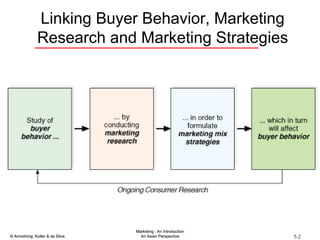
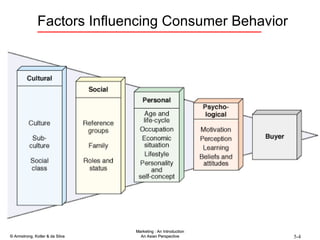
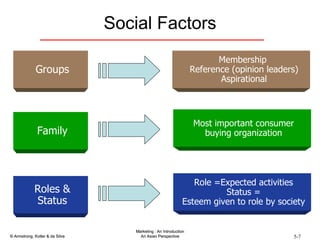
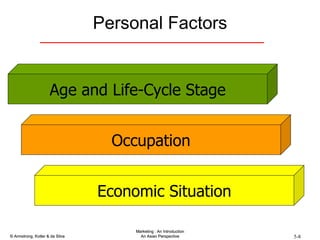
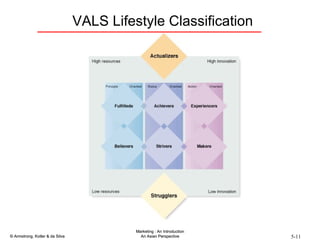
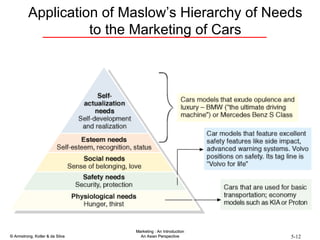
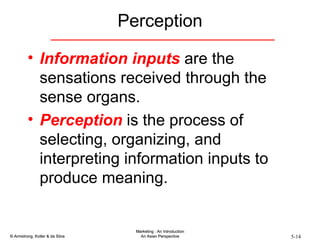
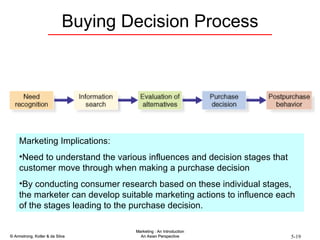
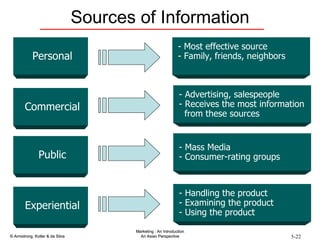
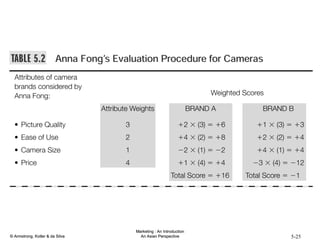
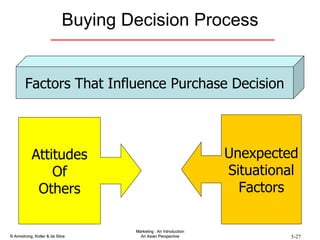
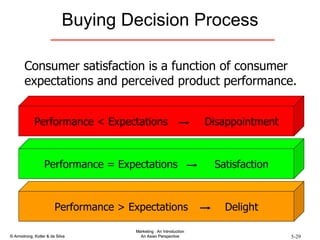
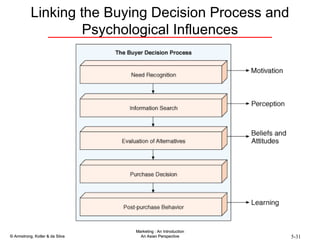
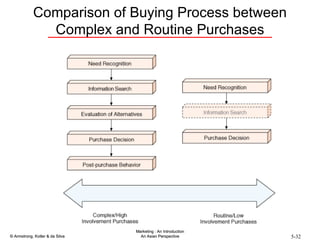
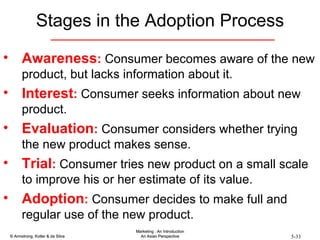
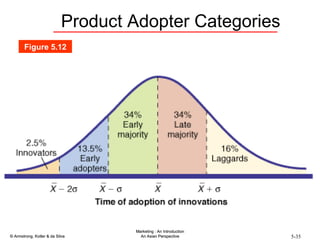
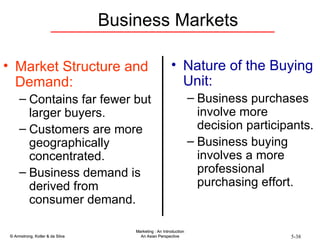
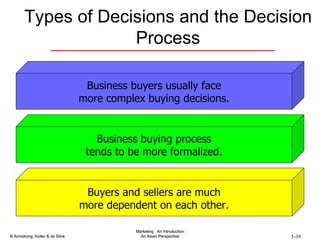
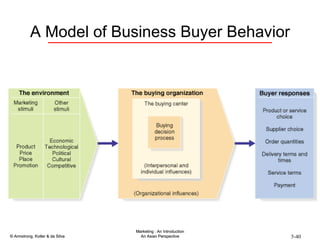
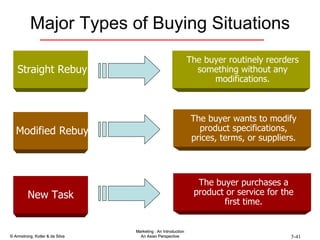
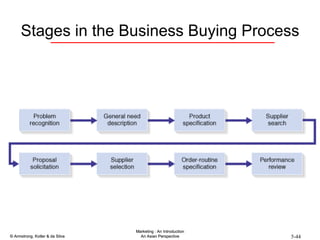
The document summarizes consumer and business buyer behavior and the factors that influence their purchasing decisions. It discusses the key stages in the consumer and business buying decision processes. Some of the main factors that influence consumer and business purchasing behaviors include culture, social class, personal characteristics, beliefs, attitudes, product perceptions, and group influences. The document also compares the buying processes for complex versus routine purchases.