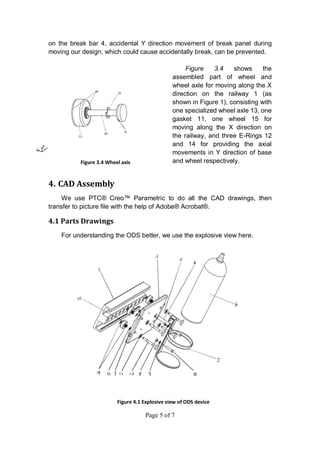
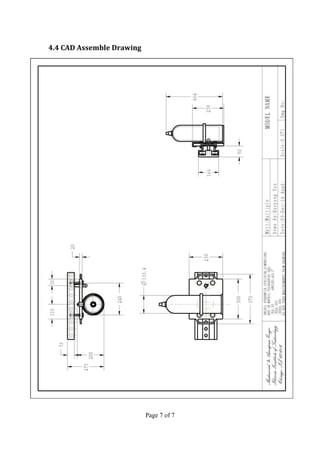
The document describes an oxygen delivery system designed for a physical therapy center. The system, called the ODS, allows multiple patients to receive oxygen while exercising freely within a 20x20 foot space. The ODS consists of an E-shaped railway installed on walls at a height parallel to the ground. Mobile bases fitted with wheels move along the railway and can be fixed in place using brakes. The bases hold oxygen cylinders and the system provides oxygen to patients through masks during physical therapy exercises. Drawings and descriptions of the railway, bases, wheels, brakes and other components are included to explain how the system works.